Alpha-Galactosyl Introduction
Accelerate Your Glycan-Based Discoveries!
Are you currently facing challenges in understanding complex glycan-antibody interactions, developing highly specific anti-glycan antibodies, or navigating immunological responses related to alpha-gal? Creative Biolabs Alpha-Galactosyl Solutions help you streamline your research into glycan-mediated immunity and develop highly specific anti-glycan reagents through advanced glycoengineering and immunology platforms.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Alpha-Galactosyl
The primary xenoantigens detected by human natural antibodies feature terminal alpha-galactosyl (Galα1-3Gal) epitopes within extended carbohydrate chains attached to diverse proteins and lipids. Most alpha-galactosyl epitopes are synthesized by α1,3GT via galactose transfer from UDP-Gal, creating α(1,3)-glycosidic bonds with glycolipid or glycoprotein acceptors ending in N-acetyllactosamine (LacNAc), Galβ(1,4)GlcNAc.
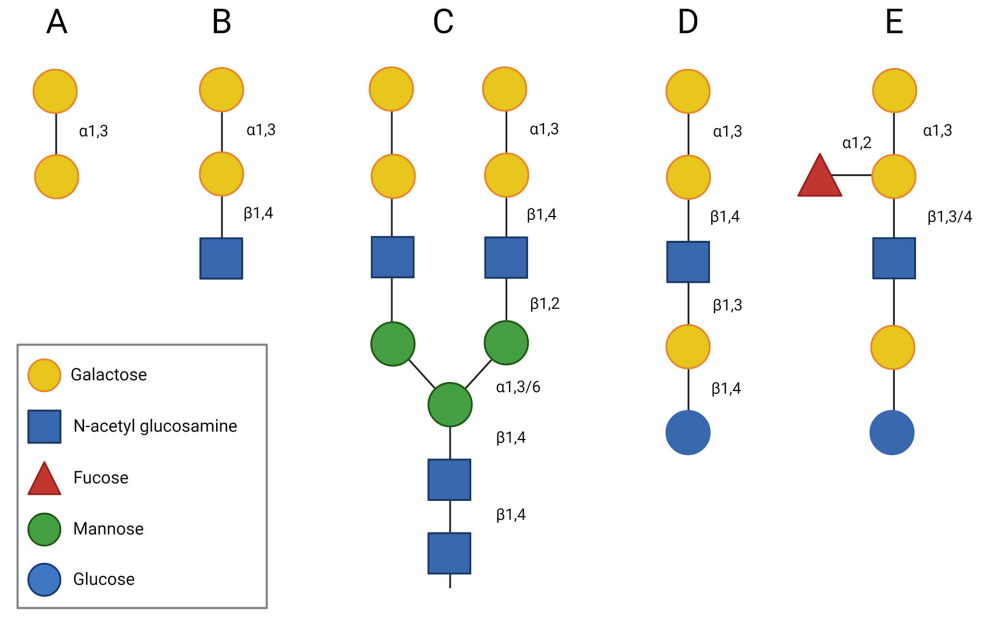 Fig.1 Structure of the α-Gal epitope.1,3
Fig.1 Structure of the α-Gal epitope.1,3
Anti-Alpha-Galactosyl Antibody
Humans and closely related hominoids like apes naturally produce anti-Galα1-3Gal antibodies. These antibodies are present in humans, apes, and Old World monkeys but are missing in New World monkeys and other mammals. This distribution pattern reflects humans, apes, and Old World monkeys lacking functional GGTA1 enzymes and therefore lacking Galα1-3Gal epitopes on their tissues.
Evidence suggests these natural antibodies develop against commensal gut microbiota, contributing significantly to innate immunity. Human anti-Gal antibodies exhibit high titers, comprising up to 1% of total serum IgG, and mediate inactivation of zoonotic enveloped viruses and retroviruses by human serum. They may additionally protect against parasitic and microbial infections.
