GM3 Ganglioside Overview: A Critical Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis & Prognosis
Introduction
The world of oncology has been transformed by the recognition that cancer is not simply a genetic disease but also a disease of altered cell surfaces and signaling landscapes. Among the most critical molecular players in this landscape are glycosphingolipids—lipid–sugar conjugates embedded in the plasma membrane. Of particular interest is GM3 ganglioside, the simplest monosialylated ganglioside, which has been consistently implicated in tumor growth, progression, and immune recognition. GM3 has been proposed as a tumor-associated antigen in multiple malignancies for a long time. Evidence from various cancer models indicates that anti-GM3 antibodies provide an additional layer of tumor control. Increased titers of anti-GM3 IgG have been noted in malignant cell cultures and in patient samples, suggesting that both direct GM3 expression and antibody-mediated recognition contribute to shaping the tumor microenvironment. GM3 emerges as a molecule with multiple overlapping roles in cancer:
- It tempers growth signals by restraining EGFR and VEGFR-2.
- It can sensitize tumors to chemotherapy.
- It acts as a brake on angiogenesis, particularly in hypoxic tumors.
- It appears in the bloodstream and tissues in ways that lend themselves to diagnostic and prognostic use.
- It provokes immune recognition, opening avenues for GM3 antibody–based therapies and vaccines.
We provide an in-depth analysis of GM3 ganglioside from the perspective of cancer research and translational applications. We examine its biological features, summarize its expression across various tumor types, explore its diagnostic and prognostic value, highlight detection technologies, and assess the therapeutic opportunities offered by GM3 antibody development. Throughout, we emphasize how Creative Biolabs supports researchers with comprehensive solutions ranging from custom antibody generation to biomarker profiling services.
GM3 and Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Translational Relevance
The link between GM3 ganglioside and cancer has become one of the most intensively investigated areas of glyco-oncology. Far beyond its role as a structural membrane component, GM3 actively participates in tumor initiation, progression, and immune modulation. Evidence accumulated across decades of research underscores its function as both a cancer biomarker and a promising therapeutic target.
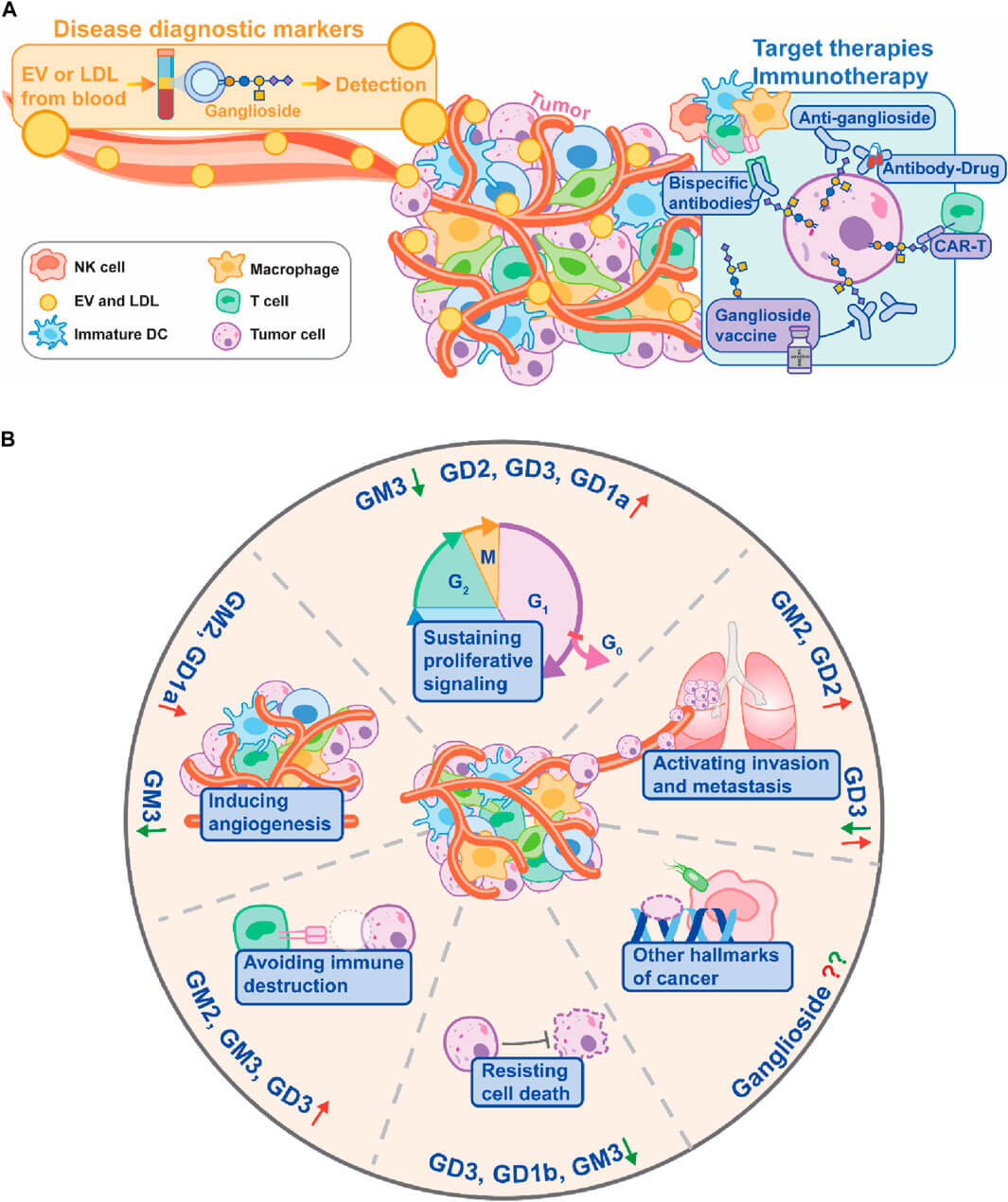 Fig.1 The role of gangliosides in cancer hallmarks and targeted therapy.1
Fig.1 The role of gangliosides in cancer hallmarks and targeted therapy.1
GM3 Synthase and Cellular Transformation
Early mechanistic studies showed that levels of mRNA encoding GM3 synthase are reduced in avian and mammalian cells transformed by oncogenic proteins. Remarkably, when GM3 synthase was overexpressed in these transformed cells, the malignant phenotype reverted to a more normal morphology. This reversal highlights the central role of GM3 biosynthesis in restraining oncogenic transformation.
