Oncology related Glycan Introduction: Altered Glycosylation in Cancer
Accelerate Your Glycan-Based Discoveries!
Glycans (including N-glycans, O-glycans, and glycosphingolipids) mediate diverse biological processes like inflammation, signaling pathways, cellular interactions, pathogen-host engagements, and oncogenesis. Altered glycosylation commonly signifies pathological conditions. Malignant cells often exhibit glycans at aberrant levels or with fundamentally distinct structures compared to healthy counterparts. Creative Biolabs is a specialized, experienced glycobiology institution continuously monitoring cancer-associated glycosylation changes. Through our support, clients achieve enhanced comprehension of carbohydrate roles in oncology.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
Advances in Cancer-Associated Glycans
Dysregulated glycosylation constitutes a defining characteristic of cancerous cells. Yet, only distinct particular glycan modifications frequently correlate with tumors. These include: elevated β1-6GlcNAc-branched N-glycans; heightened O-GlcNAc modification of numerous proteins; O-glycan shortening yielding Tn and sialyl-Tn antigen display; modifications to sialic acid abundance, linkages, and acetylation; sialylated Lewis antigen and selectin ligand levels; non-human sialic acid Neu5Gc expression; changed glycosphingolipid expression and accelerated breakdown; glycosaminoglycan sulfation shifts; upregulated galectin and poly-N-acetyllactosamine expression; increased hyaluronan production; elevated expression of enzymes catalyzing GPI-anchor attachment; and modified ABH(O) blood-group antigen expression.
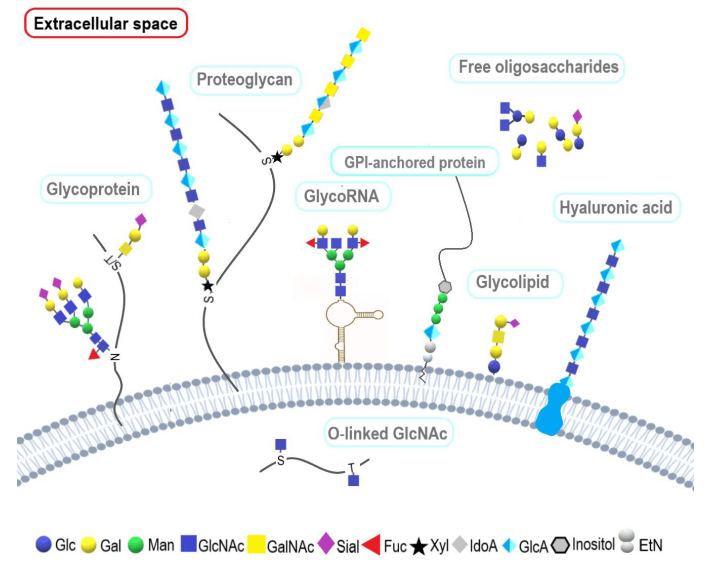 Fig.1 Schematic presentation of classes of glycoconjugates.1,3
Fig.1 Schematic presentation of classes of glycoconjugates.1,3
Glycosylation Alterations in Cancer
Glycosylation involves glycans attaching to proteins or other molecules, enhancing cellular molecular diversity and functional variety. This principal posttranslational protein modification critically influences cancer progression and metastasis. Occurring within Golgi compartments, the process relies on glycosidase and glycosyltransferase activities across varied cell types or tissues. Key alterations, sialylation and fucosylation, represent characteristic terminal alterations mediating essential biological functions with significant oncological implications.
