100 N-Glycan Microarray
Introduction
Glycans are essential in numerous physiological and pathological processes, including cell signaling, immune modulation, host-pathogen interactions, and cancer progression. Among them, N-linked glycans represent a structurally diverse and biologically critical class of oligosaccharides covalently attached to asparagine residues within glycoproteins. Yet, understanding their interactions remains challenging due to their heterogeneity and complex biosynthesis. To overcome this, Creative Biolabs offers a 100 N-glycan microarray platform, a robust and reproducible analytical solution to systematically evaluate the binding properties of glycan-interacting molecules. This platform enables comprehensive profiling of glycan-binding proteins (GBPs), antibodies, viral particles, and cells against a standardized panel of 100 well-characterized N-glycans.
What Is the 100 N-Glycan Microarray?
The 100 N-glycan microarray is a pre-printed slide containing 100 structurally verified N-glycans, selected to represent major mammalian glycosylation motifs. These include high-mannose, hybrid, and complex-type N-glycans with varied terminal residues such as sialic acids (Neu5Ac/Neu5Gc), galactose, fucose, and bisecting GlcNAc. Each glycan is covalently linked to a glass surface via a spacer arm, ensuring optimal spatial orientation and accessibility for binding assays. Slides are compatible with fluorescence-based detection and surface-sensitive imaging systems.
Why Analyze N-Glycan Interactions?
N-Glycans modulate protein folding, trafficking, and clearance. Importantly, specific N-glycan motifs act as ligands for various lectins, pathogens, or immune receptors. For instance:
- DC-SIGN, Siglecs, and galectins bind distinct N-glycan structures to regulate inflammation or tolerance.
- Tumor-specific glycan signatures serve as diagnostic and therapeutic targets.
- Viruses such as influenza, HIV, and coronaviruses exploit host N-glycans for cell entry.
- Glycoengineering of therapeutic antibodies requires precise knowledge of N-glycan-mediated effector functions.
Step by Step Workflow for N-glycan Microarray
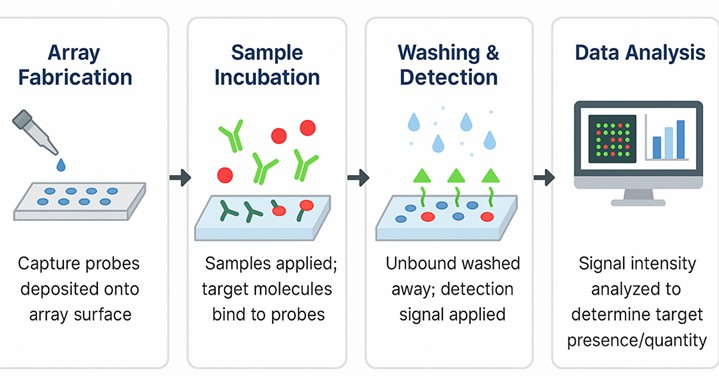 Fig.1 Standardized workflow for 100 N-glycan microarray platform.
Fig.1 Standardized workflow for 100 N-glycan microarray platform.
- Array Fabrication: Covalent attachment of 100 purified N-glycans to a chemically activated glass surface.
- Sample Incubation: Application of GBPs, antibodies, viruses, or live cells labeled with a fluorescent tag or followed by labeled secondary antibodies.
- Washing & Detection: Removal of unbound material and acquisition of signal via laser scanner or microscope.
- Data Analysis: Generation of heatmaps, glycan specificity profiles, and statistical clustering using proprietary software.
Data Interpretation & Reporting
Results are provided in a structured, publication-ready format. Our deliverables include:
- Fluorescent signal heatmaps
- Quantitative glycan-binding intensity data
- Glycan specificity clustering (PCA or hierarchical)
- Comparative plots for group analysis
Advantages of the Creative Biolabs Platform
- Structural Fidelity: All glycans are chemically or enzymatically synthesized to ensure high purity and accurate linkage definition, confirmed by LC-MS/MS.
