Glycan in Endocrinology and Metabolism
Glycans and glycan-binding proteins play important roles in the metabolic system. It is critical to detect theses glycans or glycan-binding proteins during diseases diagnosis associated with endocrinology and metabolism. Creative Biolabs provides customized antibody development services against glycans for the diagnosis and treatment of endocrine diseases with advanced technology platforms. Our professional scientists have extensive experience in antibody production and are committed to providing high-quality services to promote the development of innovative disease treatments.
Introduction
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that can produce and release hormones, which involved in regulating various important body functions. When the endocrine system is disordered, it can cause various endocrine diseases. Diabetes is a typical hormone-related endocrine disease, which causes long-term vascular complications. One cause of the disease is the high glucose increases nonenzymatic glycation, wherein the open-chain (aldehyde) form of the glucose interacts with lysine residues on various proteins, generating reversible Schiff bases. Irreversible Amadori rearrangement then gradually produces adducts resulting in the “browning” (Maillard) reactions, which eventually progress to advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in patients with diabetes.
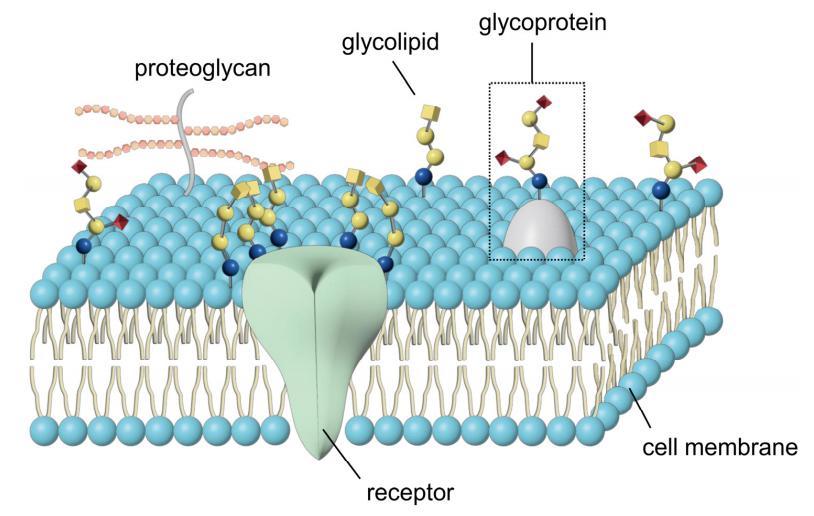 Fig.1 Glycoproteins, glycolipids, and proteoglycans in plasma membrane.1, 2
Fig.1 Glycoproteins, glycolipids, and proteoglycans in plasma membrane.1, 2
The Role of Glycans in Endocrinology and Metabolism
The excess glucose in diabetes mellitus can increase the production of UDP-GlcNAc through the glucosamine:fructose aminotransferase (GFAT) pathway. This leads to increased hyaluronan production as well as increased O-GlcNAc levels on nuclear and cytoplasmic glycoproteins, which in turn affects the phosphorylation of the same proteins and their functions. Specific molecular mechanisms associated with such altered O-GlcNAcylation have been confirmed in animal models with complications, such as diabetic cardiomyopathy (increased O-GlcNAcylation of various nuclear proteins) and erectile dysfunction (O-GlcNAcylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase).
Serious diabetic complication such as kidney dysfunction has led to high mortality. Symptoms include initial slight urinary albumin excretion (microalbuminuria) progresses to end-stage renal disease. Indeed, the proteinuria has related to a reduction in the heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycan content of the glomerular basement membrane. The potential cause of the reduction in HS synthesis by glomerular epithelial cells may be caused by the high glucose in the environment. Evidence has demonstrated that the decrease in anionic charge and loss of HS proteoglycan can affect the porosity of the glomerular basement membrane. Importantly, high glucose also can regulate the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) gene in renal glomerular mesangial cells by O-GlcNAc-mediated alterations in Sp1 (transcription factor Sp1) transcriptional activity.
What Can We Do for You?
Creative Biolabs has been a long-term expert in the field of antibodies discovery and manufacturing. We are confident in offering the best products and services for our customers to meet each of their specific demands. At present, we provide high-quality anti-glycan antibodies for the diagnosis and treatment of endocrine diseases such as diabetes. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us.
References:
- Hamamura, Kazunori, Mayu Nagao, and Koichi Furukawa. "Regulation of Glycosylation in Bone Metabolism." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.7 (2024): 3568.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
