N-Linked Glycan Introduction
Accelerate Your Glycan-Based Discoveries!
Are you currently facing challenges in protein characterization, optimizing therapeutic antibody efficacy, or developing precise disease biomarkers? Our N-Linked Glycan services at Creative Biolabs help you accelerate drug discovery and obtain high-quality, functionally optimized biopharmaceuticals through advanced glycoengineering techniques and comprehensive glycan analysis platforms. Leverage our expertise to overcome complex glycosylation challenges.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
N-Linked Glycan
N- and O-glycosylation represent the predominant protein glycoforms. N-glycans feature a conserved GlcNAc₂Man₃ core attached to asparagine (Asn) within Asn-X-Ser/Thr sequons. Glycan structural diversity stems from non-template-driven biosynthesis, expressed via diverse monosaccharide arrangements, linkage variations, branching architectures, and isomeric configurations.
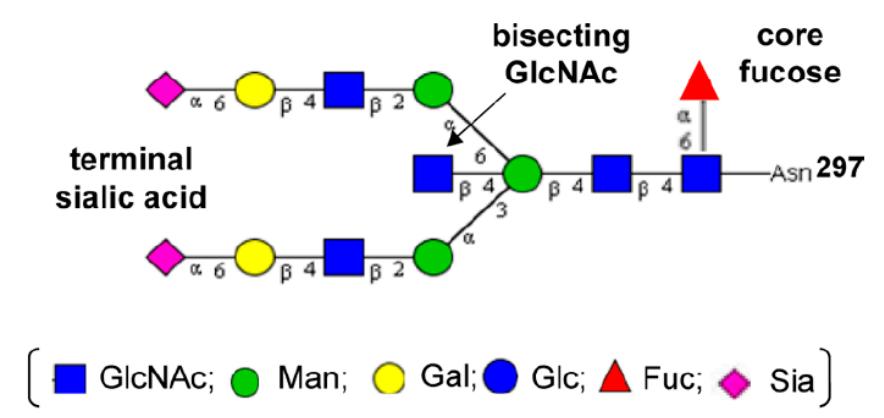 Fig.1 Biantennary N-glycan configuration containing bisecting GlcNAc at Fc region Asn-297.1,4
Fig.1 Biantennary N-glycan configuration containing bisecting GlcNAc at Fc region Asn-297.1,4
N-glycosidic bonds covalently link these glycans to proteins. Prokaryotes display diverse Asn-attached glycans, while eukaryotic N-glycans consistently initiate with GlcNAcβ1-Asn. Eukaryotic glycoproteins display three N-glycan classes at Asn-X-Ser/Thr sites: oligomannose, complex, and hybrid variants – all sharing the core structure. Complex types support ≤6 GlcNAc-initiated branches, extendable via repeating LacNAc (Galβ1-4GlcNAc) units.
Biosynthesis
N-Glycan biosynthesis initiates on dolichol-phosphate (Dol-P), a polyisoprenoid lipid carrier in eukaryotes. This two-stage pathway spans two cellular compartments: the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus. Phase one represents an evolutionarily preserved process occurring at ER membranes on Dol-P. Phase two commences with N-glycan processing by ER-lumen glycosidases and glycosyltransferases, continuing Golgi-mediated modifications exhibiting organism-, tissue-, protein-, and site-specificity. This pathway is universal among metazoans, plants, and fungi, while bacteria employ analogous mechanisms for cell wall assembly.