Regulation of Growth Factor Signaling
A well-documented function of GM3 is its inhibitory effect on the activation of growth factor receptors. GM3 suppresses the phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), thereby curbing proliferative signals in tumor cells. Similarly, GM3 interacts with fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) in lipid microdomains, further demonstrating its role in growth suppression. In endothelial systems, GM3 also modulates angiogenesis. Supplementation of GM3 has been shown to suppress the action of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in endothelial cells, reducing both proliferation and migration. Mechanistically, GM3-enriched membranes exhibited reduced phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 and downstream AKT, while inhibition of GM3 biosynthesis accelerated angiogenic signaling. These findings highlight GM3 as a natural regulator of angiogenesis and a potential target for reducing tumor vascularization.
Sialidase Activity and Tumor Progression
In many human cancers, plasma membrane-associated sialidases—enzymes that selectively remove sialic acids from GM3 and related gangliosides—are upregulated. This activity reduces GM3 levels on the cell surface, tipping the balance toward growth-promoting glycolipids and underscoring the importance of the sialosyl group in tumor suppression.
Know More about GM3 Antibody in Cancer Immunotherapy
GM3 Expression Across Tumor Types
Bladder Cancer
Increased titers of GM3 have been documented in bladder cancer cells. Interestingly, GM3 appears to enhance the anti-proliferative effect of cisplatin, promoting apoptosis in malignant cells. Supplementation of bladder cancer cells with GM3 suppresses adhesion and reduces tumor growth.
Brain Tumors
The importance of GM3 in angiogenesis control has also been demonstrated in brain tumors, where hypoxic conditions alter GM3 synthesis and influence tumor vascularization. By limiting blood vessel formation, GM3 acts as a brake against tumor expansion.
Breast Cancer
GM3 levels in serum have been identified as potential diagnostic markers to differentiate breast cancer patients from both healthy controls and those with benign breast tumors. More specifically, GM3 has been suggested as a valuable marker for discriminating the luminal B (LB) subtype of breast cancer. A positive correlation between GM3 expression and the proliferation marker Ki-67 further supports its prognostic value.
Melanoma
Studies on melanoma cell lines have revealed increased GM3 levels and GM3-dependent growth. Alterations in serum gangliosides of melanoma patients also point toward GM3 as a tumor-associated antigen. Anti-ganglioside antibodies, including anti-GM3 antibodies, have been linked with the evolution of cutaneous melanoma. Intriguingly, endogenously produced anti-GM3 antibodies may affect tumor progression, suggesting a connection between chronic inflammation and melanoma outcomes.
