Glyco-gene Microarray
What is Glyco-gene Microarray?
Glyco-gene microarray is a specific type of oligonucleotide microarray that targets genes involved in glycosylation pathways. It immobilizes nucleic acid probes that are complementary to mRNA sequences of glycogenes, such as glycosyltransferases, glycosidases, and sugar transporters, on a solid substrate and quantifies their expression levels. The principle relies on hybridization kinetics, where the labeled cDNA/cRNA from the sample binds to its complementary probe, and the signal intensity is proportional to the abundance of the target. This is in contrast to glycan microarray where glycans are immobilized on the solid surface to detect their interactions with glycan-binding proteins, for example via fluorescence or SPR. This is also different from traditional gene expression microarrays where broad-spectrum nucleic acid probes are used for genome-wide gene expression profiling without glycogene specificity. This is where the journey of discovery truly begins, and we are excited to share it with you. Creative Biolabs developed our premier glyco-gene microarray service, to be a powerful platform to help your team feel confident to decode this unexplored genetic terrain and speed up your research.
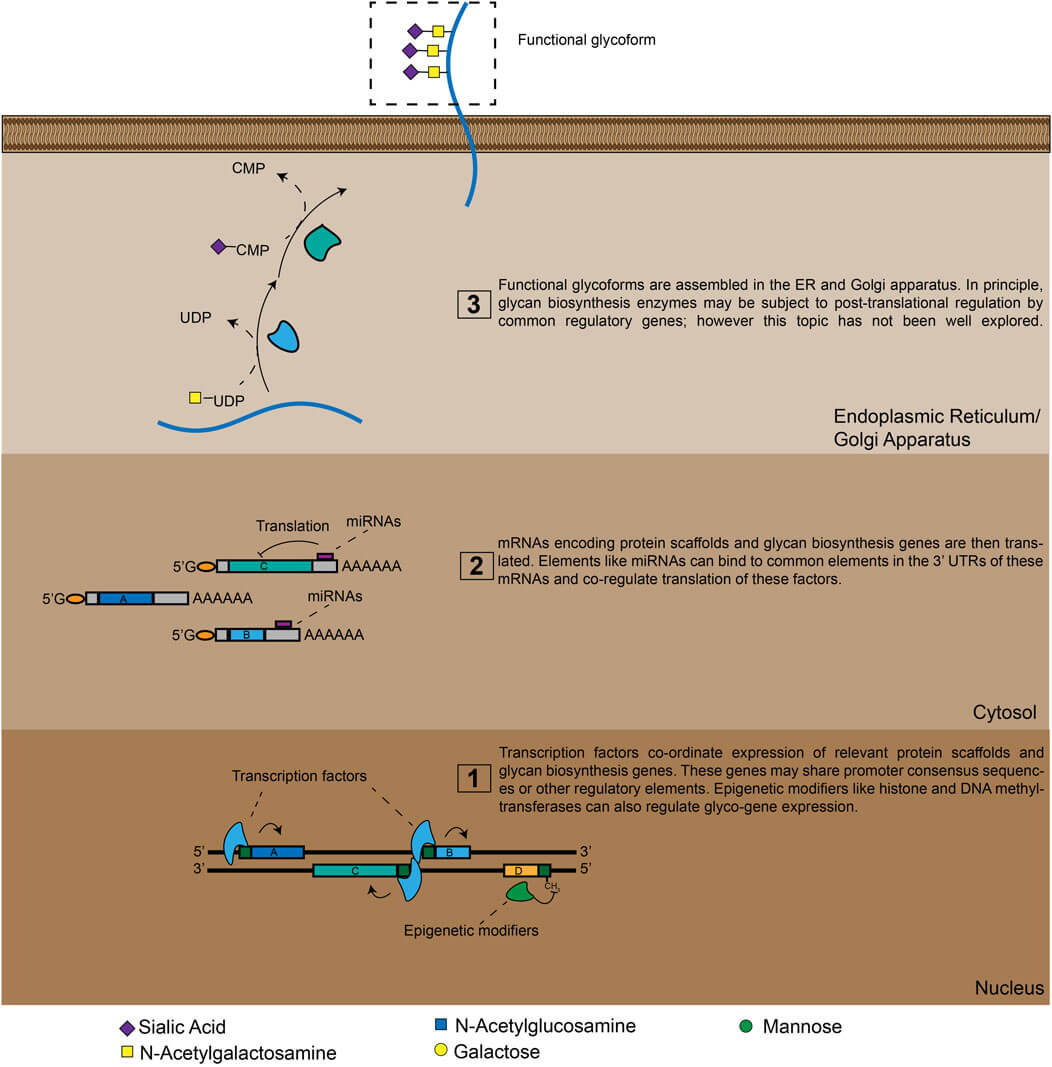 Fig.1 Glyco-genomic regulation: from gene expression to cellular function.1
Fig.1 Glyco-genomic regulation: from gene expression to cellular function.1
Step-by-Step Glyco-gene Microarray Workflow
A glyco-gene microarray is a high-throughput tool that can simultaneously measure the expression levels of hundreds or even thousands of glyco-related genes in a single experiment. At Creative Biolabs, we understand that process is a partnership, and we have designed our service keeping transparency and collaboration in mind, ensuring your research goals are the top priority at every stage.
