Custom Anti-GalC Antibody Service for Myelin & MS Research
Overview
The human nervous system is an incredibly complex network. It controls everything we do, from breathing to thinking. This network relies on nerve cells, or neurons, to send signals at high speeds. These signals travel along nerve fibers called axons. To work correctly, many axons are wrapped in a fatty layer called the myelin sheath. Myelin acts like insulation on an electrical wire. It prevents the signal from "leaking" and allows it to travel up to 100 times faster. This myelin sheath is the focus of intense medical research. Why? Because in many severe conditions, this insulation is destroyed. This process is called demyelination. When myelin is lost, nerve signals slow down or stop altogether. This leads to the life-altering symptoms of a demyelinating disease, such as multiple sclerosis (MS). At the very center of this research area is a single molecule: Galactocerebroside. This molecule, often called GalC, is a primary building block of myelin. In many diseases, the body's own immune system mistakenly attacks GalC. This attack triggers the destruction of the myelin sheath.
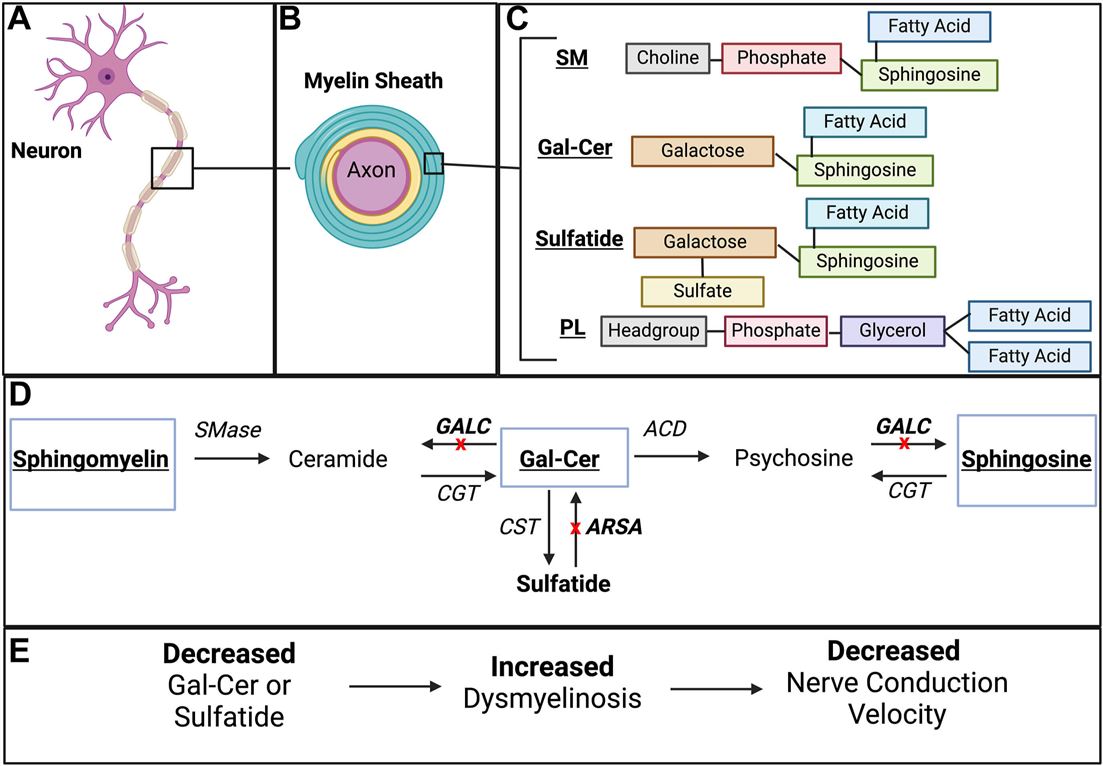 Fig.1 Galactocerebroside in myelin: structure, metabolism, and pathology.1
Fig.1 Galactocerebroside in myelin: structure, metabolism, and pathology.1
To study this process, to understand MS, and to develop new treatments, researchers need high-quality tools. While the most important tool here is a specific anti-GalC antibody, other glycolipids are also critical targets in related diseases. Creative Biolabs' comprehensive Anti-Other Glycolipid Antibody Development service provides the solution researchers urgently need. This platform includes our focused anti-galactocerebroside antibody development service, as well as custom antibody development for other key targets like sulfatide, globoside, and blood group antigens.