- Customizable Microarrays: Beyond the standard 100-N-glycan panel, we offer custom spotting with additional human or pathogen-associated glycans, glycopeptides, or lipid-linked glycoconjugates.
- Low Sample Requirement: Only ~5–20 µg of test material is needed, making this suitable for rare antibodies or expensive recombinant proteins.
- Cross-Species Applications: Validated for use with human, mouse, rat, and non-human primate samples. Compatible with academic research.
Applications in Biomedical Research
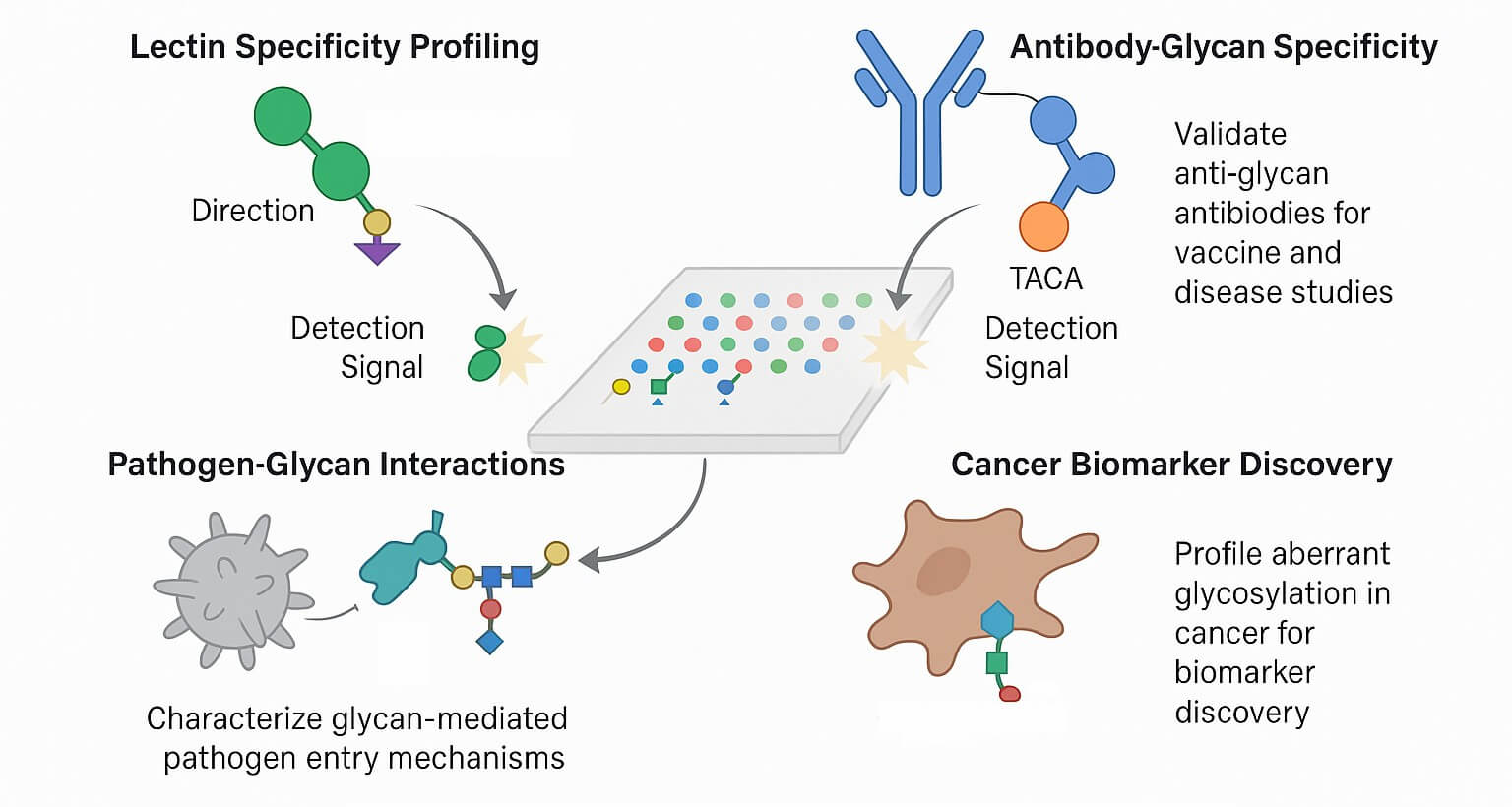 Fig.2 The application of N-glycan microarray in research.
