Anti-Podocalyxin (PODXL) Glycopeptide Antibody Development Service
Podocalyxin (PODXL) is a highly glycosylated type I transmembrane sialomucin that has emerged as a significant biomarker and therapeutic target in oncology. Originally identified as a major component of the glomerular filtration barrier in kidney podocytes and a surface marker on vascular endothelial cells, its aberrant expression has been extensively documented in a variety of malignant tumors. In the context of cancer, PODXL is not merely a passenger molecule but a driver of metastasis, facilitating cell detachment, invasion, and migration. However, targeting PODXL remains challenging due to its physiological expression in vital organs. Creative Biolabs addresses this hurdle by offering specialized custom glycopeptide antibody development services. We focus on generating antibodies that recognize tumor specific glyco-epitopes—unique carbohydrate structures or exposed peptide regions resulting from aberrant glycosylation—thereby enabling precise discrimination between malignant cells and normal healthy tissues.
Podocalyxin (PODXL): The Significance of Aberrant Glycosylation
PODXL is a member of the CD34 family of sialomucins. Structurally, it consists of a large extracellular mucin domain, a globular domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. In healthy kidney tissue, the extensive sialylation and O-glycosylation of PODXL create a negative charge barrier that maintains the filtration slits between podocytes. In vascular endothelium, it regulates cellular adhesion and permeability.
In malignancies such as renal cell carcinoma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer, PODXL is frequently overexpressed and correlates with poor prognosis. Crucially, the glycosylation machinery in tumor cells is often dysregulated. This leads to the expression of immature or truncated O-glycans, such as the Tn antigen (N-acetylgalactosamine linked to serine/threonine) and the sialyl-Tn (sTn) antigen. These tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TACAs) are virtually absent in normal adult tissues. Furthermore, incomplete glycosylation can expose specific peptide sequences that are normally masked by heavy glycan coats in healthy cells.
This biological distinction provides a therapeutic window. Traditional anti-PODXL antibodies often target the shared protein core or fully glycosylated epitopes found on normal endothelium, leading to potential on-target/off-tumor toxicity. By developing an anti-podocalyxin antibody or a PODXL glycopeptide antibody that specifically binds to these tumor-exclusive glycoforms (e.g., Tn-PODXL), researchers can develop highly specific diagnostic tools (IHC reagents) and targeted therapeutic agents (ADCs, CAR-T cells) that spare normal kidney and vascular tissues.
Comprehensive Development Workflow
Developing high-affinity antibodies against glycopeptides requires a sophisticated approach that integrates organic synthesis, immunology, and advanced screening. Our workflow is designed to overcome the low immunogenicity of carbohydrates and the challenge of cross-reactivity.
Request a Quote
Specialized Service Capabilities
Our platform allows for the precise interrogation of the cancer glycoproteome. We provide a full suite of services tailored to the complex nature of PODXL as a target.
Custom Glycopeptide Antibody Discovery
The core of our offering is the generation of antibodies that require both the peptide sequence and the specific glycan for binding. We have successfully developed antibodies targeting the Tn-antigen on PODXL, as well as other targets like MUC1 glycopeptide antibody and MUC16 glycopeptide antibody candidates. By using homogenous synthetic glycopeptides as immunogens, we ensure that the immune response is focused on the exact epitope of interest, avoiding the heterogeneity associated with natural glycoprotein immunogens.
Cancer-Specific PODXL Antibody Screening
To validate specificity early in the development process, we employ a comparative screening strategy. We utilize pairs of cell lines: one expressing the tumor-associated glycoform (e.g., renal cell carcinoma PODXL antibody positive cells) and one expressing the normal physiological form (e.g., vascular endothelium). Clones are selected based on a high binding differential—strong signal on cancer cells and background-level signal on normal cells. This process mimics the in vivo environment and de-risks downstream development.
Recombinant Antibody Engineering
Following hybridoma generation, we offer variable region sequencing and recombinant expression. We can convert murine antibodies into chimeric or fully humanized formats (IgG1, IgG4) to reduce immunogenicity for research applications involving human immune cells. Additionally, we can engineer the Fc region to modulate effector functions, such as enhancing ADCC (Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity) for potential therapeutic candidates or silencing it for diagnostic imaging reagents.
ADC & CAR-T Development Support
PODXL is an attractive target for Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) due to its internalization properties upon antibody binding. We can screen for internalizing anti-PODXL antibodies using pH-sensitive dyes or toxin-conjugated secondary antibodies. Furthermore, our tumor-specific binders are ideal for constructing CAR-T cells. By targeting a tumor specific glyco-epitope antibody, CAR-T therapies can potentially eradicate tumor cells while avoiding the fatal "on-target/off-tumor" toxicity associated with targeting widely expressed antigens on normal kidney tissue.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
Glyco-Competence
Deep expertise in synthesis of complex glycopeptides (Tn, sTn, T, LeY) for precise immunogen design.
