Anti-MUC1 Glycopeptide Antibody Development Service
The MUC1 protein, a transmembrane mucin, undergoes profound alterations during malignant transformation. In normal epithelia, MUC1 is heavily glycosylated, but in cancer cells—such as breast, ovarian, and pancreatic carcinomas—it is overexpressed and aberrantly glycosylated. This process creates unique, tumor-specific neo-epitopes like Tn and sTn antigens within the variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) region. Creative Biolabs leverages decades of expertise in custom glycopeptide antibody development to generate high-affinity antibodies targeting these specific MUC1 glycoforms. Our comprehensive platform overcomes the challenges of self-tolerance and weak immunogenicity, providing researchers with robust tools for next-generation ADC and CAR-T related research.
Background: The Challenge of Targeting MUC1
MUC1 is a highly attractive target due to its widespread overexpression in adenocarcinomas. However, developing a truly tumor specific MUC1 antibody is notoriously difficult. The key difference lies in glycosylation. In healthy cells, the VNTR region is masked by long, branched O-linked glycans. In contrast, the underglycosylated MUC1 antibody targets found on tumor cells expose truncated carbohydrate antigens (Tn, sTn) and peptide backbones that are normally hidden.
Aberrant Glycosylation
Tumors lack the enzymes to build full sugar chains, resulting in the exposure of the immunodominant MUC1 neoepitope antibody targets like Tn (GalNAc-Ser/Thr) and sTn (Neu5Ac-Tn).
Low Immunogenicity
Because MUC1 is a self-antigen, the immune system is tolerant to it. Generating a high-affinity anti-MUC1 monoclonal antibody requires specialized immunization strategies to break this tolerance.
Cross-Reactivity Risks
Antibodies must distinguish between the MUC1 glycopeptide antibody target and the naked peptide or normal MUC1 to ensure high specificity in research studies.
Our Anti-MUC1 Glycopeptide Antibody Services
We offer a complete suite of services for glycopeptide antibody production. Our scientists design synthetic glycopeptides that precisely mimic the tumor-associated VNTR structure. By controlling the glycosylation site density and chemistry, we direct the immune response toward the specific glyco-epitope of interest.
Development of MUC1-Tn Antibodies
We generate antibodies that specifically recognize the Tn antigen (GalNAc) attached to the MUC1 VNTR. These MUC1-Tn antibody candidates are ideal for CAR-T cell research, as they bind effectively to breast cancer MUC1 antibody targets while sparing normal tissues.
Development of MUC1-sTn Antibodies
The sialyl-Tn (sTn) antigen is a marker of poor prognosis in many cancers. Our MUC1-STn antibody development service utilizes sialylated glycopeptide immunogens to produce clones with exceptional specificity for this acidic glycoform, supporting ovarian cancer marker antibody research.
Novel MUC1 Subunit Targeting
Beyond the VNTR, we develop antibodies against the membrane-proximal subunits. This includes MUC1-C antibody generation for targeting oncogenic signaling and MUC1-N antibody development for shedding studies. We also explore CA-125 neoepitope antibody targets for combinatorial studies.
Glycosylation Site-Specific Screening
Our platform excels at glycosylation site specific antibody discovery. We can target specific threonine or serine residues within the MUC1 repeat, distinguishing between N-linked glycopeptide antibody targets and O-linked glycopeptide antibody modifications.
Related Glycopeptide Targets
While MUC1 is a primary target, other mucins and glycoproteins exhibit similar aberrant glycosylation in cancer. Creative Biolabs provides anti-glycopeptide antibody development for a broad range of tumor specific glyco-epitope antibody targets.
Mucin Family Targets
We support colon cancer MUC2 antibody projects targeting MUC2 glycopeptide antibody epitopes, as well as pancreatic cancer MUC4 antibody development focusing on sialylated MUC4 antibody variants. Our services also cover anti-MUC5AC antibody generation for gastric cancer research.
MUC16 (CA-125) & CD43
Our experts can develop anti-MUC16 monoclonal antibody reagents targeting the glycosylated MUC16 antibody structure. Additionally, we offer anti-CD43 antibody services for leukemia and solid tumors, focusing on the tumor associated CD43 antibody glycoforms (un-sialylated leukosialin).
PODXL & Other Glycoproteins
We generate antibodies against anti-podocalyxin antibody targets, specifically the PODXL glycopeptide antibody found in renal cell carcinoma. This extends to other secreted mucin antibody and goblet cell mucin antibody targets requiring precise glycan recognition.
Published Data: Efficacy of MUC1-Tn Targeting
A study highlights the efficacy of targeting the aberrantly glycosylated tumor form of MUC1 (tMUC1) using a novel CAR-T cell strategy. The study utilized the monoclonal antibody TAB004, which specifically recognizes the tMUC1 epitope present on triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells while sparing normal tissue MUC1.
