Hematology related Glycan Introduction
Accelerate Your Glycan-Based Discoveries!
Are you currently facing challenges in understanding complex hematological disease mechanisms, identifying novel biomarkers, or developing targeted therapies for blood disorders? Our Glycan in Hematology services at Creative Biolabs help you accelerate research and development, obtain high-quality glycan-related insights, and develop highly specific tools through advanced glycomics and glycobiology techniques.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
Hematology constitutes the medical specialty focused on investigating the etiology, prognosis, management, and prevention of blood-related disorders. Such conditions encompass hemophilia, thrombosis, additional hemorrhagic diseases, and hematologic cancers like leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. Glycans constitute a primary category of fundamental biomolecules, alongside nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. Glycans are categorized into four primary classes: N-linked glycans, O-linked glycans, glycosaminoglycans, and glycosphingolipids. Abnormal glycan biosynthesis manifests in most hematologic cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia, myeloproliferative neoplasms, and multiple myeloma, among others. Comprehensive analysis of aberrant glycosylation patterns will accelerate development of novel, improved treatments for hematological cancers.
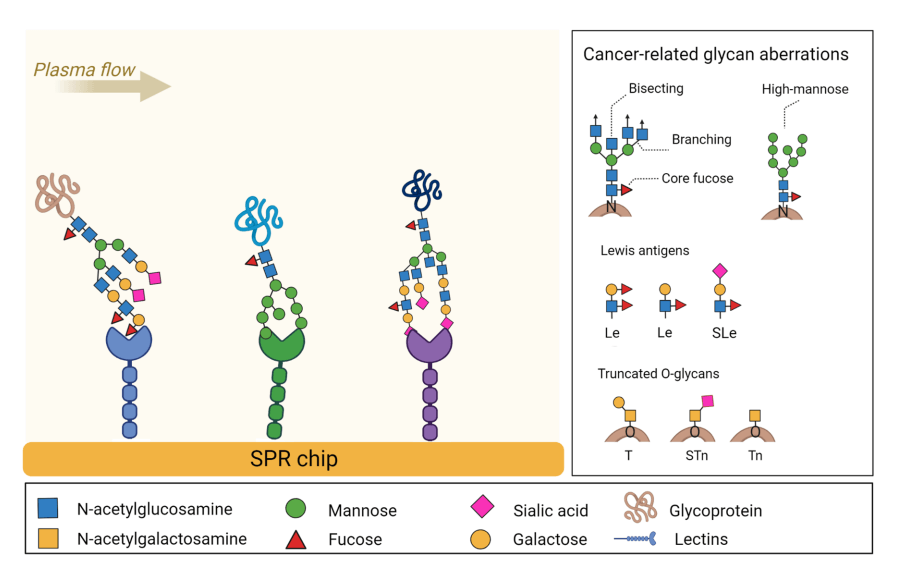 Fig.1 The principle of lectin array for the detection of glycan aberrations in blood plasma.1,3
Fig.1 The principle of lectin array for the detection of glycan aberrations in blood plasma.1,3
The Role of Glycans in Hematology
Selectin Glycoprotein Triggers Sickle Cell Crises
Sickle cell anemia constitutes an inherited hemoglobin disorder causing diverse acute and chronic painful sequelae. Current evidence indicates dysregulated cellular adhesion across multiple lineages represents the primary etiology, partially facilitated by selectins. These single-chain transmembrane glycan-binding proteins exhibit C-type lectin-like properties. Functioning as lectins—adhesion molecules recognizing carbohydrate motifs—selectins bind sugar polymers. Inhibiting selectin activity using natural ligand analogs restores blood flow in murine sickle cell disease models.
Abnormal Glycosylation of Plasma Fibrinogen in Hepatic Pathologies
Plasma fibrinogen is heavily sialylated, with sialic acids participating in calcium binding. Specific inherited fibrinogen defects correlate with modified sialylation of its N-glycans, resulting in impaired clotting function. Hepatoma and other hepatic disease patients exhibit enhanced branching or quantity of fibrinogen N-glycans, elevating total sialic acid levels. Individuals with congenital N-glycan biosynthesis defects may develop thrombotic or hemorrhagic conditions.
