Sialoside Microarray
Sialic acid influences a broad spectrum of cellular functions, from regulating leukocyte signaling to enabling pathogen entry. To support researchers in decoding intricate interactions between sialic acid and other biomolecules, we offer sialoside microarray services, featuring a high-throughput glycan profiling platform tailored for the precise study of sialic acid receptors, ligand–protein interactions, and cell-surface glycome signatures. With full customization capabilities, our platform enables high-resolution mapping of binding preferences across natural and synthetic sialosidic structures, including mag sialoside analogs and neuraminidase resistant sialosides for the detection of influenza viruses. Our service integrates the latest advancements in glycan chemistry and detection strategies to empower your studies with unmatched specificity and throughput.
Introduction to Sialic Acids and Their Functions
Sialic acids are a family of over 50 naturally occurring derivatives of neuraminic acid, often characterized by a nine-carbon backbone. The most common member, N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), frequently decorates the termini of glycoproteins and glycolipids on mammalian cell surfaces. The diversity in sialic acid structure, linkage types (α2-3, α2-6, α2-8), and chemical modifications (O-acetylation, sulfation, lactonization) allows them to serve as dynamic modulators in a variety of biological process:
- Immune regulation via engagement with cd22 sialic acid and siglec 4 sialoside receptors.
- Host–pathogen interactions, such as hemagglutinin sialic acid binding in influenza and sialic acid molecular mimicking in E. coli
- Stem cell and muscle biology, including the profiling of myoblast sialic acid signatures during differentiation.
- Oncogenesis, where altered expression of sialic acid residues contributes to immune evasion and metastatic progression.
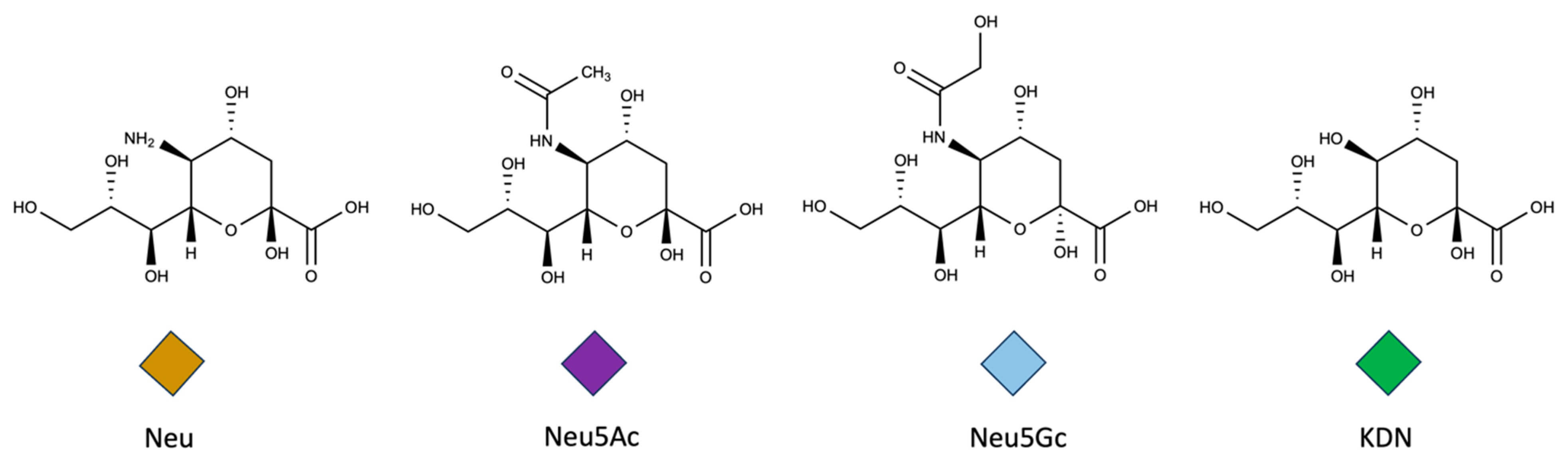 Fig.1 The most common sialic acids.1
Fig.1 The most common sialic acids.1
Sialoside Microarray Platform at Creative Biolabs
Sialylation patterns vary by species, tissue, and disease state. Hence, Creative Biolabs provides fully customized sialic acids microarray, ensuring that each array aligns with the molecular specificity and experimental design needed for your project. The sialoside microarray is a robust, slide-based platform that immobilizes chemically defined sialic acids and their derivatives on a solid substrate, enabling parallel analysis of glycan–ligand interactions. This platform is a powerful tool for:
- Screening protein, antibody, viral, or cell binding specificity against a comprehensive panel of sialosidic structures.
- Profiling functional ligands of sialic acid receptors under physiologically relevant conditions.
