Anti-MUC2 Glycopeptide Antibody Development Service
Mucins are high molecular weight glycoproteins that play critical roles in the protection and lubrication of epithelial surfaces. Among them, MUC2 is the predominant gel-forming mucin secreted by goblet cells in the human intestine. In the context of pathology, particularly colorectal cancer, the expression pattern and glycosylation status of MUC2 undergo significant alterations. Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive custom glycopeptide antibody development services to target these tumor-specific modifications. Our platform enables the generation of high-affinity anti-MUC2 glycopeptide antibodies that can distinguish between normal and aberrant glycoforms, providing powerful tools for basic cancer research and biomarker discovery.
Background: MUC2 and Aberrant Glycosylation in Cancer
MUC2 is a large, heavily glycosylated protein characterized by tandem repeat regions rich in proline, threonine, and serine (PTS domains), which serve as sites for extensive O-linked glycosylation. In healthy intestinal tissue, MUC2 is heavily glycosylated, forming a dense mucus barrier that protects the epithelium. However, in malignancy, the glycosylation machinery is often disrupted. This leads to the expression of truncated, immature O-glycans such as the Tn antigen (GalNAc-Ser/Thr) and Sialyl-Tn (sTn) antigen on the MUC2 peptide backbone.
These aberrant glycoforms create unique "glycopeptide" epitopes—regions where the peptide backbone is exposed or conformed differently due to the short sugar chains—that are virtually absent in healthy tissues. Consequently, the anti-MUC2 antibody targeting these tumor-associated glycopeptides represents a highly specific approach for identifying colorectal carcinoma (CRC) markers and studying the role of mucins in tumor progression. Specifically, while MUC2 expression is often downregulated in non-mucinous adenocarcinomas, it is significantly upregulated in mucinous carcinomas, making it a critical biomarker for subtype differentiation.
Our Service: Anti-MUC2 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
Developing antibodies against specific glycopeptides is challenging due to the low immunogenicity of carbohydrates and the difficulty in targeting the combined glycan-peptide epitope. Creative Biolabs overcomes these hurdles with a specialized platform for glycopeptide antibody production. We design synthetic glycopeptides mimicking the MUC2 VNTR (Variable Number Tandem Repeat) regions carrying tumor-associated glycans (e.g., MUC2-Tn, MUC2-sTn).
Our service encompasses the entire development pipeline:
Precision Antigen Design
We synthesize MUC2 glycopeptides with precise O-glycosylation sites. By controlling the glycan structure (Tn, T, or sTn) and the peptide sequence, we ensure the immunogen presents the exact tumor specific glyco-epitope found in vivo.
Advanced Immunization Strategies
To break tolerance and enhance immune response, we utilize proprietary adjuvant systems and carrier protein conjugation (KLH/BSA). We offer immunization in mice, rats, and rabbits to generate high-affinity monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies.
Hybridoma & Phage Display
We employ both traditional hybridoma technology and modern phage display libraries. Phage display is particularly powerful for selecting binders that strictly recognize the glycopeptide interface rather than the peptide or glycan alone.
Counter-Screening & Validation
Crucially, we perform extensive counter-screening against the non-glycosylated MUC2 peptide and irrelevant glycopeptides. This ensures the final antibody is a true anti-glycopeptide antibody with no cross-reactivity to normal tissues.
Service Workflow
Inquire About MUC2 Antibodies
Key Features and Advantages
Epitope Specificity
Targeting the unique combination of peptide sequence and glycan structure, minimizing off-target binding.
Diverse Formats
Available as IgG, IgM, Fab fragments, or scFv to suit various downstream applications.
Comprehensive Validation
Rigorous testing using glycan arrays, ELISA, and IHC to guarantee performance.
Fast Turnaround
Optimized workflows allow for rapid development without compromising quality.
Applications
Biomarker Research
MUC2 is a key marker for goblet cells and mucinous carcinomas. Antibodies against specific MUC2 glycoforms can be used in immunohistochemistry to improve the stratification of colorectal cancer subtypes and to study disease progression patterns.
Therapeutic Research
The restricted expression of tumor-associated MUC2 glycoforms makes them attractive targets for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or CAR-T cell therapies. Our high-affinity antibodies serve as excellent leads for therapeutic development.
Mechanistic Studies
Understanding the role of MUC2 in barrier function and inflammation is crucial. These antibodies facilitate the study of mucin biology in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colitis-associated cancer models.
Serum Assays
Development of sandwich ELISAs to detect circulating MUC2 or MUC2-associated glycopeptides in patient serum, offering a potential non-invasive tool for disease monitoring research.
Published Data
Research into MUC2 expression in colon cancer has elucidated its dual role in tumor biology. A pivotal study highlights the significance of MUC2 in the progression of colon cancer mediated by the cell adhesion molecule L1. The researchers utilized immunohistochemical analysis to map the expression of MUC2 in human colon cancer tissues.
The study demonstrated that while MUC2 is abundantly expressed in normal colonic mucosa, its expression is frequently lost in typical adenocarcinomas. Conversely, in the mucinous subtype of colon cancer, MUC2 expression is retained or upregulated. The accompanying figure (Fig. 1) illustrates the distinct immunohistochemical staining patterns of MUC2. The antibody used in such studies must possess high specificity to accurately differentiate MUC2 from other secreted mucins like MUC5AC or MUC6, ensuring reliable molecular stratification. This underscores the necessity for high-quality, validated antibodies in elucidating the complex landscape of mucin expression in oncology.
