Polysialic Acid Introduction
Are you currently facing challenges in developing highly specific therapeutics, optimizing drug delivery, or understanding complex cellular interactions? Our advanced Polysialic Acid solutions at Creative Biolabs help you unlock novel therapeutic avenues and enhance drug efficacy through cutting-edge glycobiology expertise and innovative engineering techniques.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Polysialic Acid
Polysialic acid (PSA) manifests as a capsular polysaccharide in neuroinvasive bacterial pathogens and as a distinctive glycan modification on select eukaryotic membrane proteins. In mammals, PSA comprises linear chains of α2,8-glycosidically linked N-acetylneuraminic acid residues with polymerization degrees varying between 8 and ~90 units, accounting for ~10% of protein-bound neuraminic acid in the developing brain. Vertebrates exhibit PSA composed of α2,8-linked N-acetylneuraminic acid, predominantly expressed during neural development. PSA biosynthesis involves two complementary sialyltransferases: ST8SiaII and ST8SiaIV. This polymer exhibits exceptional aqueous solubility, minimal viscosity, favorable biocompatibility, and in vivo degradability.
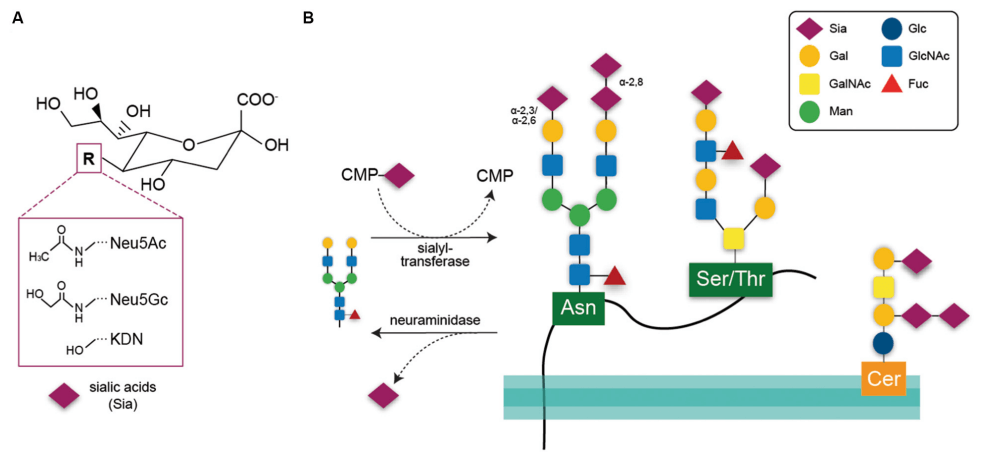 Fig.1 Molecular architecture of three principal sialic acids.1,3
Fig.1 Molecular architecture of three principal sialic acids.1,3
The Functions of PSA
-
Tumor Invasion and Recurrence
PSA significantly contributes to tumor invasion and recurrence. It has been detected in diverse tumors, including small cell and non-small cell lung carcinomas, neuroblastoma, multiple myeloma, and rhabdomyosarcoma. PSA expression on tumor cells diminishes neural adhesion molecule (NCAM) adhesion and increases cellular motility, enabling PSA-expressing cells to detach from primary tumors and establish metastases. -
Axon Guidance and Targeting
PSA is vital for axon extension and targeting. Its expression permits limb motorneurons to separate from bundles upon exiting the spinal cord, facilitating precise muscle innervation. PSA is essential for long-distance axon migration and prevents erroneous synaptic connections during pathfinding. -
Synaptic Plasticity
Adult hypothalamic PSA expression correlates with circadian rhythm regulation. Hippocampal PSA presence relates to the plasticity necessary for memory formation and learning. Furthermore, hypothalamic neurohypophysis expresses PSA, with its levels modulated by ovarian cycles, lactation, and dehydration to enable reversible synapse formation. -
The Molecular Reservoir Function
Research demonstrates PSA's capacity to bind bioactive molecules and modulate their functions. Examples include PSA interactions with neurotrophins, growth factors, neurotransmitters, cytokines, ions, membrane lipids, and membrane-associated proteins.