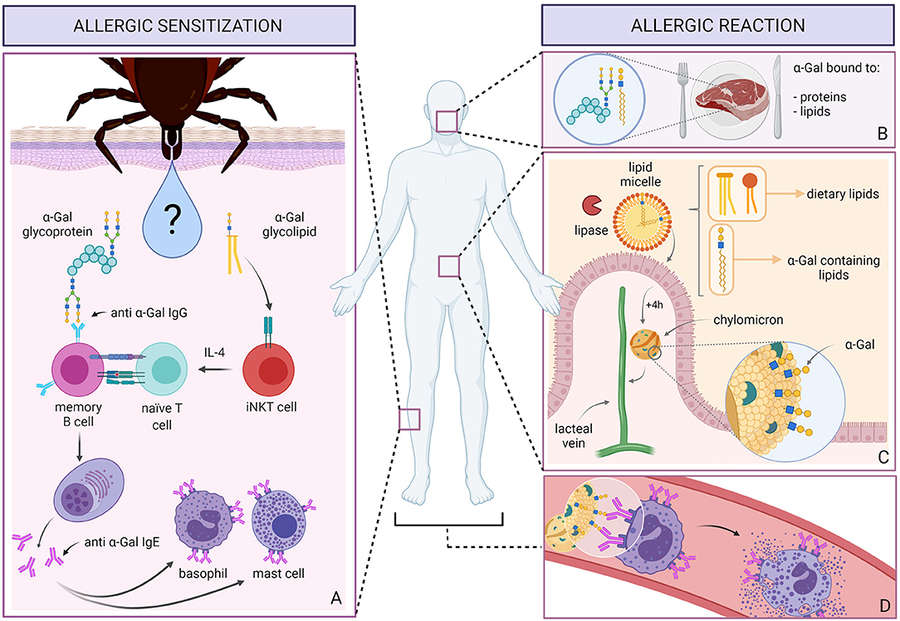 Fig.2 Allergic sensitization and reaction to α-Gal.1,3
Fig.2 Allergic sensitization and reaction to α-Gal.1,3
The carbohydrate galactose-α-1,3-galactose (α-Gal) is long recognized as a xenotransplantation barrier, hindering pig-to-human organ transplants. Rejection occurs because humans generate antibodies targeting the α-Gal epitope, prevalent on mammalian glycoproteins and glycolipids but absent in humans, apes, and Old-World monkeys. Antibody binding to α-Gal triggers complement activation, causing xenograft destruction.
A decade ago, α-Gal gained renewed focus as the causative agent of α-Gal syndrome—an atypical food allergy where patients develop IgE antibodies against α-Gal. Affected individuals experience delayed hypersensitivity after ingesting beef, pork, or lamb, and immediate reactions following intravenous α-Gal-containing therapeutics.
Published Data
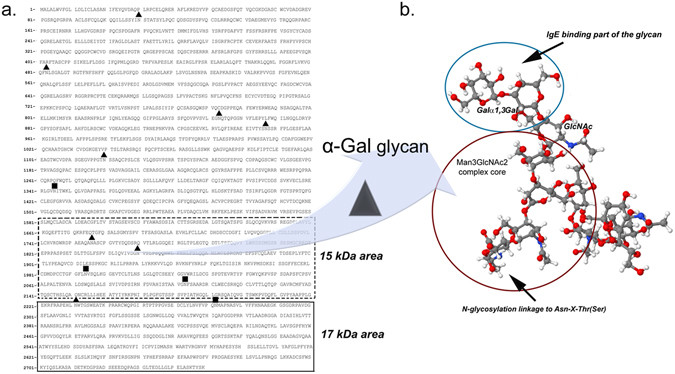 Fig.3 Peptidomic analysis of α-Gal IgE-binding peptides.2,3
Fig.3 Peptidomic analysis of α-Gal IgE-binding peptides.2,3
In a study investigating the allergenic properties of α-Gal epitopes after digestion, researchers performed in vitro pepsinolysis of bovine thyroglobulin (BTG), a model α-Gal carrying glycoprotein. The experiment aimed to determine if gastric digestion affects the stability and IgE-binding capacity of α-Gal. Using a mass spectrometry-based peptidomics approach, the scientists analyzed the digested BTG fragments. The key finding was that α-Gal epitopes remained stable and retained their allergenic activity even after extensive pepsinolysis, indicating their resilience to the gastric environment. Additionally, the study pinpointed definitive IgE-reactive α-Gal residues at Asn1756, Asn1850, and Asn2231 in internal and C-terminal domains of BTG. This demonstrated that these specific sites are crucial for IgE recognition and that small peptides containing these epitopes are sufficient to elicit an allergic response. The results reinforce the understanding that durable α-Gal epitopes, often introduced via tick bites, contribute to the delayed onset and clinical presentation of red meat allergy, providing mechanistic insights into this unique carbohydrate-mediated allergic disease.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs leverages its extensive experience and state-of-the-art technology to provide a comprehensive suite of services focused on alpha-galactosyl research and antibody development.
