Polysaccharide Microarray
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of repeating sugar units, vital in cell-cell communication, immune modulation, and microbial virulence. To decode these functions with high sensitivity and specificity, polysaccharide microarray has emerged as a transformative platform. At Creative Biolabs, we leverage decades of expertise in glycoscience and glycoarray to deliver cutting-edge high-throughput polysaccharide microarray solutions for antibody profiling, vaccine development, and biomarker discovery.
Why Study Polysaccharides with Microarray Technology?
Polysaccharides are structurally complex, non-template-driven biomolecules. Their diversity arises from variations in monosaccharide composition, glycosidic linkages, branching patterns, and chemical modifications. Unlike DNA or proteins, polysaccharides cannot be amplified, and their function is tightly linked to conformation and multivalency. Traditional techniques such as ELISA or chromatography often lack the throughput or specificity required to resolve subtle glycan-protein interactions. Polysaccharides microarray provides a transformative solution by enabling parallel analysis of hundreds of carbohydrate epitopes, sensitive detection of glycan-binding antibodies, lectins, and receptors, as well as low sample consumption.
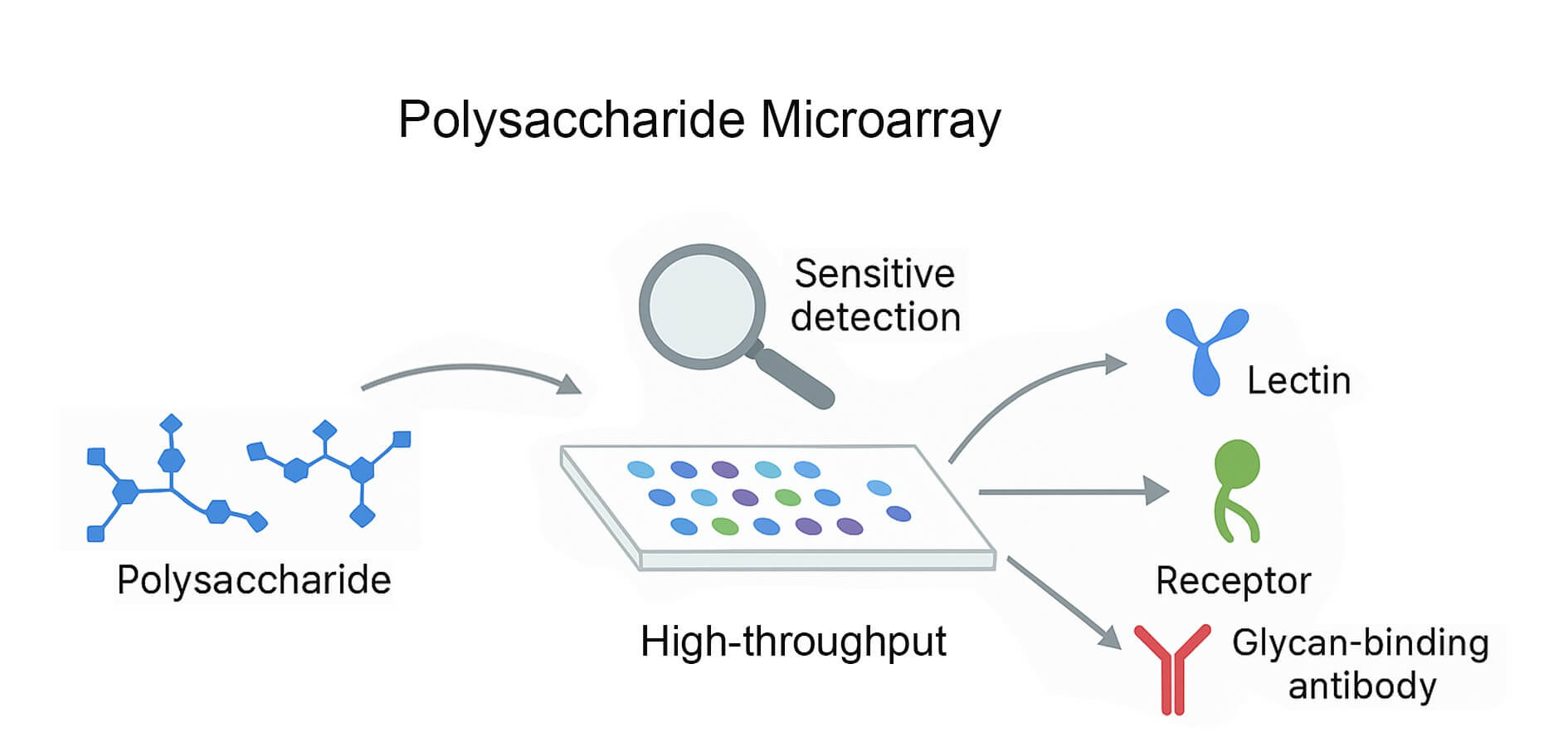 Fig.1 The schematic of polysaccharide microarray.
Fig.1 The schematic of polysaccharide microarray.