Microarray Design and Customization at Creative Biolabs
Every project at Creative Biolabs begins with your research question. At Creative Biolabs, we tailor every microarray project to your unique research objectives. Our sialoside microarray design process offers full customization, starting with the selection of diverse glycan structures—from natural and synthetic sialic acids featuring α2-3, α2-6, and α2-8 linkages to rare modified variants like mag sialoside, O-acetylated compounds, and fluorinated analogs for enhanced stability or labeling. We also provide neuraminidase-resistant sialosides to support pathogen-binding studies without enzymatic interference. Our click chemistry immobilization technique ensures consistent molecular orientation for optimal analyte presentation, while array formats can be customized as standard slides or high-density layouts to match your laboratory's instrumentation. Detection methods are equally flexible, offering fluorescent or chemiluminescent outputs designed to align with your specific research goals.
Sialoside Microarray Workflow
- Array Design: Diverse natural and synthetic sialic acids are selected and printed onto microarray slides.
- Probing: The array is incubated with target molecules (e.g., influenza virus particles, anti-siglec antibodies).
- Detection: Binding is visualized via fluorescence, chemiluminescence, or other readouts.
- Analysis: Signal intensity is quantified to assess interaction specificity and strength.
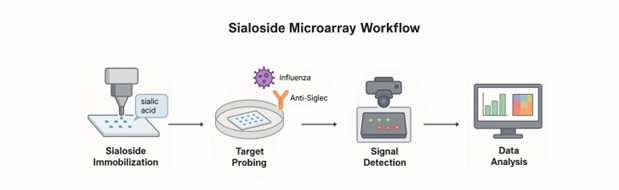 Fig.2 Workflow from sialoside immobilization to signal detection.
Fig.2 Workflow from sialoside immobilization to signal detection.
Applications of Sialoside Microarrays
Our sialoside microarray platform addresses a wide range of biological questions and translational goals:
Influenza and Viral Receptor Profiling
Investigate strain-specific receptor preferences using neuraminidase resistant sialosides for the detection of influenza viruses. By comparing α2-3 and α2-6 linkages, researchers can assess viral tropism and host adaptation mechanisms, accelerating vaccine design and antiviral screening.
Immunology and Siglec-Ligand Interactions
Explore how immune receptors engage sialic acid residues, including cd22 sialic acid on B cells and siglec 4 sialoside in neural-immune communication. Applications include autoimmunity research and development of immune-modulating therapeutics.
Oncology and Glycan Biomarker Discovery
Identify tumor-associated sialic acid group changes linked to metastasis, chemoresistance, or immune escape. Screening with defined sialosides helps discover novel biomarkers or therapeutic targets in cancers with altered sialylation patterns.
Antibody and Therapeutic Screening
Use the microarray to test binding specificity of glycoengineered antibodies, design decoy ligands, or validate sialic acid inhibitors that block sialic acid receptor engagement in infectious or inflammatory diseases.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
With over two decades of specialized experience in glycan chemistry and microarray development, Creative Biolabs stands as a reliable partner for your glycobiology research. Our advantages include but not limited to:
- Fully customized glycan content tailored to your organism, disease model, or receptor family.
- Synthetic and natural sialylated glycans, including mag sialoside and rare linkages.
- Validated detection platforms, including fluorescence, biotin–streptavidin systems, and enzymatic amplification.
- Expert consultation, from experimental design to data interpretation.
- Fast turnaround with flexible deliverables, from data-only to comprehensive reporting.
By offering fully customizable sialoside microarrays, Creative Biolabs enables researchers to probe glycan–ligand interactions with unparalleled resolution and accuracy. From mapping sialic acid receptor preferences to developing targeted sialic acid inhibitors, our platform opens new doors in basic and translational science. We invite you to explore our comprehensive glycoarray and sialylation profiling services and leverage our scientific expertise to accelerate your discoveries. Contact us and discuss your project with our glycomics specialists!
FAQs
What is CMP-sialic acid and why is it important in microarray construction?
CMP-sialic acid (cytidine monophosphate–sialic acid) is the activated donor substrate used by sialyltransferases to enzymatically attach sialic acids to glycan backbones. In sialoside microarray construction, it enables precise, linkage-specific sialylation under controlled conditions. This ensures biologically relevant presentation of terminal sialic acids, allowing high-fidelity interaction studies with lectins, antibodies, viruses, or host receptors.
How do human pathogens recognize sialic acids on host cells?
Many pathogens exploit sialic acids as molecular handles for cell entry or immune evasion. For example, influenza viruses bind to specific sialylated glycan linkages via their hemagglutinin proteins, while certain bacteria mimic host sialylation to avoid immune detection. Sialoside microarrays allow researchers to map these interactions in detail, revealing pathogen tropism, receptor preferences, and potential therapeutic targets.
Is it possible to customize the array content for specific research goals?
Absolutely. We specialize in fully customized sialoside microarrays. Clients may choose specific glycan backbones, sialylation types, or chemical modifications (e.g., fluorinated or azide-tagged sialosides). Whether your goal is pathogen binding analysis, therapeutic screening, or immune profiling, we tailor the array to your exact experimental needs.
Reference:
- Guerrero-Flores, Gerardo N., et al. "Sialic Acids in Health and Disease." Biologics 5.2 (2025): 10. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5020010