Anti-Glycan Autoantibody Triggers Cold Agglutinin Disease
Disease-causing IgM autoantibodies attack erythrocyte-expressed carbohydrate structures, triggering cold agglutinin syndrome. These immunoglobulins primarily bind the "I" antigen (β1-6-linked poly-N-acetyllactosamine) present on erythrocytes. Certain disease subtypes result from antibodies directed against sialylated N-acetyllactosamine structures. Additionally, chronic hemodialysis patients may develop this condition due to anti-sialylated blood group N antigen production.
Tn Polyagglutination Syndrome Pathogenesis
This condition features hematopoietic cells exhibiting Tn antigen (GalNAcα-O-Ser/Thr) and sialyl-Tn (Siaα2-6GalNAcα-O-Ser/Thr), detectable by naturally occurring anti-Tn antibodies prevalent in human sera. The etiology stems from somatic mutations in hematopoietic stem cells, causing functional absence of core-1 β3-galactosyltransferase (T-synthase).
Published Data
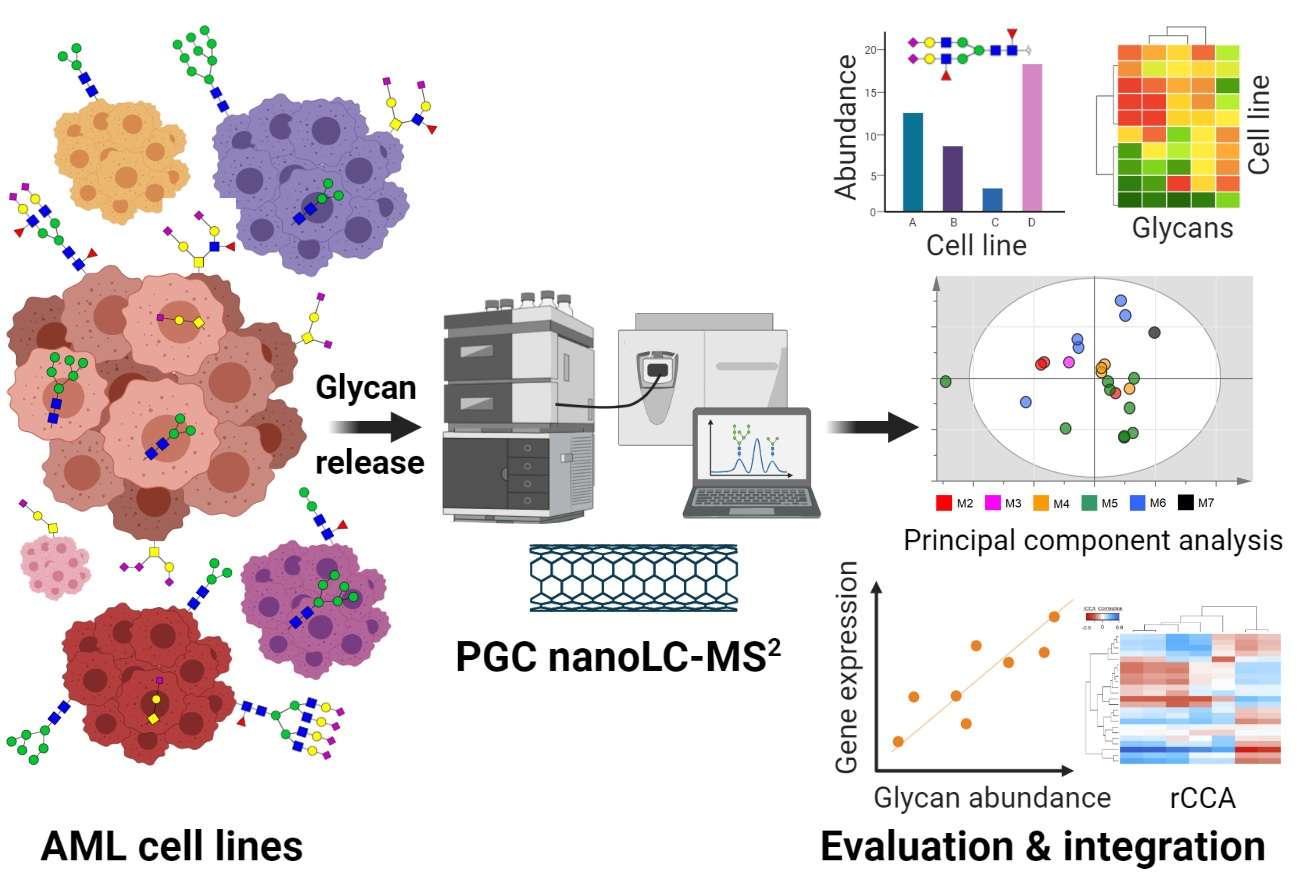 Fig.2 N- and O-glycomic profiling of commonly utilized AML cell lines.2,3
Fig.2 N- and O-glycomic profiling of commonly utilized AML cell lines.2,3
Recent research has significantly advanced our understanding of glycan roles in hematological malignancies. For instance, an integrated N- and O-glycomics study characterized 21 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines using porous graphitized carbon chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (PGC nano-LC-MS2). This comprehensive profiling revealed distinct glycan fingerprints across the AML cell lines, with specific glycan traits correlating with their cellular phenotypes as classified by the FAB system. Transcriptomic integration pinpointed specific glycosyltransferases and hematopoietic transcription factors as potential regulators of these distinctive glycan profiles. The findings highlighted varying expressions of glycan structures, including those previously associated with poor prognosis, providing crucial insights into the regulation of the AML glycan landscape and its potential for diagnostic and therapeutic targeting.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of products and services designed to empower your research and development in Glycan in Hematology:
- Anti-Glycan Antibody Development
- Glycan Profiling and Characterization
- Glycan Biomarker Discovery
- Glyco-Engineering Services
- Custom Glycan Synthesis
Discover the Creative Biolabs Edge – Obtain Your Pricing Now
Why Choose Us?