Fig.2 The application of N-glycan microarray in research.
Lectin Specificity Profiling
Lectins are glycan-binding proteins essential for immune recognition, cell adhesion, and intracellular trafficking. The microarray can reveal subtle preferences of lectins for specific glycan epitopes, including fucosylation and sialylation variants.
Antibody Glycan Specificity
In vaccine development and infectious disease studies, antibody-glycan interactions are crucial. For example, anti-glycan antibodies targeting tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TACAs) can be validated for glycoepitope specificity using the array.
Pathogen-Glycan Interactions
Viral envelope proteins (e.g., hemagglutinin, spike glycoproteins) and bacterial adhesins often target host N-glycans. Screening these proteins on the 100 N-glycan array helps identify glycan-based entry mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Cancer Biomarker Discovery
Aberrant N-glycosylation is a hallmark of many cancers. Profiling serum or tumor-derived proteins for altered glycan-binding profiles provides insights into disease progression and potential diagnostic markers.
The 100 N-glycan microarray platform from Creative Biolabs offers a powerful solution for elucidating glycan-binding interactions with high sensitivity, reproducibility, and biological relevance. This technology accelerates glycomics discovery and biomarker development for basic research. Whether characterizing immune receptors, mapping therapeutic antibody specificities, or profiling pathogen tropism, our platform provides the precision and throughput that modern glycobiology demands. Contact us to get your tailored and time-saving solutions for N-glycan related research.
Related Services You May Be Interested in
FAQs
What are the three types of N-glycans?
N-glycans can be classified into high-mannose, hybrid, and complex types. High-mannose glycans consist mainly of mannose residues. Hybrid glycans contain both mannose and GlcNAc. Complex-type N-glycans have diverse structures, including branched chains with terminal residues like galactose, sialic acid, and fucose, significantly influencing protein interactions and stability. The 100 N-glycan microarray from Creative Biolabs offers a diverse set of glycans, including high-mannose, hybrid, and complex structures, enabling detailed analysis of glycan-protein interactions. By providing a wide range of N-glycan types, our platform helps you explore their roles in cancer research, immunology, and therapeutic development.
What is N-glycan analysis?
N-glycan analysis refers to the comprehensive study of the glycan structures attached to the asparagine residues of proteins. Techniques like MS, HPLC, and microarrays are used to identify and quantify glycan composition, branching, and modifications. Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive 100 N-glycan microarray service to facilitate your N-glycan analysis needs. This platform not only provides a broad spectrum of glycan structures but also supports high-throughput analysis to accelerate your research.
Can Creative Biolabs customize the glycan content of the array?
Yes. While the standard 100 N-glycan microarray covers a comprehensive set of mammalian N-glycan structures, we recognize that some research requires tailored solutions. Creative Biolabs offers custom array fabrication, including:
- Addition of pathogen-associated or non-human glycans
- Printing of O-glycans, glycopeptides, or glycolipids
- Inclusion of synthetic analogs with specific linkages or chemical tags
We support co-development workflows where clients specify target glycans, and we handle synthesis, purification, quality control, and microarray integration. This is especially valuable for vaccine research, microbiome-host interaction studies, and rare disease biomarker validation.
Reference:
- Bojar, Daniel, et al. "A useful guide to lectin binding: machine-learning directed annotation of 57 unique lectin specificities." ACS chemical biology 17.11 (2022): 2993-3012. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.1c00689