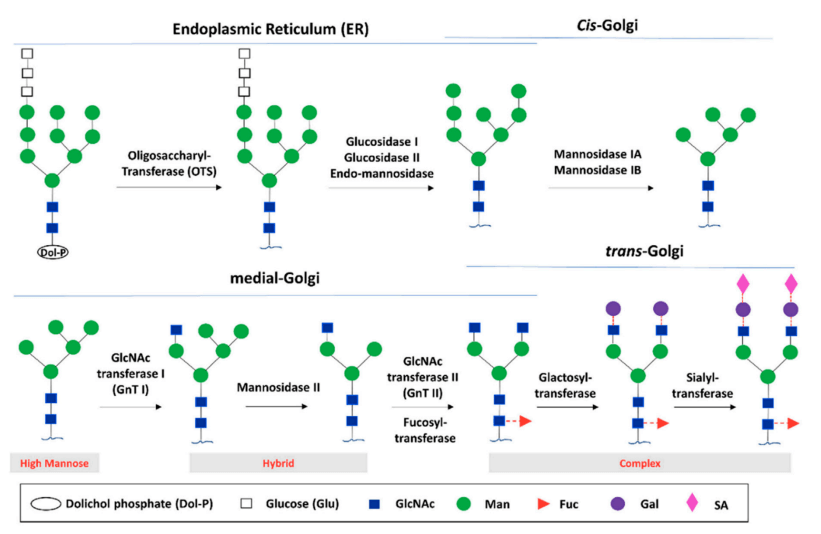 Fig.2 Glycan biosynthesis through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi glycosylation pathways.2,4
Fig.2 Glycan biosynthesis through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi glycosylation pathways.2,4
Protein attachment of N-glycans occurs co-translationally within the ER lumen. The precursor oligosaccharide (Glc₃Man₉GlcNAc₂) is assembled at ER membranes before transfer to sequon-containing polypeptides. Following 14-saccharide transfer, processing enzymes (glucosidases/mannosidases) trim the glycan during ER and early Golgi protein folding. Final maturation in the Golgi involves glycosyltransferase activity, producing the structural diversity depicted in Fig.2.
Functional & Clinical Significance
- Critical for eukaryotic protein folding fidelity
- Facilitate folding via steric stabilization
- Reinforce cellular walls and extracellular matrices
- Govern intercellular signaling and matrix adhesion
- Alter protein characteristics and guide glycoprotein trafficking
- Regulate immune cell motility patterns
N-glycan roles exhibit remarkable diversity, modulating numerous molecular activities. Aberrant N-glycan structures on specific glycoproteins significantly contribute to human pathologies, including type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and malignancies, justifying glycan directed biomarker and therapeutic development. Clinically, glycoproteins bearing defined N-glycan epitopes serve as diagnostic indicators, particularly in oncology.
Glycan biomarkers (e.g., N-glycans) hold substantial promise for precision medicine. Heavy-isotope methodologies and isotope-labeled glycan standards will deliver essential precision and robustness for clinical utilization.
Published Data
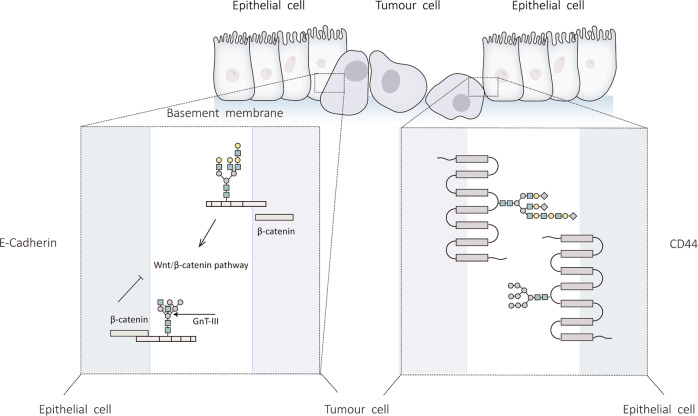 Fig.3 Effect of N-glycosylation modification on EMT (Epithelial-mesenchymal transition).3,4
Fig.3 Effect of N-glycosylation modification on EMT (Epithelial-mesenchymal transition).3,4
Research published in the field of N-glycosylation, particularly concerning its role in disease progression, provides strong evidence for the significance of glycan analysis. For instance, studies investigating hepatocarcinogenesis have systematically analyzed changes in N-glycan patterns during the development of liver lesions into full-blown liver cancer. These experiments often employ advanced glycomics techniques, such as mass spectrometry-based approaches, to profile the N-glycome of patient samples at different disease stages. A key finding consistently reported is the observation of increased levels of sialylation and fucosylation on N-glycan chains as liver cancer progresses. These alterations are not merely correlative; experimental evidence suggests they functionally impact tumor-related proteins, such as Laminin, influencing processes critical for tumorigenesis. These published insights underscore how aberrant glycosylation serves as a valuable indicator for disease state and a potential target for novel therapeutic strategies, reinforcing the importance of precise glycan characterization in biomedical research.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs serves as your integrated collaborator within the N-Linked Glycan research domain. We leverage our extensive expertise and cutting-edge technology to provide a suite of services designed to advance your biopharmaceutical projects.
