ABH-Glycan Microarray
ABH antigens, key determinants of human blood groups, are structurally complex glycans displayed on erythrocytes, epithelial cells, and secretions. These glycans define the A, B, and H blood group phenotypes, playing critical roles in transfusion medicine, transplantation compatibility, and pathogen-host interactions. Recent advances in glycan microarray technologies have enabled the high-throughput, quantitative, and structure-specific analysis of ABH antigens. At Creative Biolabs, we offer a robust ABH-glycan microarray platform, enabling precise profiling of anti-human blood group antigen ABH antibodies, blood group antigen glycan mapping, and predictive modeling of complex ABO glycan interactions.
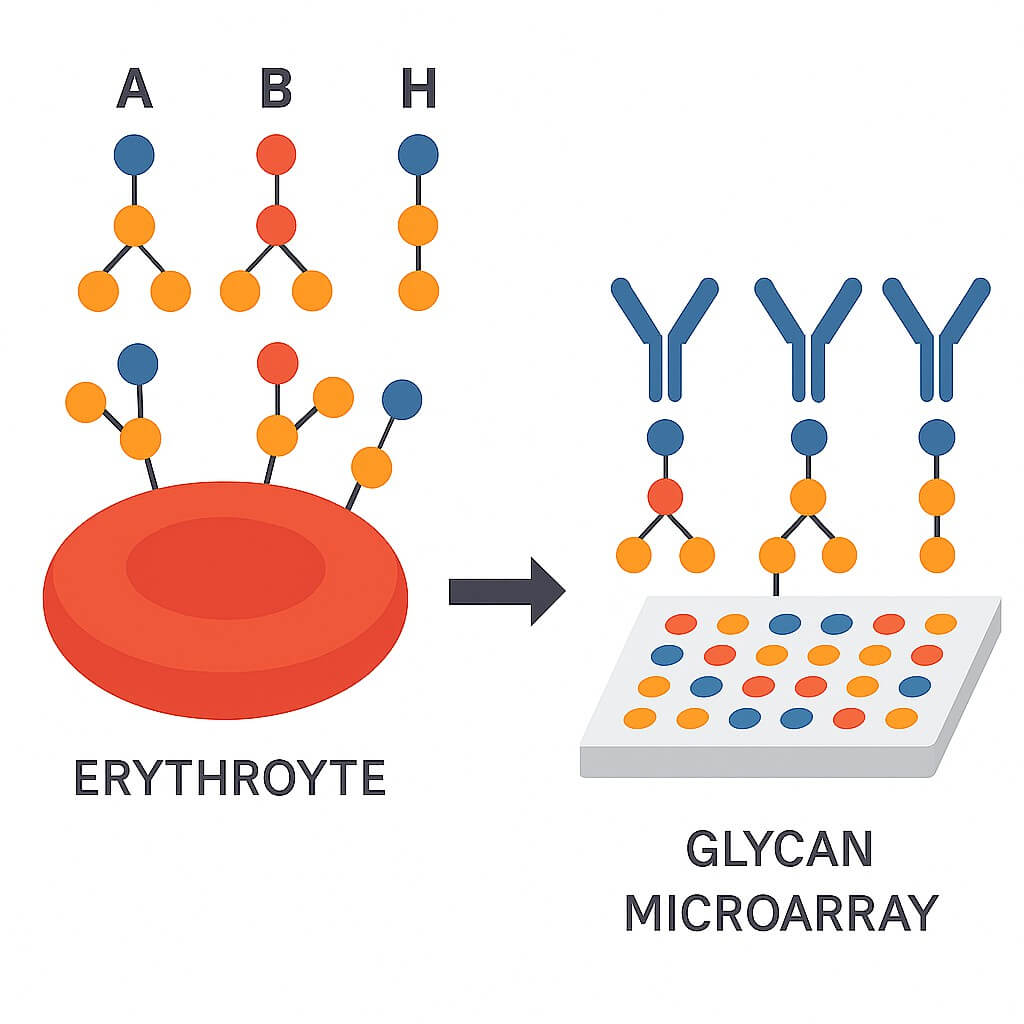 Fig.1 ABH antigens on red blood cells and ABH-glycan microarray platform.
Fig.1 ABH antigens on red blood cells and ABH-glycan microarray platform.
