Heparan Sulfate Microarray
Introduction
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a structurally diverse class of linear polysaccharide that orchestrates critical biological interactions through its sulfation patterns and conformational flexibility. In recent years, heparan sulfate microarrays have emerged as a transformative analytical platform for mapping HS-protein interactions with high throughput and specificity. At Creative Biolabs, we offer fully customized heparan sulfate microarray services designed to accelerate drug discovery and glycomics research.
Overview HS and HSPGs
Heparan sulfates are versatile glycosaminoglycans composed of repeated GlcA/IdoA-GlcNAc units that are intricately changed at the N-, 2-O-, 3-O-, and 6-O- positions. These finely controlled sulfation patterns encode extremely specialized interactions with growth factors, chemokines, morphogens, and even virus proteins. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) consist of a core protein covalently linked to HS chains. They act as co-receptors that facilitate ligand-receptor interactions. One extensively studied HSPG is HSPG2 (also known as perlecan), and they perform critical functions in regulating basement membrane integrity, angiogenesis, and tissue regeneration. Disruption in their biosynthesis—mediated by enzymes such as HS2ST1 and HS3ST6—has been implicated in cancer, viral infection, and rare genetic syndromes.
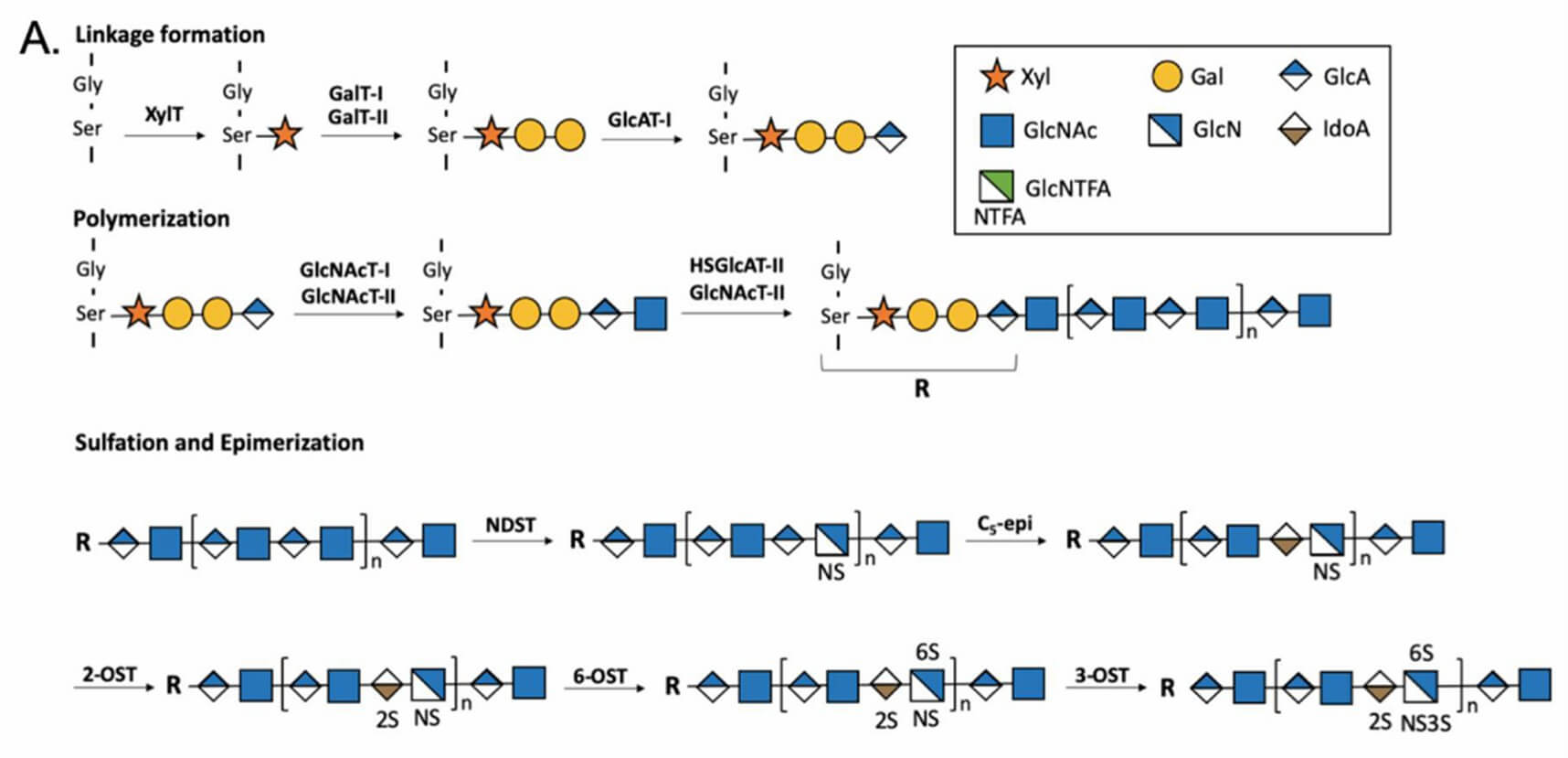 Fig.1 HS biosynthesis process.1
Fig.1 HS biosynthesis process.1
The Heparan Sulfate Microarray Platform
The heparan sulfate microarray is a chemically defined glycan profiling system that enables parallel interrogation of protein–glycan interactions. By immobilizing structurally precise heparan sulfates on solid supports, this tool offers a high-throughput, quantitative, and reproducible platform for ligand binding studies. Our platform:
- Includes N-, 2-O-, 6-O-, and 3-O-sulfated HS structures, with variable backbone lengths and epimerization patterns.