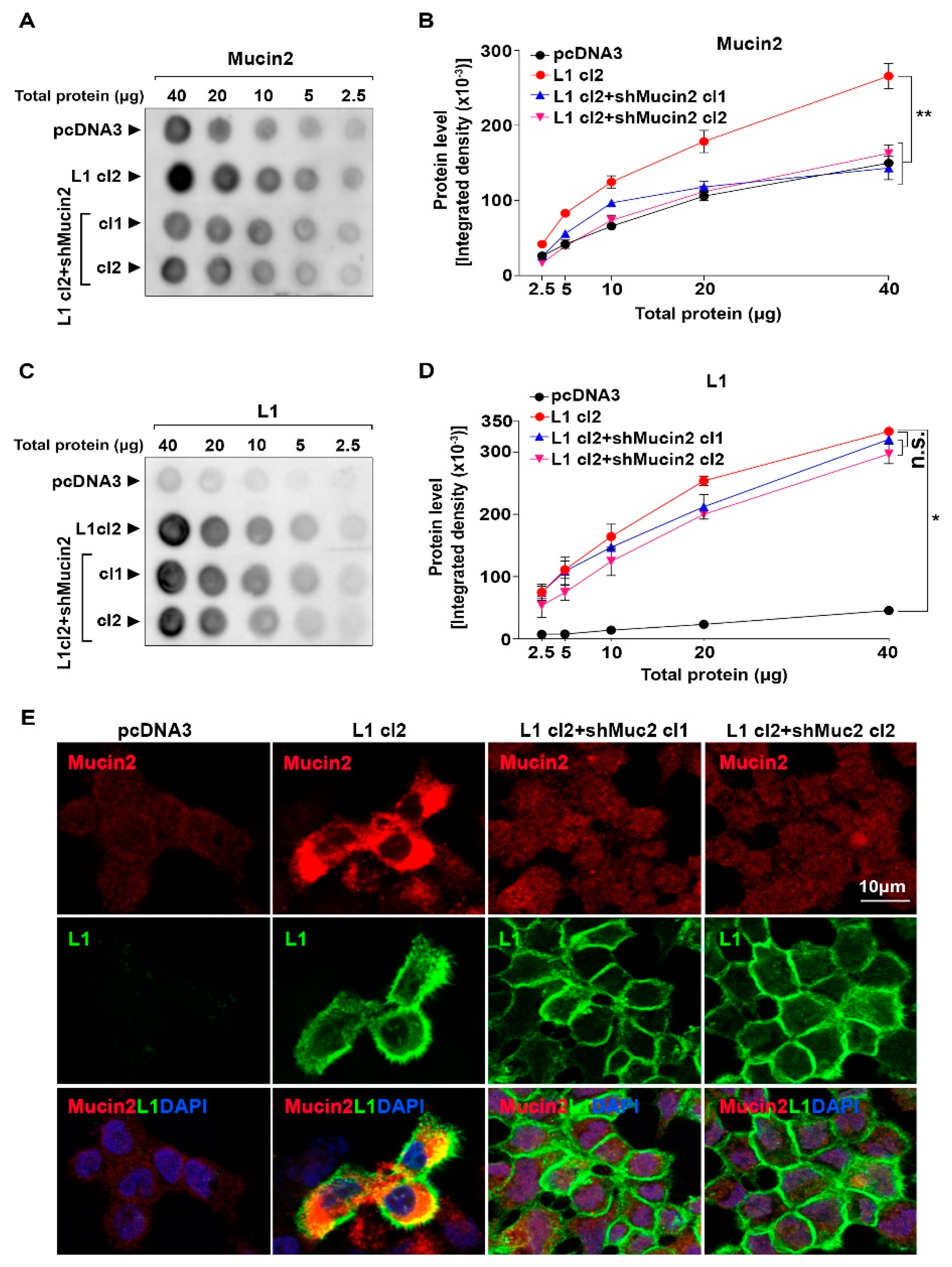 Fig.1 Immunohistochemical Analysis of MUC2 Expression in Colon Cancer.1
Fig.1 Immunohistochemical Analysis of MUC2 Expression in Colon Cancer.1
FAQs
How do you ensure the antibody is specific to MUC2 and not other mucins?
We utilize a unique peptide sequence from the MUC2 VNTR region that is distinct from other mucins like MUC5AC or MUC1. Combined with our glycopeptide screening platform, we select clones that recognize this specific sequence only when it carries the target glycan.
Can you generate antibodies against both the Tn and sTn antigens on MUC2?
Yes. We can synthesize MUC2 glycopeptides carrying various tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TACAs), including Tn, sTn, and T antigens. You can specify the desired glycoform during the project consultation phase.
What species can be used for antibody production?
We offer antibody development in mice (monoclonal), rats, rabbits (polyclonal and monoclonal), and llamas (VHH). Rabbit monoclonal antibodies are particularly recommended for glycopeptide targets due to their high affinity and diversity.
Are these antibodies suitable for use in immunohistochemistry (IHC)?
Yes. IHC is a primary validation method for our anti-MUC2 antibodies. We test them on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) colon cancer tissue arrays to confirm their ability to bind the native antigen in a tissue sample context.
Reference:
- Naama, M., et al. "An Increase in Mucin2 Expression Is Required for Colon Cancer Progression Mediated by L1." Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24.17 (2023): 13418. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713418
Supports
- Anti-MUC1 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC4 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC16 (CA-125) Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC5AC Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC2 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-Podocalyxin (PODXL) Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-CD43 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Custom Glycopeptide Target Antibody Development