- Custom Anti-Alpha-Gal Antibody Development
- Alpha-Gal Epitope Synthesis & Conjugation
- Glycan Array Screening
- Immunological Assay Development
Leveraging profound antibody research expertise, Creative Biolabs is delighted to present clients with specialized anti-glycan antibody development services featuring optimal quality at market-leading rates. Supported by cutting-edge platforms and a specialized research team, we enable global partners to generate anti-carbohydrate antibodies, encompassing both monoclonal and polyclonal formats.
Discover the Creative Biolabs Edge – Obtain Your Pricing Now
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of glycoscience, offering unparalleled expertise and cutting-edge technology in alpha-galactosyl research. Our commitment to precision, quality, and client success makes us the ideal partner for your projects.
- Unrivaled Expertise: Over years of specialized experience in glycan research and antibody development.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Utilization of advanced glycoengineering platforms and high-throughput screening methodologies.
- Customized Solutions: Tailored project design to meet your unique research objectives and specific deliverables.
- Comprehensive Characterization: Rigorous validation of antibody specificity, affinity, and functional activity.
FAQs
Q: How do alpha-gal epitopes contribute to immunological responses, and why is their study important?
A: Alpha-gal epitopes are unique carbohydrate structures that trigger significant immune responses in humans, primarily due to their absence in the human body. Their study is crucial for understanding hyperacute rejection in xenotransplantation, developing therapies for the Alpha-Gal Syndrome (a tick-borne allergy), and exploring novel strategies for viral inactivation. Gaining precise insights into these interactions can unlock new therapeutic and diagnostic avenues.
Q: What are the key considerations when designing an antibody against a carbohydrate epitope like alpha-gal?
A: Designing antibodies against carbohydrate epitopes requires specialized expertise due to their often repetitive nature and conformational flexibility. Key considerations include selecting appropriate immunization strategies to elicit strong immune responses, optimizing screening methods for high specificity, and ensuring the resulting antibodies can bind effectively to the target glycan in its native biological context. Detailed characterization of binding affinity and specificity is paramount.
Q: What are the primary biomedical applications of tailored anti-glycan antibodies?
A: Custom anti-carbohydrate antibodies have diverse applications, including diagnostics for infectious diseases and allergies (like AGS), tools for studying cell surface glycans in cancer and developmental biology, reagents for xenotransplantation research, and components in vaccine development. Their ability to target specific glycan signatures makes them invaluable for understanding complex biological processes.
Related Products and Services
To further advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a portfolio of solutions:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Román-Carrasco, Patricia et al. "The α-Gal Syndrome and Potential Mechanisms." Frontiers in allergy vol. 2 783279. 16 Dec. 2021, https://doi.org/10.3389/falgy.2021.783279
- Apostolovic, D et al. "Peptidomics of an in vitro digested α-Gal carrying protein revealed IgE-reactive peptides." Scientific reports vol. 7,1 5201. 12 Jul. 2017, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05355-4
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