Custom Polysaccharide Microarrays at Creative Biolabs
Polysaccharide microarrays are miniaturized platforms that immobilize structurally defined microbial or plant-derived polysaccharides onto solid surfaces. These immobilized arrays are then probed with sera, purified antibodies, or lectins to evaluate binding interactions, providing a molecular fingerprint of carbohydrate recognition patterns. At Creative Biolabs, we provide fully customizable polysaccharide microarray services tailored to your research objectives. Our customization options include but are not limited to:
- Polysaccharide sourcing and conjugation: Including bacterial CPS, LPS, fungal β-glucans, heparan sulfates, plant pectins and so on.
- Slide printing formats: Standard 16-well to high-density 96-well configurations
- Detection systems: Fluorescence, chemiluminescence
- Data analysis: Normalization, heatmap generation, statistical comparison
Our polysaccharide microarray platform offers:
- Nanogram-level sensitivity
- Simultaneous testing of 100+ targets
- Small sample input (1–2 μL serum)
Workflow for Polysaccharide Microarrays
The development of a polysaccharide microarray involves several critical steps:
1. Polysaccharide Preparation
Polysaccharides are obtained through natural extraction and chemical or enzymatic synthesis. Chemical derivatization is necessary when epoxy-coated glass slides are needed for covalent immobilization to attach to polysaccharides. Usually, polysaccharides are converted into glycosylamine derivatives via reductive amination. This process ensures stable attachment and maintains antigenicity for subsequent detection.
2. Microarray Printing
The derivatized polysaccharides are printed at defined concentrations (often in serial dilutions) onto functionalized glass slides or nitrocellulose membranes using robotic microarrayers, ensuring reproducible spot morphology and density.
3. Probing and Detection
Arrays are blocked with BSA and incubated with biological samples, including sera, monoclonal antibodies, or lectins. After washing, fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies or glycan-binding proteins are applied to detect specific interactions.
4. Data Acquisition and Analysis
Fluorescence signals are scanned using high-resolution microarray scanners. Image analysis software quantifies spot intensities, generating heatmaps or binding curves to characterize glycan-recognition profiles.
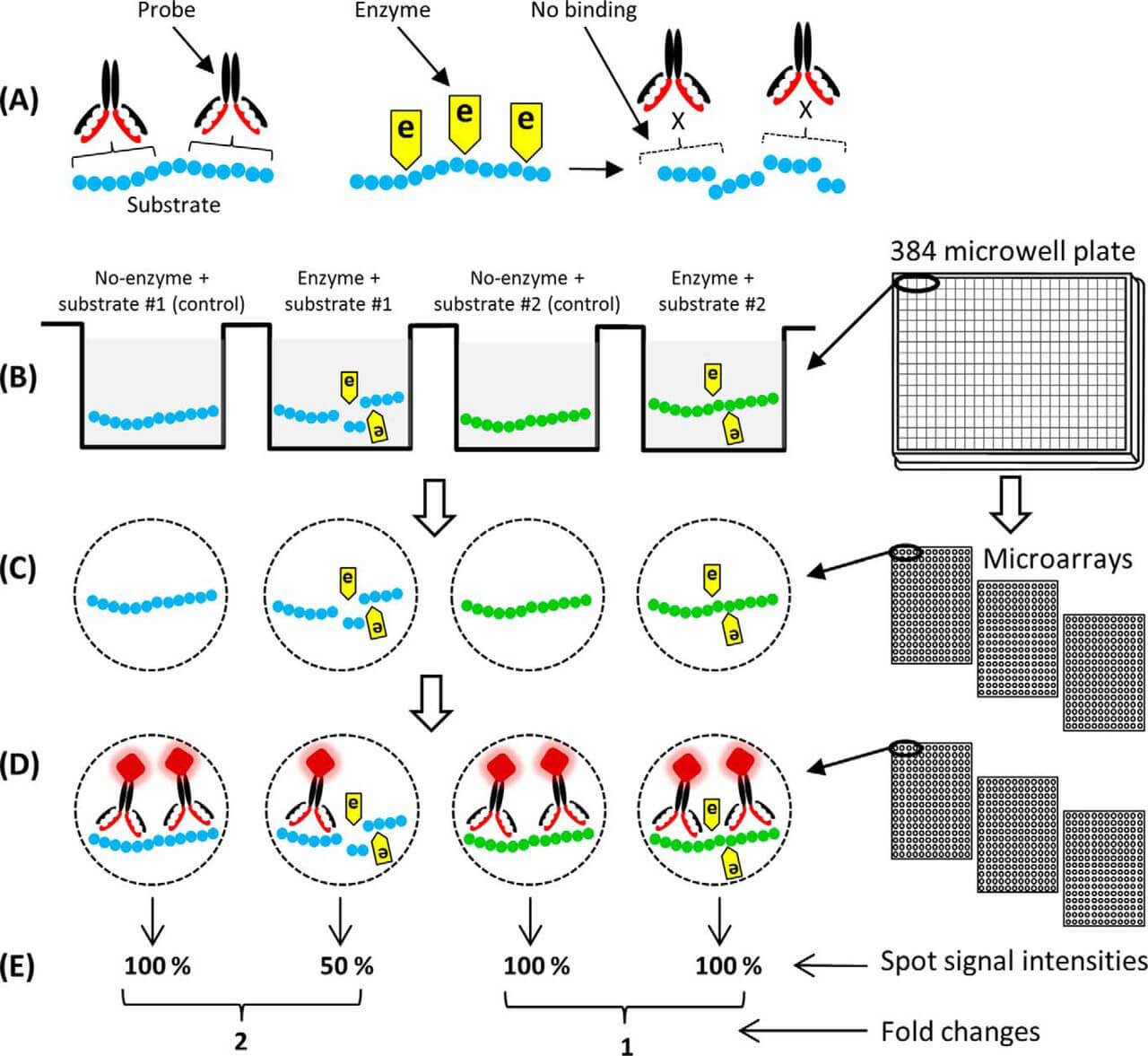 Fig.2 Polysaccharide microarray workflow.1
Fig.2 Polysaccharide microarray workflow.1
Applications
Infectious Disease Diagnostics
Polysaccharide microarrays have proven highly effective in identifying pathogen-specific immune responses. For example, arrays constructed with capsular polysaccharides from Burkholderia pseudomallei and B. mallei successfully differentiated convalescent from naïve sera, enabling precise serological diagnosis of melioidosis and glanders. This diagnostic specificity is critical given the limitations of conventional serological methods like indirect hemagglutination, which rely on crude bacterial extracts and suffer from cross-reactivity.