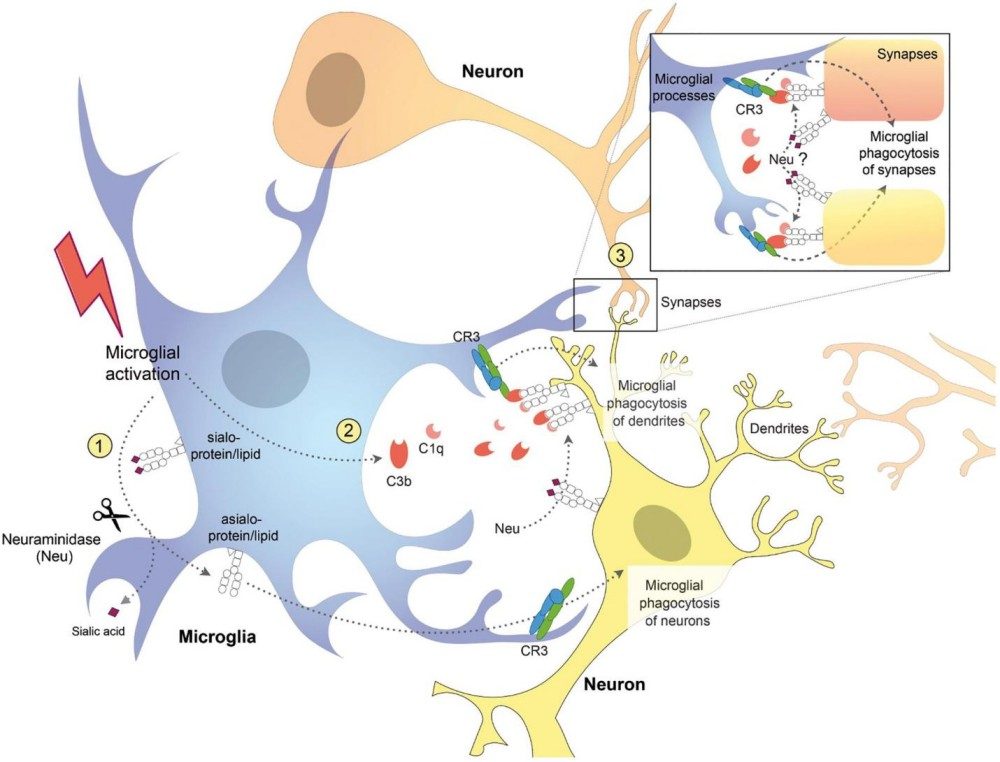 Fig.2 Hypothesized pathways for microglial-triggered neurophagy involving galectin-3 (Gal-3) and desialylation of neuronal/microglial receptors.1,3
Fig.2 Hypothesized pathways for microglial-triggered neurophagy involving galectin-3 (Gal-3) and desialylation of neuronal/microglial receptors.1,3
Therapeutic Applications of PSA
-
Drug Delivery System
PSA functions as an endogenous material, minimally immunogenic, biodegradable, and biocompatible. Specifically, PSA modification diminishes immunogenicity of proteins or polypeptides and extends circulation duration for modified drugs and carriers in blood, achieving targeted delivery outcomes. -
Promote Nervous System Regeneration and Repair
Within the nervous system, PSA coats migratory precursor cells, facilitating rapid transit to destinations while preventing premature differentiation and improper connections. PSA also adorns long-distance neuronal axons, regulating fasciculation, sprouting, and navigation. PSA up-regulation occurs at nerve damage sites in both peripheral and central nervous systems (CNS). Researchers note transient PSA expression on scar-associated astrocyte subpopulations, with axons adjacent to these PSA-positive astrocytes displaying enhanced sprouting. -
PSA-Based Vaccines for Invasive Meningitis
Serogroup B meningitis constitutes the foremost origin of meningococcal disease and septicemia in industrialized countries, with potential lethality under 24 hours. Scientists created altered α2,8-PSA configurations featuring N-propionyl-neuraminic acid rather than N-acetyl-neuraminic acid, conjugating these to tetanus toxoid. Subsequent assessment of this N-propionyl-2,8-PSA-tetanus toxoid vaccine in healthy male volunteers revealed boosted pre-existing IgM antibodies against group B PSA and N-propionyl-PSA, plus induced IgG antibodies targeting N-propionyl-PSA.
The physicochemical and biological characteristics of PSA render it valuable for diverse applications to enhance bioavailability of therapeutic proteins employed in replacement therapies. For inquiries regarding our PSA-based solutions or antibodies targeting PSA, contact our scientific team for comprehensive technical specifications.
