Breaking Immune Tolerance: Leveraging Rhamnose and AuNP to Potentiate MUC1 Antigen Presentation
The fundamental obstacle in developing cancer vaccines against Mucin 1 (MUC1) is not identification, but visibility. As a transmembrane protein expressed on normal epithelium, MUC1 is largely treated as a self-antigen by the immune system due to central and peripheral tolerance mechanisms. While the aberrant glycosylation of tumor-associated MUC1 offers a unique target, the immune system often fails to process and present these glycopeptides effectively enough to trigger a robust cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response. To overcome this, researchers are moving beyond simple peptide injections. The frontier of vaccine development now focuses on delivery mechanisms designed to hijack the body's natural uptake pathways. Two of the most innovative strategies reviewed in recent literature involve the use of antibody-mediated antigen uptake via rhamnose targeting and the use of gold nanoparticles (AuNP) to enhance major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presentation.
Unraveling these complex uptake mechanisms requires sophisticated detection reagents. At Creative Biolabs, our Anti-MUC1 Glycopeptide Antibody Development Service provides the specialized tools researchers need to track antigen fate, verify immune complex formation, and validate the specificity of the resulting immune response.
Hijacking Natural Antibodies: The Rhamnose Targeting Strategy
One of the most ingenious methods for enhancing MUC1 immunogenicity, as described in the literature, utilizes a "Trojan Horse" approach known as antibody-mediated antigen uptake. This strategy leverages the presence of naturally occurring antibodies in the human bloodstream to prompt antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to respond to the vaccine.
The mechanism works through a defined immunological cascade. Researchers have chemically coupled the bacterial monosaccharide L-rhamnose to MUC1 vaccine constructs. Upon injection, the host's circulating anti-rhamnose antibodies bind to the rhamnose moieties on the surface of the vaccine. The Fc region of these bound antibodies is then recognized by Fc receptors on the surface of APCs, triggering rapid internalization of the immune complex.
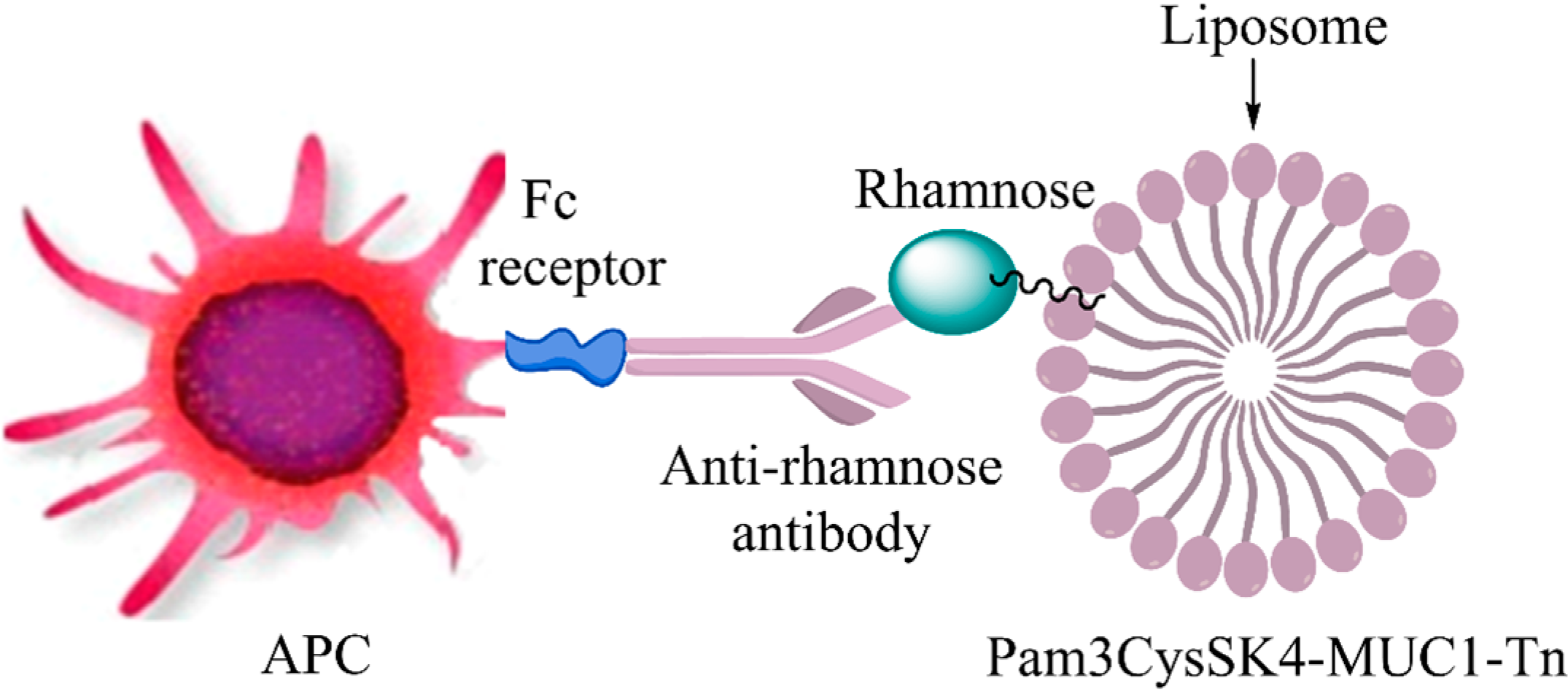 Fig.1
Mechanism of antibody-mediated antigen uptake.1
Fig.1
Mechanism of antibody-mediated antigen uptake.1
The true power of this antibody-mediated uptake lies in how the APC processes the cargo. In studies involving liposomes bearing a Pam3Cys-modified MUC1 glycopeptide and rhamnose, the interactions facilitated vaccine uptake and presentation. This mechanism enabled the presentation of CD4+ epitopes on MHC class II and, crucially, the cross-presentation of CD8+ epitopes on MHC class I. This led to an enhancement of both antibody production and CD8+ mediated cytotoxicity compared to controls lacking the rhamnose targeting moiety.
