Custom Anti-GD1a Antibody Service for GBS (AMAN) Research
Background: GD1a, AMAN, and Research Needs
Ganglioside GD1a is a disialylated glycosphingolipid enriched at motor nodes of Ranvier. Anti-GD1a antibodies are tightly linked to the axonal variants of Guillain–Barré Syndrome (GBS), especially acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN); notably, anti-GD1a associates with axonal—but not demyelinating—forms of GBS. In some regions (e.g., parts of East Asia), AMAN accounts for a substantial fraction of GBS cases, underscoring strong geographic heterogeneity that research tools must respect. Mechanistically, molecular mimicry between Campylobacter jejuni lipo-oligosaccharides (LOS) and host gangliosides helps explain the emergence of anti-ganglioside responses; LOS bearing GM1- or GD1a-like epitopes have been described. Anti-ganglioside antibodies occur in a large subset of GBS; measuring these titers is important in research settings that model GBS diagnostics workflows and explore disease biology.
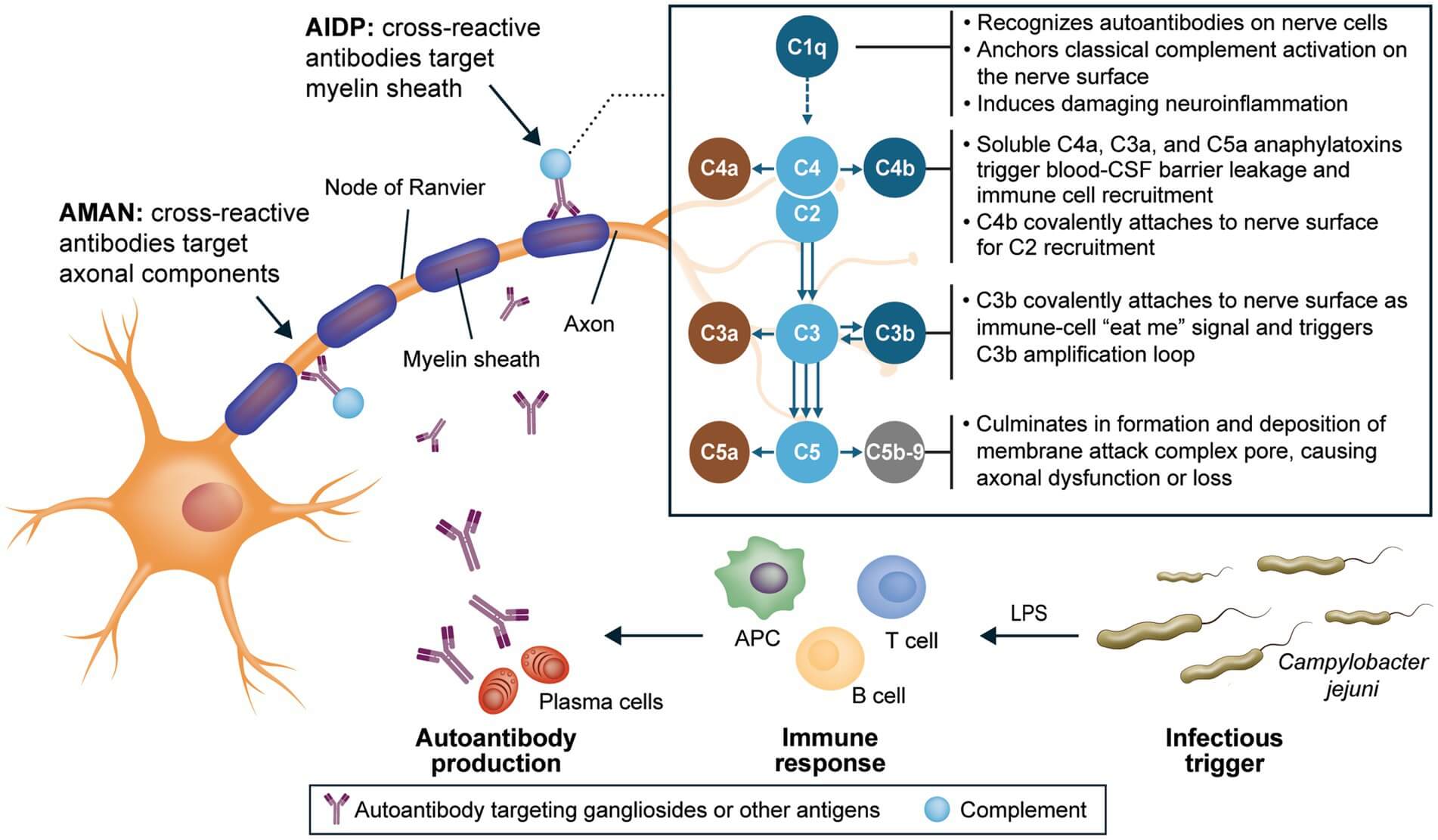 Fig.1 GBS pathogenesis & anti-ganglioside antibodies.1
Fig.1 GBS pathogenesis & anti-ganglioside antibodies.1
At Creative Biolabs, we design, generate, and validate high-specificity anti-ganglioside antibodies, including anti-GD1a antibodies that help you probe AMAN-relevant mechanisms, build robust research-grade immunoassays, and de-risk cross-reactivity against structurally similar gangliosides and ganglioside complexes. Our platform integrates glycolipid chemistry, membrane-mimetic antigen presentation, discovery technologies (hybridoma, phage display, single-B cell), and glycan microarray specificity screening to deliver reliable GD1a antibody tools for rigorous, reproducible studies. Ready-to-use anti-GD1a antibody products are available at Creative Biolabs to help you get a quick project start!
What We Offer: Custom Anti-GD1a Antibody