Dual Screening
Simultaneous screening against tumor and normal tissue libraries to eliminate off-target binders early.
Broad Application
Antibodies validated for Flow Cytometry, IHC, Western Blot, and functional inhibition assays.
PhD Support
Dedicated project managers with glyco-immunology backgrounds to guide your epitope selection.
How to Start Your Project
Starting a custom glycopeptide antibody development project with us is straightforward. Simply provide us with the target sequence or the specific glycosylation profile you wish to target (e.g., Tn-antigen on PODXL). If you are unsure about the best epitope, our team can perform an initial antigenicity analysis. We will then propose a tailored strategy, from antigen synthesis to final antibody delivery. We can also assist in exploring other targets such as gastric cancer MUC5AC antibody or anti-MUC4 monoclonal antibody projects if your research scope expands.
Contact Us to Discuss Your PODXL Target
Published Data
The development of cancer-specific antibodies against PODXL has shown immense promise in preclinical studies. A recent research highlights the generation of a Cancer-Specific Monoclonal Antibody (CasMab), designated PcMab-6. This antibody was engineered to recognize a tumor-associated glyco-epitope on PODXL that is distinct from the epitope recognized by standard pan-PODXL antibodies.
In the study, the specificity of PcMab-6 was rigorously evaluated using flow cytometry. As illustrated in Fig. 1, PcMab-6 exhibited strong binding to PODXL-positive glioblastoma cells (LN229) and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells (MIA PaCa-2). Importantly, while a non-specific anti-PODXL antibody (PcMab-47) bound to both cancer cells and normal cells, PcMab-6 showed negligible reactivity with normal lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) and renal epithelial cells. This data confirms that by targeting the specific glyco-epitope, it is possible to achieve high tumor specificity, significantly reducing the risk of binding to normal physiological tissues. This level of specificity is a prerequisite for the development of safe and effective antibody-based therapies, including Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) and Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies.
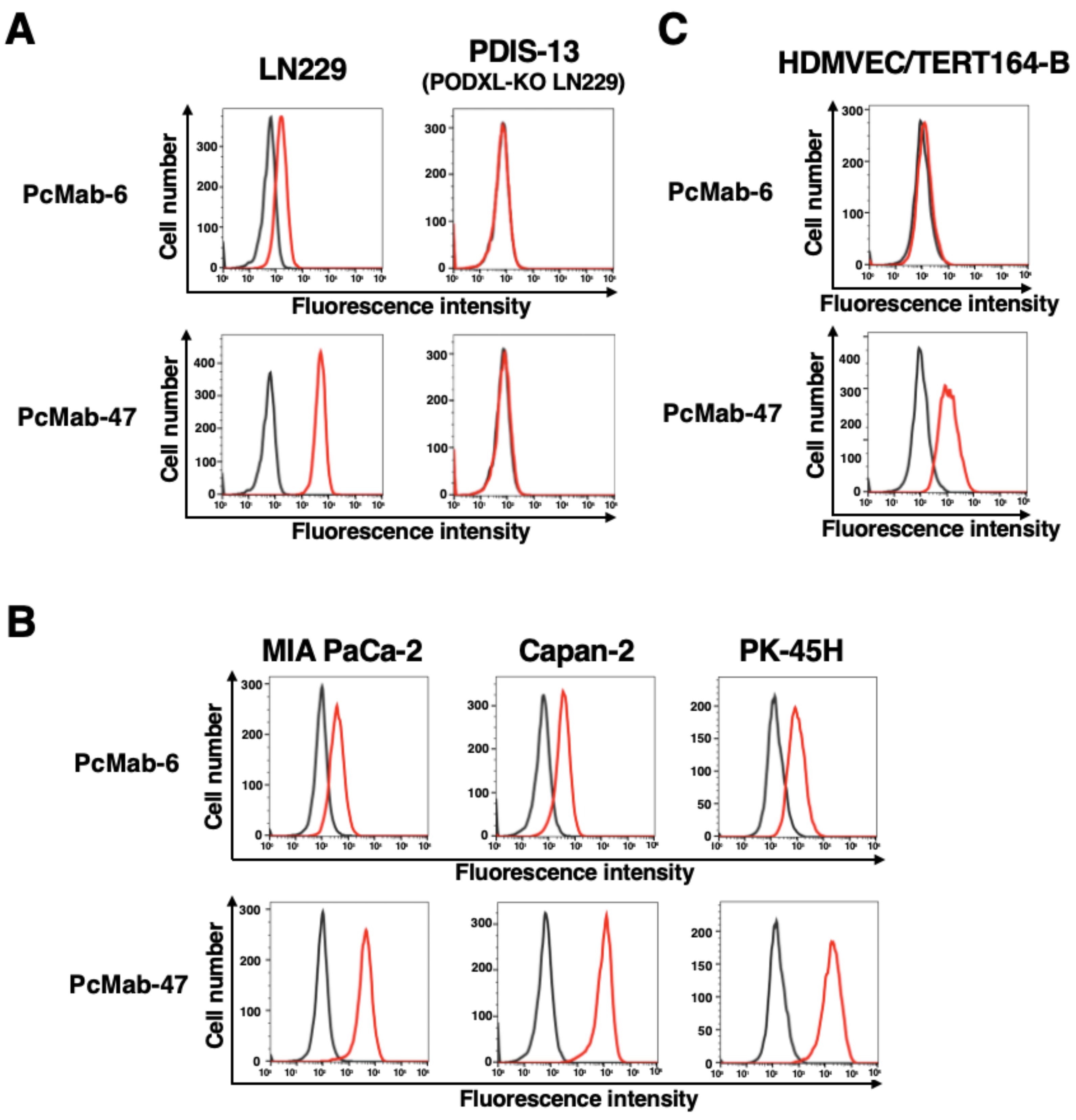 Fig.1 Specificity analysis of anti-PODXL antibody (PcMab-6) by flow cytometry.1
Fig.1 Specificity analysis of anti-PODXL antibody (PcMab-6) by flow cytometry.1
FAQs
How do you ensure the antibody binds the glycopeptide and not just the peptide backbone?
We employ a rigorous dual-screening process to guarantee epitope specificity. During the screening phase, we perform positive selection using the specific glycosylated peptide (the target). Crucially, we conduct parallel negative selection (counter-screening) using the non-glycosylated version of the same peptide sequence. We also screen against irrelevant glycopeptides carrying the same glycan but on a different peptide backbone. Only clones that bind to the glycosylated target but show no affinity for the naked peptide or irrelevant glycopeptides are selected. This ensures that the antibody recognition is dependent on the specific combination of the glycan and the amino acid sequence, defining a true glycopeptide antibody.
What types of aberrant glycosylation on PODXL can you target?