Host-Pathogen Interaction Studies
By profiling immune sera or lectin-binding patterns across a diverse set of polysaccharide structures, glycan microarrays reveal critical insights into pathogen recognition, innate immunity, and microbial evasion strategies. The ability to differentiate interactions with glucan, xylan, or pectin epitopes, for example, can clarify the specificity of pattern recognition receptors in the innate immune system.
| Target | Representative Epitope | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Fungal pathogens | (1→3)-β-glucan | Immunogenicity assessment |
| Gram-negative bacteria | LPS O-antigen, CPS | Antibody binding & vaccine design |
| Plant cell wall models | Xyloglucan, arabinoxylan | Cell wall deconstruction studies |
Vaccine Development
The use of polysaccharide microarray services enables rapid evaluation of polysaccharide antigens for immunogenicity and epitope mapping. This is particularly valuable in conjugate vaccine design, where identifying protective glycotopes is essential. Using defined arrays, researchers can assess the binding affinity and breadth of antibody responses elicited by vaccine candidates, streamlining the preclinical pipeline.
Biomarker Discovery
Differential recognition of polysaccharides can serve as a proxy for disease states or immune history. By comparing serum profiles on glycoarrays, one can identify glycan markers associated with infection, inflammation, or autoimmunity. For example, specific anti-α-glucan or anti-mannan antibodies can distinguish fungal infections, while changes in heparan sulfate-binding profiles might reflect tumor-associated glycosylation changes, paving the way for biomarker discovery.
Interested in Anti-glycan Antibodies
Comparison with Other Carbohydrate Microarrays
With the diversity of glycan structures and biological roles, multiple specialized microarray platforms have been developed. Each type of glycan microarray offers distinct analytical advantages depending on the carbohydrate class and research goal. The table below compares major formats currently used in glycomics and immunological research:
| Platform | Target | Unique Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Polysaccharide microarray | Native long-chain glycans | Realistic antigen conformation; pathogen-specific CPS |
| Oligosaccharide Microarray | Targeted short-chain glycans | Ideal for profiling interactions of specific oligosaccharides |
| Glucan microarray | β-glucans (fungal, cereal) | Immunological detection of fungal pathogens |
| Heparan sulfate microarray | Sulfated GAGs | Cancer and viral entry research |
| GAG microarray | Broad glycosaminoglycans | ECM interactions; inflammation and wound healing studies |
| ABH-Glycan microarray | ABO blood group glycans | Blood group antibody screening and xenotransplantation safety |
| HMO microarray | Human milk oligosaccharides | Infant immunity, microbiota interaction, and maternal-neonatal health |
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs combines scientific rigor with customized service. Our polysaccharide microarray solutions stand out for:
- Custom polysaccharide synthesis upon your request
- High-density array formats tailored for multiplexed screening
- Comprehensive profiling of sera, antibodies, and lectins
- Rapid project delivery timelines to meet publication or regulatory needs
- Flexible slide formats adapted to your experimental design
- Seamless collaboration with clients across the world
The evolution of microarray technology to study polysaccharides has opened new frontiers in biomedical research. From high-throughput polysaccharide analysis to precision diagnostics and vaccine development, the polysaccharide microarray represents a convergence of analytical rigor and translational potential. At Creative Biolabs, we are expanding our polysaccharide microarray platforms to include customized heparan sulfate microarray and glucan microarray for advanced biomedical applications. For tailored glycan profiling solutions or to design your next glycoarray, do not hesitate to contact us.
Reference:
- Vidal-Melgosa, Silvia, et al. "A new versatile microarray-based method for high throughput screening of carbohydrate-active enzymes." Journal of Biological Chemistry 290.14 (2015): 9020-9036. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.630673