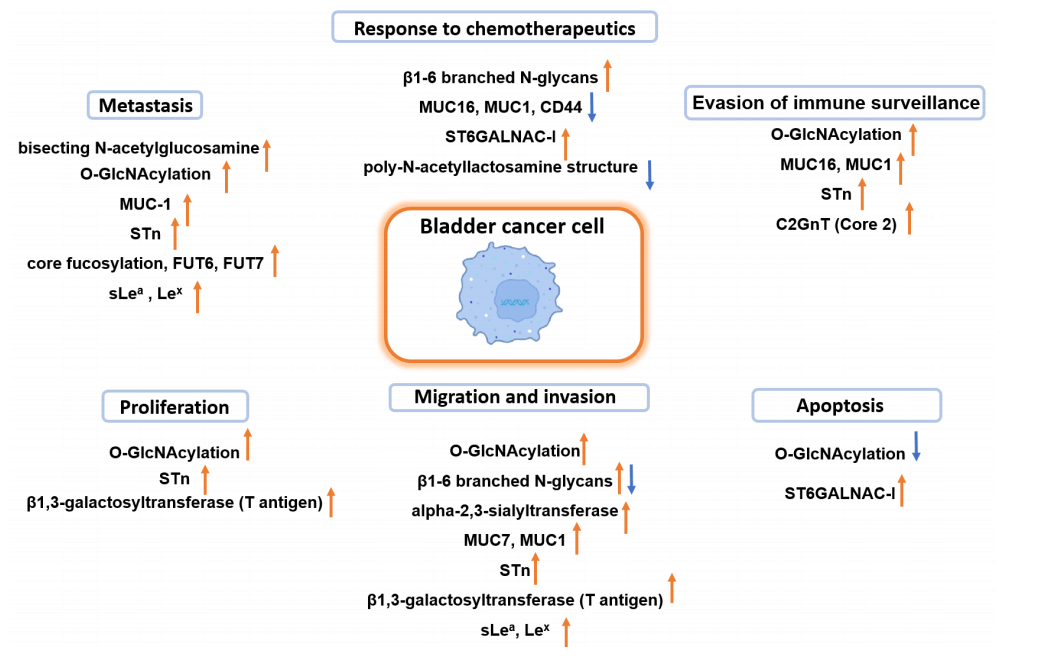 Fig.2 Illustrated involvement of modified glycosylation in urothelial carcinoma advancement.1,3
Fig.2 Illustrated involvement of modified glycosylation in urothelial carcinoma advancement.1,3
Malignant cells exhibit extensive glycosylation aberrations relative to healthy counterparts. Typically, dysregulation of canonical glycosylation mechanisms in malignancies leads to aberrant glycan profiles through multiple mechanisms. Primary contributors include: 1) dysregulated expression levels of glycosyltransferases, 2) modified spatial configurations of polypeptide backbones and immature glycan chains altering carbohydrate presentation, and 3) differential availability of acceptor substrates combined with fluctuating concentrations of nucleotide sugar donors and enzymatic cofactors. These glycan modifications fundamentally depend on the precise subcellular distribution and functional activity of Golgi-resident glycosyltransferases.
Glycans' Potential for Therapeutics
Initially, glycosylation alterations in oncogenesis were documented over sixty years ago. These discoveries gained validation through monoclonal antibody technology, revealing tumor-selective antibodies targeting carbohydrate epitopes—typically oncofetal antigens expressed on malignant glycoproteins and glycosphingolipids. Presently, anticancer vaccines employ synthetic tumor-associated glycans multivalently conjugated to carrier proteins. Presently, various glycan-derived immunotherapies undergoing clinical evaluation have shown promise.
Conversely, therapeutic strategies blocking cancer glycan synthesis or their downstream interactions prove effective only when such glycans significantly contribute to pathology. For instance, clear causal relationships exist—specific β1,6GlcNAc-branching and sLex structures promote oncogenic signaling and metastasis.