We tailor anti-GD1a antibody solutions for both exploratory biology and translational assay development. Typical deliverables include monoclonal clones (mouse, rabbit, camelid), recombinant formats (IgG, scFv, Fab, VHH), affinity-qualified lots, and validated application data. Here are anti-GD1a antibody development service details you can get from Creative Biolabs:
- Antigen design for ganglioside GD1a. Synthetic GD1a or chemo-enzymatic analogs; conjugation to KLH/BSA; liposome or nanoparticle presentation to mimic membrane context.
- Discovery & cloning. Hybridoma, phage display, or single-B-cell cloning; species and isotype per study design.
- Specificity assurance. Cross-reactivity profiling on glycan arrays and multi-ganglioside panels (GM1, GD1b, GT1a, GQ1b).
- Application validation. ELISA/TLC-immunostaining; liposome-incorporated antigens when membrane context matters.
- Scale-up & QC. Recombinant expression, affinity chromatography, lot release, and stability data packages.
Discuss Your Anti-GD1a Project with Our Experienced Expertise
Ready-To-Use GD1a Antibodies
Need off-the-shelf options to jump-start a project? Explore our GD1a antibody catalog and datasheets here:
-
Mouse Anti-GD1a Monoclonal Antibody (AGM-036YJ)(CAT#: AGM-036YJ)Online InquiryHost: MouseAntibody Isotype: IgG1Species Reactivity: Fish, Human, Rat, Mouse, CattleApplication: ELISA, IHC
-
Mouse Anti-GD1a Monoclonal Antibody (AGM-037YJ)(CAT#: AGM-037YJ)Online InquiryHost: MouseAntibody Isotype: IgM, κSpecies Reactivity: OtherApplication: ICC, IHC, TLC, FC, ELISA
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
- Membrane-mimetic antigens. We present ganglioside GD1a in liposomes/nanoparticles to select clones that bind the epitope in a native-like environment.
- Cross-reactivity risk managed. Every anti-GD1a antibody undergoes glycan-array and mixed-ganglioside panel testing—including GD1a-related complexes—to document true specificity.