Quick Facts: Galactocerebroside (GalC)
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Molecule Type | Glycosphingolipid (a lipid with a sugar) |
| Primary Location | Myelin Sheath |
| Found In | Central Nervous System (CNS) & Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) |
| Producing Cells | Oligodendrocytes (CNS) & Schwann Cells (PNS) |
| Key Functions | Myelin structural stability, axon-glia signaling, and myelin maturation |
Know More about Galactocerebroside
Our Solution: A Service Built for the GalC Challenge
The research bottlenecks are clear. Standard, off-the-shelf tools are not good enough. They lack the specificity, purity, and custom formats needed to answer the most difficult questions about galactocerebroside. This is why we created our custom anti-GalC antibody service. Our service is not a catalog of pre-made products. It is a complete, end-to-end solution designed to overcome the exact challenges you face. We are experts in developing antibodies against complex lipid antigens. We partner with you to design, build, and validate a custom antibody that is perfectly suited for your specific research goal. We solve the three main problems:
- The Antigen Problem: We use proprietary immunization strategies with high-purity galactocerebroside to generate a strong, specific immune response.
- The Specificity Problem: Our development process includes rigorous screening and purification. We guarantee that your antibody binds to GalC and does not cross-react with other similar lipids, like sulfatide.
- The Application Problem: We build the precise tool you need. Whether it's a specific isotype for functional studies (like IgM or IgG3) or an antibody validated for a sensitive application like IHC, we deliver a tool that is ready to work.
What is Galactocerebroside?
To fully appreciate why a specialized, custom antibody is so critical, we must first understand the target. Galactocerebroside is a type of lipid, or fat molecule. Specifically, it is a glycosphingolipid. This means it has a complex head (a sugar) and a fatty tail.
- "Glyco-" means it contains a sugar. In this case, the sugar is galactose.
- "-cerebroside" means it is a lipid found in the brain.
GalC is not just a random molecule. It is one of the most abundant and important lipids in the entire nervous system.
Where is GalC Found?
GalC is found almost exclusively in the myelin sheath. It is a defining feature of the cells that produce myelin. There are two types of myelin-producing cells:
- Oligodendrocytes: These cells are found in the Central Nervous System (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. They wrap axons in the CNS with myelin. GalC is a significant component of this myelin.
- Schwann Cells: These cells are in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), which includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. They wrap peripheral axons with myelin. GalC is also a significant component of this myelin.
In short, GalC is everywhere that myelin is. It is a fundamental part of the nervous system's "insulation."
What is the Function of GalC?
GalC is not just a passive structural filler. It performs several critical jobs that keep the myelin sheath healthy and stable.
- Structural Integrity: GalC molecules are very good at packing tightly together. They interact with other lipids and proteins, helping to hold the many layers of the myelin sheath in a compact, stable structure.
- Axon-Glia Interaction: Myelin must communicate with the axon it wraps. GalC is involved in this signaling. It helps ensure the axon and its myelin sheath are correctly connected and work together.
- Myelin Maturation: GalC is essential for the development of oligodendrocytes. These cells must mature properly before they can create myelin. GalC plays a key role in this maturation process.
- Organizing Membrane Domains: GalC helps organize other essential molecules, like ion channels, at specific points along the axon. This organization is necessary for high-speed signal transmission.
Why is GalC Hard to Study?
Studying galactocerebroside is difficult. The main problem is a lack of precise research tools. Developing good antibodies to GalC faces three major challenges.
Lipids are Poor Antigens
First, lipids are not good antigens. The immune system responds strongly to proteins but weakly to lipids. GalC is a small molecule and is often hidden in cell membranes. It does not easily trigger a strong immune response, which makes creating high-affinity antibodies difficult.
The Problem of Cross-Reactivity
Second, cross-reactivity is a major issue. The nervous system contains many lipids, like sulfatide, that have a similar structure to GalC. Many available anti-GalC antibodies are not specific. They also bind to these other lipids. This non-specific binding leads to false positives and unreliable data.
Antibody Isotype Matters
Third, the antibody type, or isotype, is essential. Different isotypes (like IgM or IgG) cause damage in various ways. To understand a demyelinating disease, researchers must be able to study these specific isotypes. Most standard tools do not provide this capability.
Galactocerebroside & Diseases
GalC and Demyelinating Disease
A demyelinating disease is any condition that results in damage to the myelin sheath. Multiple sclerosis is the most well-known example. In many of these diseases, the problem starts with the immune system. This is called autoimmunity. An autoimmune disease is one where the immune system gets confused and attacks the body's own healthy tissues. For reasons we are still trying to understand, the immune system can learn to see GalC as a foreign invader. It treats this vital molecule as a threat. When the immune system identifies a target, it creates antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that find and tag specific molecules for destruction. In this case, the immune system produces anti-galactocerebroside antibodies. These are also known as galactocerebroside antibodies. This is the central event of the disease. Here is the step-by-step process of the attack:
- Production: Immune cells (B-cells) start producing anti-galactocerebroside antibodies.
- Circulation: These antibodies travel through the bloodstream.
- Binding: The antibodies find their way into the nervous system. They search for and find galactocerebroside molecules on the surface of the myelin sheath.