- Utilizes amine-reactive or azide-alkyne click surfaces on glass or nitrocellulose slides for stable glycan immobilization.
- Scan up to hundreds of distinct HS structures per slide, printed in multiple replicates to ensure statistical confidence.
Streamlined Workflow at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we've simplified the complex into a seamless 4-step workflow, designed for flexibility, scientific rigor, and your convenience.
-
Custom Array Fabrication
We begin by printing structurally defined heparan sulfate oligosaccharides—each with precise sulfation patterns—onto activated glass or nitrocellulose slides. Every spot is reproducibly arranged to ensure consistency and data quality. -
Sample Binding Made Easy
Your samples, such as proteins, antibodies, viruses, bacterial components, or cells, are gently incubated on the array under optimized conditions. Before this, we block the surface to minimize background and maximize signal clarity. -
Reliable Detection
Following incubation, we remove unbound materials and detect specific binding using fluorescent or enzyme-tagged reagents. Our protocols are tuned to maintain sensitivity while avoiding false positives. -
Data You Can Trust
Using high-resolution scanners and analytical software, we quantify signal intensities and generate clean, interpretable binding profiles. You'll receive ready-to-publish heatmaps and ranked interaction data customized to your project goals.
Comparative Advantages
- We offer high-throughput binding analysis to profile hundreds of HS structures within a single experiment.
- Our service uses fully characterized and sulfation-pattern-specific HS oligosaccharides for defined glycan composition.
- Our HS microarray platform requires minimal sample volume for efficient detection.
- We provide custom array content tailored to your project, incorporating specific modifications like HS2ST1 or HS3ST6 variants.
- Our approach is quantitative and reproducible, as fluorescent detection enables sensitive and linear signal quantification.
- With versatile ligand compatibility, our platform works with proteins, antibodies, whole cells, viruses, and bacterial fractions.
- Designed for comparative analysis, our service allows direct parallel comparison across ligands or experimental conditions.
Applications of Heparan Sulfate Microarrays
Heparan sulfate microarrays are proving incredibly useful in several key research fields:
Virus-Host Interactions
Many viruses exploit heparan or heparan sulphate moieties as attachment factors. For example, herpes simplex virus (HSV) and SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins bind specific sulfated motifs. Microarrays help map these interactions to inform antiviral strategies.
Antibody Epitope Mapping
Monoclonal antibodies targeting HS epitopes—termed heparan sulfate mimetics—can be evaluated for specificity and affinity using microarrays, guiding therapeutic antibody development.
Functional Glycomics
Profiling of heparan sulfate-binding growth factors (e.g., FGF2, VEGF) helps delineate the roles of sulfation and backbone structure. This is crucial in regenerative medicine and cancer biology.
Microbial Pathogenesis
Certain pathogens exploit heparan sulphate bacteria interactions to adhere and invade host cells. The microarray enables comparative studies of bacterial adhesins across strains.
Related Services You May Be Interested In
Creative Biolabs also provides comprehensive glycan microarray solutions:
- 100 Glycan Microarray – Broad-spectrum glycan profiling using 100 distinct structures.
- 100 N-Glycan Microarray – Specializing in complex and hybrid N-glycans.
- Oligosaccharide Microarray – Targeted short-chain sugar interaction profiling.
- Polysaccharide Microarray – High-molecular-weight polysaccharide ligand binding arrays.
- Glucan Microarray – Ideal for beta-glucan and fungal carbohydrate analysis.
- Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Microarray – Includes chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, and keratan sulfate profiling.
- ABH-Glycan Microarray – Useful for profiling ABO blood group–related antigen binding.
- Human Milk Oligosaccharide (HMO) Microarray – Tailored for microbiome, immunity, and infant nutrition studies.
Our heparan sulfate microarray service help you turn complex glycan data into meaningful biological insights with expert support at every step. Contact us today to customize your array or discuss how our platform can accelerate your discovery.
Reference:
- Arnold, Katelyn, Yi-En Liao, and Jian Liu. "Potential use of anti-inflammatory synthetic heparan sulfate to attenuate liver damage." Biomedicines 8.11 (2020): 503. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The graph was cropped, leaving only part A. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8110503