- AMAN-relevant insight. We understand AMAN biology (anti-GD1a, complement, nodal injury) and help you design assays that capture those mechanisms.
- Flexible formats, clear paper trail. Hybridoma, phage display, single-B-cell; recombinant reformatting on demand; robust documentation for reproducibility.
How Scientists Use GD1a Antibodies
Reports indicate anti-GD1a and GM1 co-reactivity in AMAN cohorts, emphasizing careful antigen selection and specificity control in assay design.
| Application Area | Typical Readout | Where GD1a Antibodies Help |
|---|---|---|
| AMAN Mechanisms | Complement-linked nodal injury, motor conduction failure | Map antibody binding at nodes of Ranvier; test complement-dependent injury hypotheses. |
| GBS Diagnostics Research | ELISA/TLC-immunostaining titer curves; cross-reactivity matrices | Build research-grade assays that reflect clinical patterns while avoiding off-target signals. |
| Infection–Autoimmunity Links | LOS-ganglioside mimicry evidence | Model mimicry between C. jejuni LOS and GD1a to contextualize serology results. |
| Complex Antigen Biology | Binding to GalNAc-GD1a and other GSCs | Differentiate single-ganglioside vs complex-dependent epitopes in AMAN subsets. |
Services You May Be Interested in
- Custom Anti-GM1 Antibody & Development
- Anti-GD1b / Anti-GT1a / Anti-GQ1b Antibody Development
- Glycosphingolipids Analysis Service
If your study interrogates AMAN pathogenesis, compares GBS diagnostics workflows, or screens clones against ganglioside GD1a and its complexes, we'll help you deliver data you can defend. Tell us your model, matrix, and assay endpoints, our scientists will propose an antibody and validation plan that fits. Contact us to Start your custom anti-GD1a antibody project, share your targets and intended applications, and we'll respond with a tailored plan and quote.
FAQs
What makes your custom anti-GD1a antibody service valuable for GBS (AMAN) research?
Our service is designed to generate highly selective antibodies against ganglioside GD1a, which is closely linked to GBS and AMAN pathogenesis. By combining advanced antigen design, multi-platform discovery, and rigorous specificity screening, we deliver antibodies that are not only reliable for biomarker validation but also tailored for mechanistic studies in autoimmune neuropathy research.
Can your GD1a antibodies be used across different assay formats?
Yes. We validate antibodies across multiple formats, including ELISA, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and surface plasmon resonance. Each antibody undergoes functional and cross-reactivity testing to ensure compatibility. Clients receive validated data packages and SOPs, making it easier to integrate the antibodies into a variety of experimental systems.
Do you offer ready-to-use anti-GD1a antibodies for quick studies?
Yes, we provide a selection of ready-to-use antibodies targeting GD1a for immediate application in research. These are available with full technical datasheets, including host species, isotypes, validated assay formats, and recommended applications. While they are ideal for pilot studies, we encourage custom programs for clients who need antibodies optimized for their specific research goals.
Can you humanize or reformat GD1a antibodies for translational studies?
Absolutely. Our antibody engineering team can humanize murine or rabbit clones while preserving their GD1a-specific binding pockets. We also provide reformatting into IgG subtypes, Fab, or scFv fragments. Each engineered antibody undergoes affinity and specificity validation, ensuring that the final product is suitable for both fundamental research and preclinical assay development in autoimmune neuropathy studies.
What experience does Creative Biolabs have with ganglioside-targeting antibodies?
We have experience in glycobiology and anti-glycolipid antibody discovery, with successful programs targeting GM1, GM2, GD1a, GD1b, and other gangliosides. This accumulated expertise allows us to navigate the challenges of glycan immunogenicity and cross-reactivity, providing antibodies that are both highly specific and research-ready for GBS and AMAN investigations.
Reference:
- Gorson, Kenneth C. "Evolving understanding of Guillain-Barré syndrome pathophysiology and the central role of the classical complement pathway in axonal injury." Frontiers in Neurology 16 (2025): 1572949. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2025.1572949
