Custom Glycosylation of Bacterial Membranes
Introduction
Despite their underutilized status, bacterial membrane glycoconjugates provide a very versatile substrate for synthetic biology, immunomodulation, and next-generation vaccine production. Unlike template-driven glycosylation in eukaryotes, bacterial glycosylation is architecturally varied, modular, and flexible. This provides a strong method for designing glycoforms for the cell surface. Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive methods for changing the glycosylation of bacterial membranes, allowing for exact changes to the cell surface structure. This might have important consequences for a variety of biological and medicinal applications.
Glycosylation in E. coli
As a microbial workhorse, E. coli offers a tractable chassis for membrane glycosylation engineering:
- Supports pgl pathway integration for N-linked glycosylation
- Capable of producing bioconjugate vaccines with high batch consistency
- Enables surface display of engineered glycans for receptor-binding studies
Why Bacterial Membrane Glycosylation Matters
The bacterial cytoplasmic membrane is like a central control center for biosynthesis and transport, coordinating the assembly of glycans, exporting proteins and modifying glycoproteins. It has a role that is more than just structure. It starts important processes like putting together glycans and using lipids to flip membranes. It also affects how proteins fold, how antigenic they are, and how they are transported. And it makes surface glycoconjugates, including things like lipopolysaccharides (LPS), capsular polysaccharides (CPS), and glycoproteins. Through targeted glycoengineering of this membrane system, researchers can change the way bacteria behave to make them useful in different ways.
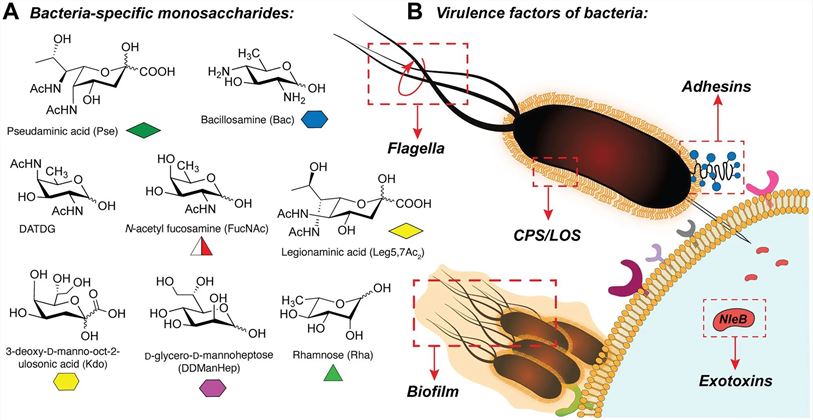 Fig.1 Bacterial monosaccharides and glyco-virulence schematic.1
Fig.1 Bacterial monosaccharides and glyco-virulence schematic.1
Focus on Glycosylation in Bacteria: A Platform for Engineering Complexity
Bacteria possess unique glycosylation systems with enormous design potential. Our platform focuses on:
N-linked and O-linked Glycosylation Pathways
- Campylobacter jejuni's N-glycosylation system reconstituted in E. coli
- Diverse O-glycosylation strategies for flagellar proteins, adhesins, and outer membrane components
Membrane-Integrated Glycan Assembly
- Glycans are typically assembled at the inner membrane and flipped outward
- Final glycoprotein or glycolipid structures vary by species and strain, allowing customization
Custom Workflow at Creative Biolabs
Our service accommodates projects involving E. coli, Campylobacter, Neisseria, Helicobacter, and other customizable hosts. We deliver tailored glycosylation projects through a modular and highly configurable process:
| 1. Design | Glycosylation site selection, donor/acceptor optimization |
| 2. Construction | Host strain engineering, pathway integration |
| 3. Expression | Controlled induction under precise conditions |
| 4. Analysis | LC-MS, lectin blot, glycan array, HPAEC-PAD |
| 5. Delivery | Glycosylated membrane fractions, intact bacteria, or vesicles |
Send Inquiry
Analytical Support for Structure–Function Insights
Reliable membrane glycosylation projects demand robust analytical tools. Creative Biolabs offers:
| LC-MS/MS | Peptide- and lipid-linked glycan profiling |
| HPAEC-PAD | Monosaccharide composition analysis |
| Lectin Microarray | Functional glycan epitope mapping |
| SDS-PAGE/Western Blot | Glycosylation-induced mobility shift characterization |
Application Highlights
Our custom glycosylation services support multiple high-impact application areas:
Vaccine Antigen Engineering
- Produce defined glycoforms for glycoconjugate vaccine development
- Modify LPS/LOS structures for attenuated yet immunogenic strains
Glyco-Targeted Therapeutics
- Mimic or block host glycans implicated in immune signaling or infection
- Develop glyco-adorned membrane vesicles for targeted drug delivery
Synthetic Biology & Diagnostics
- Create bacterial display systems with defined glycan motifs
- Support glycan–lectin interaction studies and biosensor design
Why Partner with Creative Biolabs?