- Probe Design: Designing and synthesizing tens of thousands of short, single-stranded DNA sequences (probes), each one perfectly complementary to a specific glyco-gene.
- Array Fabrication: Spotting and immobilizing these probes onto a solid surface, typically a glass slide, in an organized grid where each spot represents a unique gene.
- Sample Hybridization: Extracting RNA from your biological samples (e.g., control vs. treated cells), converting it to cDNA, and then reverse-transcribing it into fluorescently labeled cDNA. This labeled cDNA is then washed over the microarray.
- Signal Detection: The labeled cDNA from your sample will bind (hybridize) to its complementary probe on the array. The intensity of the fluorescent signal at each spot is directly proportional to the expression level of that specific gene in your sample.
- Data Analysis: Capturing the fluorescent signals using a high-resolution scanner and using bioinformatic software to translate these light patterns into quantitative gene expression data. Background subtraction, normalization, and statistical analysis to identify differentially expressed glycogenes.
Key Features of Our Service
- Comprehensive Coverage: Our arrays cover the entire known glyco-genome, including glycosyltransferases, glycosidases and other glycan-related proteins.
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: Optimized probe design and stringent hybridization conditions allow for the detection of even low-abundance transcripts with minimal cross-hybridization.
- Custom Array Design: Have a specific set of genes or a non-model organism you're interested in? We can design and fabricate a fully custom microarray tailored to your project.
- Expert Bioinformatic Support: Our service includes a full analysis package. We don't just give you a spreadsheet; we help you understand what your data means.
- Fast Turnaround Time: Our streamlined workflow ensures you get your results quickly, helping you stay ahead in your research.
Applications of Glyco-gene Microarray
In the context of disease research, glyco-gene microarray technology shows great value and technical advantages. For example, it has been used successfully to compare the gene expression profiles of normal vs tumor tissue, in diseases such as glioblastoma and liver cancer cell lines, allowing for the identification of dozens of differentially expressed glyco-genes, like the upregulation of POFUT1 in glioblastoma and MAN2A2 in normal brain tissue that provide critical clues to develop new therapeutic targets. This microarray has also been used to screen relevant glyco-genes in other diseases such as glaucoma. The fundamental advantages of using a microarray approach are its high-throughput, which enables the simultaneous detection of hundreds of glyco-genes, far outperforming traditional single-gene methods. In addition, it has a high sensitivity, which allows for the identification of low-abundance transcripts in clinical samples. Combined, these strengths greatly accelerate the power of glycoscience to further explore disease mechanism, biomarkers, and discover new drug targets.
Understanding the mechanisms behind disease progression and cellular behavior requires deciphering their unique glycosylation patterns. Our glyco-gene microarray service is your key to decoding this complex genetic code. Creative Biolabs is an extension of your team. From custom array design to in-depth bioinformatic analysis that transforms raw data into a clear biological story, we facilitate your research. Contact us and let our decades of experience accelerate your journey to discovery.
FAQs
Q: How is this different from RNA-seq or standard expression arrays?
A: RNA-seq is broad and discovery-driven but costly to filter for glycobiology. Our array concentrates on the glyco-genome with optimized probes and tight hybridization controls, delivering high signal-to-noise and fast interpretation for glycosylation research. It plugs directly into glycomics workflows and reduces analysis overhead on irrelevant genes.
Q: Which genes are covered, and can you support non-model organisms?
A: The standard panel spans core glycosyltransferases, glycosidases, sugar transporters, chaperones, and auxiliary factors across the glycosylation pathway. For non-model species or bespoke gene sets, we design and print custom probes against your transcripts, validate hybridization performance in vitro, and lay out positive/negative controls on-array.
Q: How do you ensure sensitivity and specificity on-array?
A: We optimize probe length and Tm, use stringent hybridization/wash conditions, and include technical replicates and internal controls to monitor signal consistency. Design filters minimize cross-hybridization. The result is reliable detection of low-abundance transcripts with clean backgrounds and tight replicate concordance.
Q: How many biological replicates do I need for confident calls?
A: For case–control designs, we generally recommend ≥3 biological replicates per arm as a minimum, with power rising notably at 5–6. Technical replicates help assess precision but do not replace biological variance. We'll run a quick power check on your expected effect sizes and variability to align replicate counts with your study's decision thresholds.
Reference:
- Stewart, Natalie, and Simon Wisnovsky. "Bridging glycomics and genomics: new uses of functional genetics in the study of cellular glycosylation." Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 9 (2022): 934584. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.934584
Related Services
Glycosyltransferase & Glycosidase Substrate Microarray
Microbial Glycan Antigen Microarray
Viral Receptor Specificity Microarray