GM3 Functions in Cancer
| Mechanism | Effect on Tumors | Therapeutic Implication |
|---|---|---|
| GM3 synthase overexpression | Reverts transformed cells to the normal phenotype | Enzyme modulation as therapy |
| EGFR inhibition | Suppresses proliferation | GM3 mimetics, custom antibody synergy |
| VEGFR-2 inhibition | Blocks angiogenesis | Anti-angiogenic therapy development |
| Cisplatin enhancement | Boosts chemotherapy-induced apoptosis | Combination regimens with GM3 |
| Anti-adhesion effects | Reduces tumor spread | Metastasis prevention strategies |
| Serum GM3 elevation | Differentiates patients from controls | Diagnostic biomarker |
| Anti-GM3 antibodies | Correlates with inflammation and cancer | Prognostic biomarker and immunotherapy |
GM3 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker
Diagnostic Utility
Serological and tissue-based studies support GM3 as a promising diagnostic tool:
- Serum GM3 levels: Clinical cohorts reveal that serum GM3 is significantly elevated in cancer patients compared with healthy controls. In some metabolic disorders, GM3 also rises, but cancer-associated increases can reach 1.5-fold or more.
- Neu5Gc-GM3 specificity: Because humans cannot synthesize Neu5Gc, the presence of Neu5Gc-GM3 in tumors provides a particular biomarker for malignancy.
Prognostic Significance
The value of GM3 extends beyond diagnosis into prognosis:
- GM3/GD3 ratio: Studies in melanoma show that a low GM3/GD3 ratio is associated with highly invasive, metastatic disease. Conversely, a higher GM3/GD3 ratio is associated with less aggressive phenotypes.
- Clinical outcomes: Patients with tumors rich in GM3 often demonstrate altered survival patterns, suggesting GM3 quantification could refine risk stratification in oncology.
Established Detection Technologies for GM3 Biomarker Research
| Technology | Application | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | Serum GM3 quantitation | Accessible, high throughput | Limited isoform specificity |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Tumor tissue GM3 visualization | Spatial resolution, routine pathology-compatible | Semi-quantitative |
| Flow Cytometry | Cell surface GM3 quantification | High resolution, dynamic monitoring | Requires fresh cells |
| LC-MS/MS | Isoform-specific GM3 profiling | High specificity for Neu5Gc-GM3 | High technical complexity |
Role of GM3 Antibodies in Research
The identification of GM3 as a tumor antigen was made possible by the development of GM3 antibodies that confirmed GM3's selective expression on melanoma cells. Since then, GM3 antibodies have become indispensable tools for:
- Immunohistochemical staining of tumor tissues.
- Flow cytometry-based tumor immunophenotyping.
- Functional studies of GM3's role in cell signaling.
Therapeutic Applications
- ADCC and CDC: Therapeutic GM3 antibodies can mediate ADCC and CDC, directly eliminating tumor cells.
- Anti-idiotype vaccines: An anti-idiotype antibody that mimics Neu5Gc-GM3 has shown promise in NSCLC clinical studies, stimulating host immune responses against Neu5Gc-GM3.
GM3 Biomarker Support Services at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in overcoming these barriers through custom antibody programs dedicated to glycolipid targets, such as GM3. We recognize that advancing GM3 research requires not only scientific rigor but also flexible technical solutions. We provide a comprehensive suite of services tailored to academic, biotech, and pharmaceutical teams working in glycoscience and oncology.
- Ready-to-use research-grade GM3 antibodies validated for multiple applications.
- Custom antibody generation against GM3 and Neu5Gc-GM3, including humanized formats for translational work.
Our Approach
- Antigen design and conjugation: Preparing GM3 or Neu5Gc-GM3 in native-like liposomal states, or coupling to strong carrier proteins for immunization.
- Discovery technologies: Hybridoma, phage display, yeast display, and single B-cell cloning to maximize epitope diversity.
- Validation and specificity testing: Employing ELISA, IHC, flow cytometry, and glycan arrays to confirm selectivity and minimize cross-reactivity.
- Functional screening: Assessing ADCC, CDC, and ADCP with human immune effector cells to ensure therapeutic potential.
- Engineering and optimization: Humanization, Fc engineering, and stability enhancement to prepare antibodies for translational use.
The story of GM3 ganglioside illustrates how a single glycosphingolipid can become central to cancer biology and translational research. As both a regulator of key signaling pathways and a selective cancer biomarker, GM3 provides actionable information for diagnosis, prognosis, and the development of targeted therapies. The development of GM3 antibodies, whether for detection or treatment, has transformed the landscape of GM3 research. Whether the goal is to map GM3 expression, validate it as a cancer biomarker, or develop antibody-based therapies, GM3 antibodies remain indispensable tools driving progress in oncology. At Creative Biolabs, we combine decades of expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver tailored services that enable researchers to move seamlessly from GM3 hypothesis to high-quality data. Our offerings, from custom antibody development to biomarker assay design, ensure that GM3-focused projects reach their full potential in shaping the future of oncology.
Reference:
- Zhuang, Hongda, et al. "Pharmacology of gangliosides." Frontiers in Pharmacology 15 (2024): 1449928. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1449928
Supports
- Glycolipid
- GM3 Antibody in Cancer Immunotherapy
- GM3 Ganglioside in Disease & Anti-GM3 Antibody Tools