Choosing Creative Biolabs for your Glycan in Hematology research means partnering with a leader in advanced glycomics. Our distinct advantages ensure your project's success:
- Unrivaled Expertise
- Cutting-Edge Technology
- Comprehensive Solutions
- Customization and Flexibility
- Quality and Reliability
FAQs
Q: How do highly specific anti-glycan antibodies contribute to hematological research?
A: Highly specific anti-glycan antibodies are invaluable reagents for detecting, quantifying, and functionally studying glycans in hematology. These biomolecules enable analytical techniques including flow cytometry, immunohistochemical staining, immunoblotting, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays to distinguish cellular subtypes, profile pathological conditions, or inhibit carbohydrate-dependent binding events, yielding essential insights into pathological processes and druggable molecular targets.
Q: What are the key advantages of specialized glycomics services for hematology research?
A: Specialized glycomics services offer deep expertise in the complex field of glycobiology, combined with advanced analytical platforms. This ensures highly accurate, sensitive, and comprehensive glycan analysis, leading to reliable and biologically meaningful results. Such services can accelerate research by providing customized project designs, rigorous quality control, and in-depth data interpretation.
Q: Can glycan analysis facilitate the identification of novel biomarkers for hematological malignancies?
A: Yes, glycan analysis is a powerful approach for identifying novel glycan biomarkers for specific hematological malignancies. By comparing glycan profiles from healthy and diseased samples, unique glycan signatures associated with various leukemias, lymphomas, or myelomas can be identified. These findings hold significant potential for developing new diagnostic tools or prognostic indicators.
Related Products and Services
To further advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a portfolio of solutions:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Chrastinová, Leona et al. "Linking aberrant glycosylation of plasma glycoproteins with progression of myelodysplastic syndromes: a study based on plasmonic biosensor and lectin array." Scientific reports vol. 13,1 12816. 7 Aug. 2023, DOI:10.1038/s41598-023-39927-4
- Blöchl, Constantin et al. "Integrated N- and O-Glycomics of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cell Lines." Cells vol. 10,11 3058. 6 Nov. 2021, DOI:10.3390/cells10113058
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