The Gold Standard: AuNP for Enhanced MHC Efficiency
While rhamnose relies on recruiting endogenous antibodies, gold nanoparticles (AuNP) function as a physical scaffold that fundamentally alters how the antigen is perceived by the immune system. Recent research highlighted in the review demonstrates the utility of AuNPs as carriers for three-component vaccines containing MUC1 glycopeptide and a CD4+ T cell peptide epitope. The AuNP-based vaccine elicited promising antibody titers, predominantly IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b.
Remarkably, the AuNP vaccine achieved these results utilizing ten times lower antigen concentration than a comparable non-AuNP formulation. This dose-sparing effect suggests that presenting the antigen through the MHC pathway is significantly more effective when the antigen is delivered via AuNPs. The production of IgG2a and IgG2b isotypes indicates that this delivery system supports a Th1-biased immune response, which is favorable for tumor clearance, and the induced antibodies maintained specific binding to MUC1-expressing breast cancer cells.
Scientific Significance: Overcoming the "Self" Barrier
The shift from simple conjugates to sophisticated delivery vehicles like rhamnose-displaying liposomes and AuNPs represents a maturation in antigen presentation enhancement strategies. The challenge with MUC1 has never been a lack of a target, but rather a lack of an efficient signal to break tolerance.
By coating a self-antigen with a foreign tag, such as rhamnose, or presenting it on a particulate carrier, like AuNP, these strategies create the immunogenic context required to activate APCs. The ability of rhamnose-mediated uptake to facilitate cross-presentation solves one of the biggest hurdles in subunit vaccine development: priming CD8+ killer T cells without using a live viral vector.
Conclusion & Service
The future of MUC1 immunotherapy lies in the intersection of glycobiology and nanotechnology. The evidence indicates that how an antigen is delivered is just as critical as the antigen's structure. These mechanisms provide a reproducible way to amplify the immune signal against weak tumor antigens. For researchers exploring these advanced delivery platforms, validating the downstream effects is essential. You must verify that your delivery system actually leads to the production of specific antibodies and T-cell activation against the target glycopeptide.
Validate Your Vaccine Delivery Efficiency
Creative Biolabs specializes in the custom development of antibodies and assay reagents tailored for these complex validations. Whether you need to detect MUC1-specific IgG subclasses or verify the binding of your vaccine-induced antibodies to tumor cell surfaces, our team is ready to assist. Validate your vaccine delivery efficiency with our Custom Anti-MUC1 Antibody Development Services.
Discuss Your Project with Creative Biolabs