Published Data
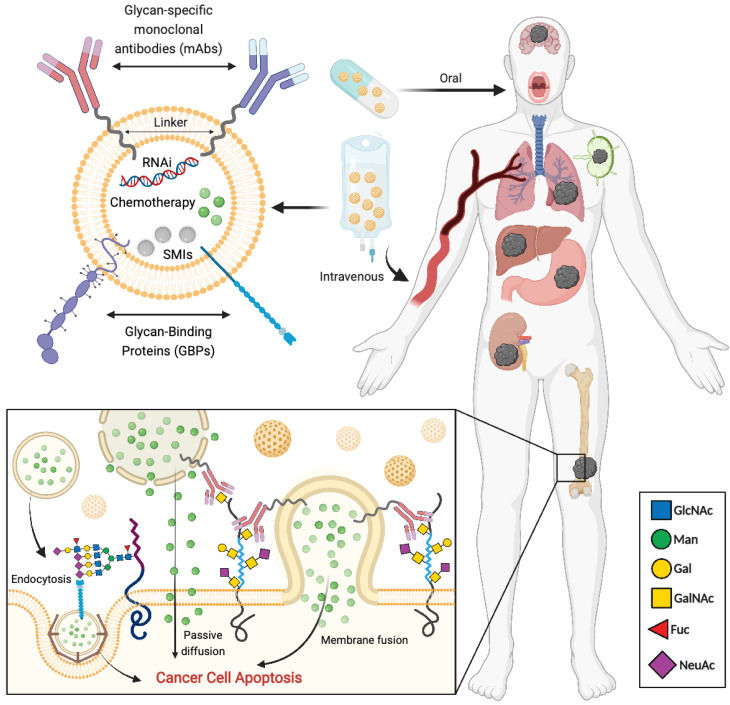 Fig.3 Approaches focused on targeting tumor-associated glycans for precision-targeted drug delivery platforms.2,3
Fig.3 Approaches focused on targeting tumor-associated glycans for precision-targeted drug delivery platforms.2,3
Research increasingly emphasizes the importance of dysregulated glycosylation in cancer, enabling development of sophisticated precision therapies. Studies have focused on developing strategies that specifically target cancer-associated glycans on tumor cells, including monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and nanoparticles. These experimental approaches aim to enhance the selective delivery of clinically approved drugs to the tumor microenvironment. The high prevalence of glycosylation alterations within the glycocalyx of tumor cells makes them appealing candidates for antibody-based targeted delivery of nanoparticles. Furthermore, the development of glycan-recognizing molecules, such as antibodies, lectins, and other glycan-binding proteins (GBPs), unlocks several potential strategies for clinically beneficial targeted therapeutics, ultimately improving patient outcomes. These findings underscore the major opportunity presented by the aberrant glycosylation landscape of tumor cells for developing advanced targeted therapies.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is at the forefront of glycan research in oncology, offering a comprehensive suite of products and services designed to empower your cancer research and drug development initiatives.
- Comprehensive Glycan Profiling Services
- Custom Anti-Glycan Antibody Development
- Glycoengineering Services for Therapeutic Antibodies
- Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Development Support
- Glycan-Based Biomarker Discovery and Validation
- Functional Studies of Glycan-Mediated Cancer Processes
Discover the Creative Biolabs Edge – Obtain Your Pricing Now
Why Choose Us?
Choosing Creative Biolabs for your Glycan in Oncology research means partnering with a leader in the field, dedicated to delivering exceptional scientific solutions and unparalleled client support.
- Cutting-Edge Glycoanalysis Platforms
- Extensive Expertise in Cancer Glycobiology
- Proprietary Antibody Development Technologies
- Comprehensive Service from Discovery to Validation
- Commitment to Data Quality and Scientific Rigor
- Customizable Solutions
FAQs
Here are some common questions potential clients have about Glycan in Oncology and related services:
Q: How can advanced glycan analysis contribute to identifying novel cancer biomarkers?
A: Advanced glycan profiling technologies enable the comprehensive analysis of altered glycosylation patterns in cancer cells and tissues. By identifying specific tumor-associated glycans, researchers can pinpoint novel biomarkers for early detection, diagnosis, and prognosis, offering a unique advantage over traditional protein-based markers. This precision can significantly enhance diagnostic capabilities.
Q: What types of therapeutic approaches can be explored by leveraging glycan expertise in oncology?
A: Expertise in glycans supports the development of various glycan-targeted therapeutics, including highly specific anti-glycan antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and even insights for vaccine and CAR-T cell strategies. The focus is on developing agents that selectively target cancer cells while minimizing off-target effects, leading to potentially more effective and safer treatments.
Q: Is glycan analysis technology broadly applicable across different cancer types?
A: Yes, aberrant glycosylation is a universal hallmark across many cancer types, making these analytical approaches broadly applicable. Platforms designed for glycan analysis can analyze changes in a wide range of cancers, from solid tumors to hematological malignancies, providing versatile and adaptable solutions for diverse oncology research projects.
Related Products and Services
To further advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a portfolio of solutions:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Wilczak, Magdalena et al. "Altered Glycosylation in Progression and Management of Bladder Cancer." Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 28,8 3436. 13 Apr. 2023, DOI:10.3390/molecules28083436
- Diniz, Francisca et al. "Glycans as Targets for Drug Delivery in Cancer." Cancers vol. 14,4 911. 12 Feb. 2022, DOI:10.3390/cancers14040911
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