- Tagging: The antibody binds tightly to the GalC molecule. This binding event is the trigger.
- Destruction: The antibody acts as a flag. It signals to other parts (like the complement system or immune cells) of the immune system to attack this spot.
The result is demyelination. The axon is left exposed, like a live wire without its insulation. Nerve signals can no longer travel properly. This leads directly to the symptoms of a demyelinating disease: weakness, numbness, vision problems, and loss of coordination.
Krabbe Disease: A Different GalC Problem
GalC is also central to another, different type of demyelinating disease: Krabbe disease. Krabbe disease is not an autoimmune condition. It is a genetic (lysosomal storage) disorder. In healthy people, the body has an enzyme that breaks down and recycles old GalC. In Krabbe disease, this enzyme is missing or broken. As a result, galactocerebroside builds up to toxic levels inside cells. This poisonous buildup kills the myelin-producing oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. The result is the same: a catastrophic loss of myelin. Studying Krabbe disease also requires precise tools to track this toxic buildup of GalC.
Our Comprehensive Custom Antibody Platform
We have streamlined the complex process of antibody development into a single, integrated platform. Our team manages every step, from initial design to final validation, ensuring you receive a galc antibody that works for your specific application. Our service is a complete workflow, not just a collection of parts. We provide a full partnership to deliver the exact reagent you need.
Strategic Design & Antigen Preparation
It all starts with a consultation. You tell us your research goal:
- Are you staining brain tissue (IHC)?
- Are you detecting anti-galactocerebroside antibodies in an ELISA?
- Are you blocking a function in live cells?
Based on your goal, our experts design the project. We use high-purity galactocerebroside and our advanced immunization protocols to ensure we generate a high-quality, targeted antibody response.
Advanced Development & Production
We offer a full suite of development platforms. We will recommend the best choice for your project.
- Custom Polyclonal Antibodies (pAbs): Ideal for strong, robust detection in applications like ELISA and Western blotting. We use affinity purification against GalC to ensure the final product is highly specific.
- Custom Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs): The best choice for applications demanding absolute specificity and consistency, such as immunohistochemistry (IHC) and flow cytometry. We find and isolate the single best antibody clone for your needs.
- Recombinant Antibodies (rAbs): This is our most advanced platform, offering complete control. We can produce your antibody on any backbone (mouse, human, rabbit) and in any format (full-size IgG, Fab fragment, etc.). This is essential for isotype-specific functional studies and for developing reliable, renewable assay standards.
Rigorous, Application-Specific Validation
This is the most critical step and is a core part of our service. An antibody is useless if it is not proven to work.
- Guaranteed Specificity: We do not just claim specificity; we prove it. Your custom antibody is tested against a panel of related lipids, including sulfatide, GM1, and ceramide. We provide you with the data that shows your antibody only binds to GalC.
- Application Validation: We validate the antibody in the specific application you need. If you order an antibody for IHC, you will receive a tool that is confirmed to work for IHC, complete with a recommended protocol.
When you partner with us, you receive a complete solution. You get a fully validated, high-specificity galc antibody that is guaranteed to be free of the cross-reactivity issues that hold back research.
Related Services
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Anti-Sulfatide Antibody Development | We create high-specificity custom antibodies for sulfatide, another critical glycolipid in the myelin sheath. |
| Anti-Globoside Antibody Development | This service provides custom antibodies to study globoside, a neutral glycosphingolipid found on various cell membranes. |
| Anti-Blood Group Antigens Antibody Development | We develop specific antibodies against the critical A, B, and H blood group antigens for use in research. |
The study of demyelinating disease is at a critical point. We know the key players, like galactocerebroside and anti-galactocerebroside antibodies. But progress is blocked by a lack of good tools. You cannot afford to waste time, samples, and grant money on unreliable, non-specific antibodies. Our custom anti-GalC antibody service removes that bottleneck. We provide the specialized, high-quality, and fully validated tools you need to ask the hard questions and get clear answers. Stop letting poor reagents define the limits of your research—partner with our team of lipid-antibody experts. Contact us today to discuss your project. Let's build the tool that leads to your next breakthrough.
Reference:
- Luetzen, Matthew A et al. "Purifying selection of the lysosomal enzymes arylsulfatase A and beta-galactocerebrosidase and their evolutionary impact on myelin integrity." Journal of lipid research vol. 66,4 (2025): 100769. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100769
Supports
- Glycolipid
- GM3 Antibody in Cancer Immunotherapy
- GM3 Ganglioside in Disease & Anti-GM3 Antibody Tools
- Engineering High-Affinity scFv for Next-Generation GD2-CAR-T Therapy
- A Simple Guide to CANOMAD Syndrome
- Anti-Glycolipid Antibody Overview
- GM3 Ganglioside Overview
- Sulfatide and Anti-Sulfatide Antibodies Overview