Published Data
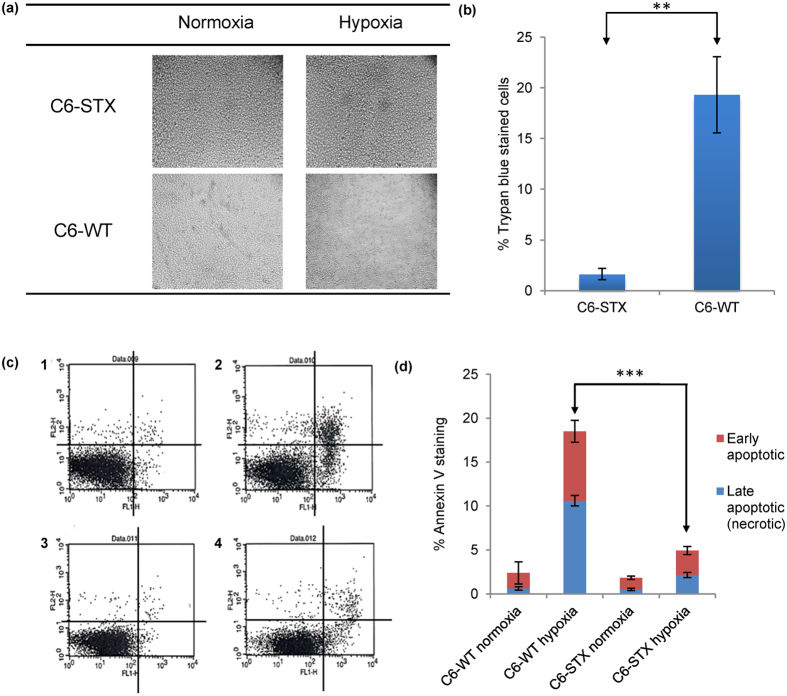 Fig.3 Effect of polySia expression on the survival of cancer cells in hypoxia.2,3
Fig.3 Effect of polySia expression on the survival of cancer cells in hypoxia.2,3
Recent experimental findings highlight the critical role of polysialic acid (polySia) in cancer cell survival and migration, particularly under hypoxic conditions. Studies utilizing C6 glioma, neuroblastoma, and DLD-1 colorectal cancer cell lines demonstrated that while hypoxia generally reduces polySia expression, its presence is crucial for sustaining the migratory capacity of tumor cells. This was quantitatively assessed using scratch assays, revealing a direct correlation between polySia and cellular movement. Furthermore, initial mechanistic investigations suggested that Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 (HIF-1) may contribute to maintaining polySia-mediated migratory capacity, although not directly to cell survival under hypoxic stress. PolySia detection in C6-STX cells under varying oxygen conditions was precisely determined via Mild acidic hydrolysis combined with UPLC/MS/MS analysis, confirming the dynamic regulation of polySia expression. These results underscore polysialyltransferase (polyST) enzymes (ST8SiaII and ST8SiaIV) as promising targets for developing anti-metastatic therapeutic strategies.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing cutting-edge solutions in glycobiology, with a specialized focus on Polysialic Acid. Leveraging proven expertise in antibody research, Creative Biolabs delivers comprehensive anti-carbohydrate antibody development services with premium quality at competitive pricing.
Our comprehensive offerings include:
- Custom Polysialic Acid Synthesis
- Polysialylated Protein Production
- Anti-Polysialic Acid Antibody Development
- Glycoconjugate Engineering
- Functional Characterization Services
Unlock Exclusive Advantages – Secure Your Quote Today
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs leads in glycobiology, providing unmatched proficiency and advanced methodologies for Polysialic Acid R&D. Our dedication to research excellence and client achievement distinguishes our services.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: We utilize advanced platforms for PSA synthesis, conjugation, and characterization, ensuring high-quality and precisely engineered products.
- Customized Solutions: Our services are highly adaptable, designed to meet the unique needs of each research and development project, from novel therapeutic design to diagnostic tool development.
- Robust Quality Control: Every PSA construct and service undergoes stringent quality control measures to guarantee purity, consistency, and biological activity.
FAQs
Here are some common questions potential clients have about Polysialic Acid and its applications:
Q: What are the key therapeutic benefits of incorporating polysialic acid into biopharmaceutical designs?
A: Polysialic acid offers several key advantages, including significantly extending the half-life of therapeutic proteins by reducing renal clearance and proteolytic degradation, masking immunogenic epitopes to decrease unwanted immune responses, and facilitating targeted drug delivery. Its unique anti-adhesive properties can also be leveraged in specific applications.
Q: How is the quality and consistency of polysialic acid products typically ensured in biopharmaceutical applications?
A: Ensuring quality and consistency in polysialic acid products involves rigorous control measures throughout the production process. This typically includes advanced analytical techniques to verify polySia chain length, purity, and conjugation efficiency, ensuring consistent and high-quality results for various projects.
Q: Is polysialic acid modification universally applicable across all protein and therapeutic molecules?
A: While polysialic acid can be broadly applied to various molecules, the optimal strategy for conjugation and the resulting functional benefits can vary depending on the specific protein or therapeutic. Careful evaluation and tailored modification strategies are often employed to maximize its therapeutic potential for each unique molecule.
Related Products and Services
To further advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a portfolio of solutions:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
Creative Biolabs offers a series of anti-glycan antibody-related services for worldwide customers. To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Puigdellívol, Mar et al. "Sialylation and Galectin-3 in Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration." Frontiers in cellular neuroscience vol. 14 162. 9 Jun. 2020, https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00162
- Elkashef, Sara M et al. "Polysialic acid sustains cancer cell survival and migratory capacity in a hypoxic environment." Scientific reports vol. 6 33026. 9 Sep. 2016, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33026
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