Our platform is versatile and can target a wide range of tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TACAs) presented on the PODXL backbone. The most common targets include truncated O-glycans such as the Tn antigen (GalNAc-Ser/Thr) and the sTn antigen (NeuAc-alpha-2,6-GalNAc-Ser/Thr), which are hallmarks of incomplete glycosylation in cancer. Additionally, we can target specific N-linked glycan alterations or unique conformational epitopes created by the interplay between the peptide and the glycan chain. If you have a specific glycan profile identified from mass spectrometry data, we can design an immunogen to match it.
Can you develop antibodies for other mucins or glycoproteins besides PODXL?
Yes, our expertise extends across the entire mucin family and other heavily glycosylated proteins. We have extensive experience in MUC1 antibody development (targeting VNTR regions), MUC4 antibody development (for pancreatic cancer), anti-MUC16 monoclonal antibody generation (for ovarian cancer), and projects involving CD43 glycopeptide antibody and MUC2 glycopeptide antibody. The technologies we use for PODXL—including peptide synthesis screening—are fully applicable to these other targets.
What species can be used for immunization to generate these antibodies?
We offer a broad range of host species to suit different project needs. Standard immunization is typically performed in BALB/c mice or rats. For higher affinity or challenging antigens, we recommend rabbits, which often produce antibodies with higher specificity against small epitopes like haptens and glycans. We also offer llama immunization for the production of VHH, which are excellent for tissue penetration and imaging applications. For projects requiring fully human antibodies for potential therapeutic development, we can utilize transgenic mice platforms that produce human IgG directly.
Is this service suitable for developing diagnostic IHC reagents for clinical research?
Absolutely. Many of our clients utilize this service to generate highly specific reagents for Immunohistochemistry (IHC). During the validation phase, we can screen clones specifically for their performance in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue arrays. We compare staining patterns on tumor tissues versus normal tissues to ensure the antibody discriminates effectively. This is vital for developing potential diagnostic markers, such as an ovarian cancer marker antibody or a colon cancer MUC2 antibody, where specificity is paramount to avoid false positives from normal tissue expression.
Reference:
- Suzuki, Hiroyuki, et al. "A Cancer-Specific Monoclonal Antibody against Podocalyxin Exerted Antitumor Activities in Pancreatic Cancer Xenografts." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.1 (2024): 161. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010161
Supports
- Anti-MUC1 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC4 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC16 (CA-125) Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC5AC Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC2 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-Podocalyxin (PODXL) Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-CD43 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Custom Glycopeptide Target Antibody Development