Biological Basis of Blood Group Antigens
ABH antigens are not proteins, but specific terminal carbohydrate structures presented on glycoproteins and glycolipids. They are synthesized by glycosyltransferases encoded by the ABO gene locus, which modifies a shared precursor, the H antigen, as follows:
- Type A: Addition of N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) by A-transferase
- Type B: Addition of galactose by B-transferase
- Type O (H antigen): Unmodified, expressing fucose only
Glycan Structures Defining Blood Group Antigens
| Blood Group | Terminal Glycan Structure | Key Enzyme | Core Sugar | Precursor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | GalNAcα1→3(Fucα1→2)Galβ1 | A-transferase | GalNAc | H antigen |
| B | Galα1→3(Fucα1→2)Galβ1 | B-transferase | Gal | H antigen |
| O (H) | Fucα1→2Galβ1 | - | Fucose | Type 1 or 2 chain |
The expression and recognition of these glycans are critical in:
- Blood transfusion compatibility
- Organ transplantation (especially in ABO-incompatible cases)
- Host susceptibility to infectious diseases
Advantages Over Traditional Method
| Feature | ABH-Glycan Microarray | Traditional Hemagglutination |
|---|---|---|
| Glycan Subtype Resolution | High | Limited |
| Quantification | Yes | Semi-quantitative |
| Multiplexing | 100+ antigens/sample | One at a time |
| Cross-reactivity detection | Yes | No |
| Custom glycan panel options | Available | Not feasible |
Technological Platform: ABH-Glycan Microarray
The ABH-glycan microarray platform is a synthetic glycan-based screening platform that immobilizes structurally defined A, B, and H glycans onto glass or nitrocellulose slides. This allows precise interrogation of glycan-antibody interactions.
- Defined glycan structures, including multiple A/B subtypes
- Using fluorescently labeled anti-human blood group antibodies for quantitative detection
- Over 100 glycan variants per array
- Compatibility with serum, plasma, or purified IgG
Detection Targets
- Anti-A, anti-B, and anti-H antibodies
- Subtype-specific reactivity
- Cross-reactivity with other glycan motifs (e.g., Lewis antigens, sialylated structures)
ABH-Glycan Analysis Workflow
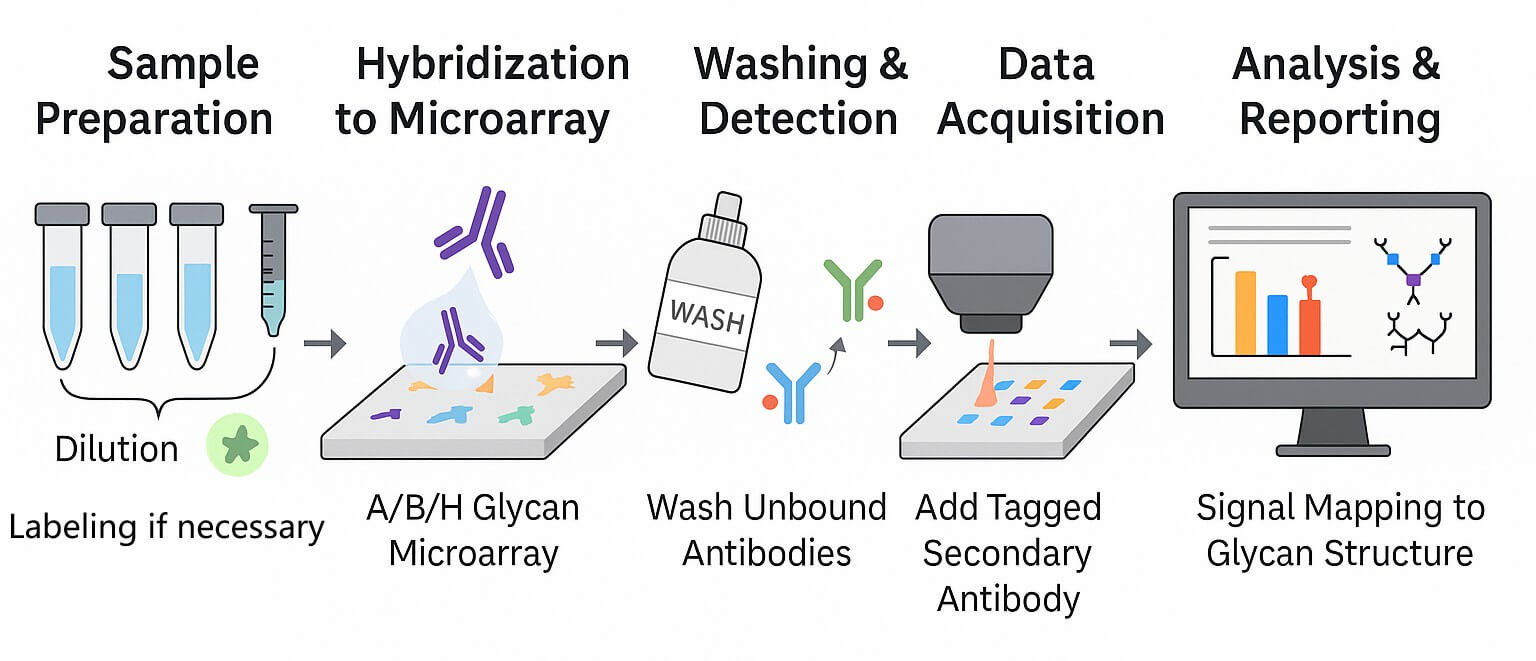 Fig.2 The workflow for ABH-glycan microarray.