Researchers engineered human T cells to express MUC28z, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) derived from the scFv of TAB004. These MUC28z CAR T cells demonstrated significant antigen-specific cytotoxicity against a panel of human TNBC cell lines in vitro, characterized by increased production of Granzyme B and IFN-γ. Most importantly, in a TNBC xenograft model, a single dose of MUC28z CAR T cells significantly reduced tumor growth compared to controls. This data validates the TAB004-derived CAR as a potent tool for targeting MUC1-Tn/tMUC1 in solid tumor research.
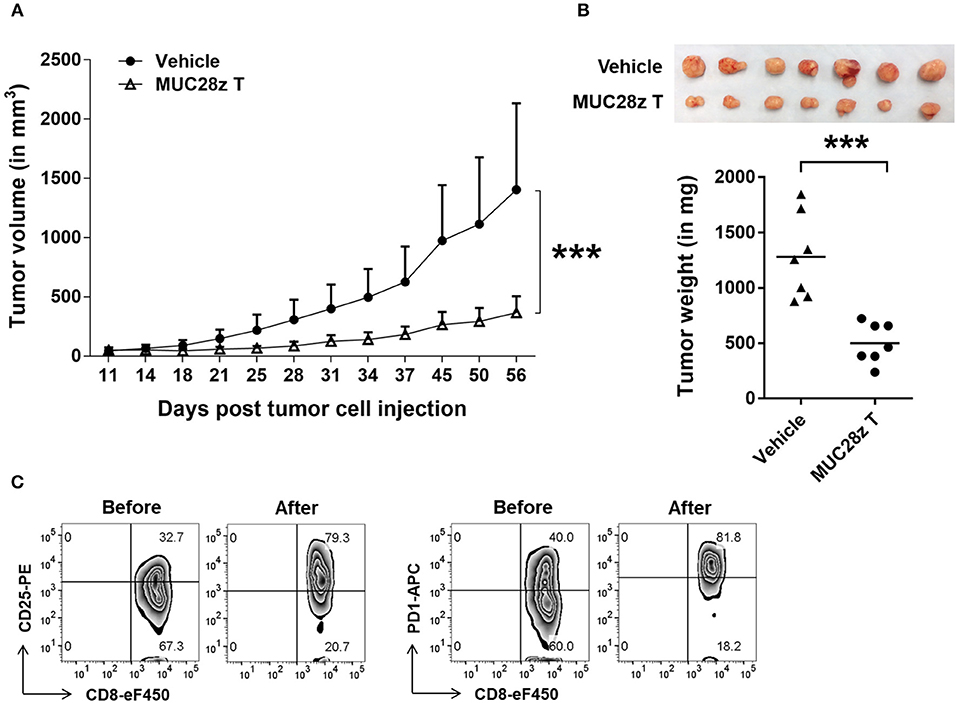
Fig.1 MUC28z CAR T cells reduce tumor growth.1
Workflow: From Glycopeptide Design to Antibody
Request a Quote for MUC1 Antibody Development
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
High Specificity
Our protocols ensure antibodies bind only to the neo-glycopeptide antibody target, not healthy tissue.
Versatile Formats
From IgG to scFv and VHH, we produce formats suitable for CAR-T, ADC, and diagnostic assay development.
Broad Experience
Expertise in sialophorin antibody (CD43) and anti-PODXL antibody development alongside MUC1.
Validation Support
We offer extensive validation using glycan arrays and tumor cell lines to guarantee anti-glycopeptide antibody performance.
FAQs
How do you ensure the antibody binds to the glycopeptide and not just the peptide?
We utilize a rigorous counter-screening process. During the screening phase, we test all clones against the naked MUC1 peptide and the glycopeptide simultaneously. Only clones that show strong binding to the glycosylated form (e.g., MUC1-Tn) and negligible binding to the naked peptide are selected for further development.
Can you develop antibodies for other mucins like MUC16 or MUC4?
Yes, our platform is applicable to all mucins. We have experience with anti-MUC16 antibody projects for ovarian cancer (CA-125) and anti-MUC4 monoclonal antibody projects for pancreatic cancer. We custom synthesize the relevant glycopeptide sequences for each target.
What is the difference between MUC1-Tn and MUC1-C antibodies?
MUC1-Tn antibodies target the aberrant glycosylation on the extracellular VNTR region, making them excellent for tumor recognition. MUC1-C antibody targets the C-terminal transmembrane subunit, which is involved in oncogenic signaling pathways and is often targeted to block tumor growth mechanisms.
Do you offer antibodies against sialylated targets like CD43?
Yes, we can target CD43 (leukosialin) in its various glycoforms. In cancer, CD43 is often hypesialylated. We can generate cancer specific CD43 antibody candidates that recognize the CD43 glycopeptide antibody epitope exposed by this altered glycosylation, often referred to as the UN1 antigen.
Reference:
- Zhou, R., et al. "CAR T Cells Targeting the Tumor MUC1 Glycoprotein Reduce Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth." Frontiers in Immunology 10 (2019): 1149. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01149