- High-Resolution N-Glycan Profiling
- Comparative Glycosylation Analysis
- Targeted Glycoengineering
- Glycoprotein Structural Characterization
- Anti-Carbohydrate Antibody Development
Discover the Creative Biolabs Advantage—Contact Us to Get a Quote Today
Why Choose Us?
Choosing Creative Biolabs for your N-Linked Glycan needs means partnering with a leader dedicated to precision, innovation, and client success. Our commitment to excellence permeates every service dimension.
- Unparalleled Expertise: Our team comprises over 20 years of experience in glycobiology, offering deep scientific understanding and practical solutions.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: We utilize advanced analytical platforms, including high-resolution mass spectrometry and advanced chromatography, ensuring accurate and comprehensive glycan characterization.
- Customized Solutions: We provide tailored approaches, from detailed glycan profiling to sophisticated glycoengineering, to meet your unique project requirements.
- Robust Quality Control: Every step of our process is subjected to stringent quality control measures, guaranteeing reliable and reproducible results.
FAQs
Here are some common questions about N-Linked Glycan applications and considerations:
Q: What is the primary advantage of analyzing N-linked glycans in protein therapeutics?
A: Analyzing N-linked glycans is crucial for therapeutic proteins because these modifications directly impact a drug's stability, efficacy, and immunogenicity. Understanding the glycan profile allows for targeted optimization to enhance pharmacokinetics, improve binding affinity to target receptors, and minimize unwanted immune responses, leading to safer and more effective treatments. Exploring these aspects can significantly accelerate drug development.
Q: How do aberrant N-glycan patterns relate to disease progression?
A: Aberrant N-glycan patterns are increasingly recognized as hallmarks in various diseases, including cancer and autoimmune disorders. Changes in glycan structures, such as increased sialylation or fucosylation, can alter cell-cell communication, modulate immune responses, and influence the function of key proteins involved in disease pathways. These insights offer promising avenues for diagnostic biomarker discovery and therapeutic intervention.
Q: Can specific N-glycan modifications improve the therapeutic function of an antibody?
A: Absolutely. Specific N-glycan modifications on antibodies, particularly in the Fc region, are known to significantly influence effector functions like Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) and Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC). For example, afucosylation can enhance ADCC, while increased sialylation can confer anti-inflammatory properties. Tailoring these modifications can lead to antibodies with optimized therapeutic profiles. Consider how specific glycan engineering could benefit your next project.
Related Products and Services
To advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a comprehensive product portfolio:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
Creative Biolabs delivers varied anti-glycan antibody solutions for international clientele. To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Boune, Souad et al. "Principles of N-Linked Glycosylation Variations of IgG-Based Therapeutics: Pharmacokinetic and Functional Considerations." Antibodies (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 9,2 22. 10 Jun. 2020, DOI:10.3390/antib9020022
- Hu, Mengyu et al. "The role of N-glycosylation modification in the pathogenesis of liver cancer." Cell death & disease vol. 14,3 222. 29 Mar. 2023, DOI:10.1038/s41419-023-05733-z
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