- Decades of expertise in glycoscience solutions
- Dedicated team for bacterial glycosylation and membrane biology
- Fully customizable service model — from target design to analytical validation
Related Services
| We Provide | Brief Service Description |
|---|---|
| Custom Protein Glycosylation | Precision design of protein glycoforms to improve structure, stability, or function. |
| Custom Peptide Glycosylation | Tailored sugar modification of peptides to enhance bioactivity and proteolytic resistance. |
| Custom Antibody Glycosylation | Fc and Fab glycoengineering to modulate effector function and pharmacokinetics. |
| Custom Cell Membrane Glycosylation | Site-specific glycosylation of membrane proteins and receptors for functional studies. |
| Custom Glycosylation of Small Molecules & Nucleic Acids | Conjugation of glycans to small molecules or nucleic acid scaffolds for delivery or targeting. |
| Custom Lipid Glycosylation | Synthesis of glycolipids for membrane remodeling, vaccine adjuvants, or liposome formulation. |
Whatever your research aims, Creative Biolabs has the scientific expertise and technical infrastructure to deliver measurable results. Whether you want to change microbial phenotypes, build targeted glycovaccines, or examine membrane glycan function, we are your best partner! If you would like to know more about a custom bacterial membrane glycosylation project, please contact us today to schedule a feasibility discussion and receive a detailed proposal.
FAQs
What types of glycosylation can be engineered on bacterial membranes, and how customizable are the glycan structures?
At Creative Biolabs, we offer fully customizable engineering of both N-linked and O-linked glycosylation pathways on bacterial membranes. This includes native glycosylation systems, such as the pgl locus from Campylobacter jejuni, as well as synthetic or hybrid glycosylation modules introduced into E. coli or other Gram-negative hosts. We can tailor the sugar composition, linkage type, branching patterns, and even glycan density based on your application, whether it's vaccine antigen display, receptor mimicry, or surface functionalization. Our platform supports site-specific or global glycosylation strategies, and we provide full structure–function correlation via glycomic and proteomic analytics.
How do you ensure the correct localization of engineered glycans on the bacterial surface?
For the downstream function, glycan localization must be correct. In the cytoplasmic membrane, we design glycans to be built on undecaprenyl phosphate (Und-P) lipid carriers, which are then flipped to the periplasmic side by specific flippases. Glycan moieties are then deposited onto lipids or acceptor proteins that are meant to be part of the outer membrane. We make sure that glycosylation happens in time with membrane integration by using sophisticated membrane protein targeting sequences and ideal expression conditions. Flow cytometry, surface biotinylation, immunogold TEM, and lectin labeling experiments are used for verification.
Can your bacterial glycosylation platform be used to generate glycoconjugate vaccine candidates?
Absolutely. One of the primary uses of our bacterial membrane glycosylation platform is to produce reliable, immunogenic glycoconjugates for vaccine development. We can generate glycosylated outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), LPS-deficient strains with engineered glyco-epitopes, and pure glycoproteins with pathogen-mimicking glycans. These structures can be tuned for immunogenicity, stability, and host compatibility. We also provide endotoxin-free expression platforms and scalable fermentation to suit preclinical supply requirements.
Reference:
- Yakovlieva, Liubov, Julius A. Fülleborn, and Marthe TC Walvoort. "Opportunities and challenges of bacterial glycosylation for the development of novel antibacterial strategies." Frontiers in Microbiology 12 (2021): 745702. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.745702