Fig.2 The workflow for ABH-glycan microarray.
-
Sample Preparation
Serum, plasma, or antibody sample is diluted and labeled if necessary. -
Hybridization to Microarray
Incubation with printed slides containing A/B/H glycans. -
Washing & Detection
Removal of unbound antibodies; addition of fluorescence- or enzyme-tagged secondary antibody. -
Data Acquisition
Fluorescence scanning and spot quantification. -
Analysis & Reporting
Signal intensities mapped to glycan structure; antibody specificity profiled.
Applications of ABH-Glycan Microarray
Transplantation Immunology
ABO-incompatible organ transplantation is associated with hyperacute rejection due to preformed anti-ABH antibodies. Microarray profiling allows:
- Pre-transplant antibody screening
- Risk stratification for rejection
- Post-transplant monitoring of desensitization
Transfusion Safety
Blood transfusion mismatches can be fatal. The ABH-glycan microarray helps:
- Characterize alloantibodies in complex cases
- Analyze weak subgroups
- Support rare blood group identification
Infectious Disease Susceptibility
Certain pathogens exploit ABH glycans as entry receptors:
- Noroviruses bind to A/B/H glycans on epithelial cells
- Helicobacter pylori adheres to fucosylated glycans (H-antigen-like)
ABH microarrays enable correlation of host glycan profiles with infection risk.
Therapeutic Antibody Specificity Testing
Evaluate off-target binding of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to ABH-like structures to avoid unintended cross-reactivity in glycoengineered drugs.
A Case Example: Predictive Modeling of ABO Glycan Binding
A study conducted in 2020 has developed a machine learning model using ABO glycan microarray datasets to predict the binding specificity of serum antibodies. This approach supports personalized diagnostics and precision matching in transfusion/transplantation.
- Trained on 244 glycan structures
- Assessed 189 serum samples
- Showed >90% accuracy in identifying anti-A and anti-B binding preferences
- Enabled prediction of complex subtype preferences
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
With over two decades of expertise in glycan chemistry, immunology, and microarray engineering, Creative Biolabs offers:
- Custom glycan design and immobilization
- High-resolution antibody profiling for ABH antigens
- Data interpretation support by glycoimmunologists
- Secure, traceable workflows with full documentation
Related Services You May Be Interested In
In addition to the ABH-glycan microarray, Creative Biolabs offers high-throughput microarray platforms that cover a wide range of glycan structures, including N-glycans, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), and more. Each microarray platform is customizable to your research needs, with detailed glycan libraries and expert data interpretation support.
| Microarray Type | Highlights | Application Scope |
|---|---|---|
| 100 Glycan Microarray | Covers major human glycan epitopes including ABO, Lewis, and tumor-associated antigens | Broad-spectrum glycan-binding antibody screening |
| 100 N-Glycan Microarray | Structurally defined N-linked glycans from high-mannose to complex types | Antibody profiling, glycoprotein receptor mapping |
| Oligosaccharide Microarray | Short-chain linear and branched oligosaccharides | Carbohydrate–protein interaction studies |
| Polysaccharide Microarray | Bacterial, fungal, and plant polysaccharide antigens | Anti-polysaccharide antibody analysis, vaccine development |
| Glucan Microarray | β-glucans of different linkages and lengths | Fungal immunology, PRR binding assays |
| Heparan Sulfate Microarray | Sulfation-defined HS chains for ligand screening | Growth factor binding, viral entry, ECM studies |
| Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Microarray | Chondroitin, dermatan, heparin, and hybrid GAG structures | Biomarker validation, inflammation research |
| Human Milk Oligosaccharide (HMO) Microarray | 2'-FL, LNnT, LNT and sialylated/fucosylated HMOs | Infant nutrition, microbiome–glycan interaction profiling |
Interested in integrating ABH-glycan profiling into your research? Contact our specialists to design your custom microarray study or learn more about our glycan-based screening solutions.
Reference:
- Heimburg-Molinaro, Jamie, et al. "Insights into Glycobiology and the Protein-Glycan Interactome Using Glycan Microarray Technologies." Molecular & Cellular Proteomics (2024): 100844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100844
