Anti-MUC5AC Glycopeptide Antibody Development Service
In the rapidly evolving landscape of oncology research, the precise identification of tumor-specific biomarkers remains a cornerstone of diagnostic and therapeutic advancement. Among the myriad of potential targets, Mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) has emerged as a molecule of significant interest, particularly in the context of gastrointestinal and respiratory malignancies. Normally, MUC5AC is a gel-forming mucin expressed by the gastric mucosa and the respiratory tract, where it plays a critical protective role. However, in pathological states, particularly in gastric, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers, MUC5AC undergoes aberrant glycosylation, leading to the expression of unique tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TACAs) on its protein backbone. At Creative Biolabs, we leverage decades of expertise in glyco-immunology to offer a comprehensive Anti-Glycopeptide Antibody Development Service dedicated to the development of high-affinity, high-specificity antibodies targeting these MUC5AC glycopeptide epitopes. Our service is designed to support researchers in unraveling the complexities of mucin biology and developing next-generation tools for precision oncology.
The Biology of MUC5AC and Aberrant Glycosylation
MUC5AC is a large, heavily glycosylated protein belonging to the family of secreted mucins. Its structure is characterized by extensive tandem repeat domains rich in serine and threonine residues, which serve as attachment sites for O-linked glycans. In healthy tissues, these glycan chains are elongated and complex, effectively masking the peptide backbone. However, the process of malignant transformation is frequently accompanied by the dysregulation of the cellular glycosylation machinery. This disruption often results in the premature truncation of glycan chains, leading to the exposure of simple, tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens such as Tn (GalNAc-Ser/Thr), sTn (NeuAc-alpha-2,6-GalNAc-Ser/Thr), and T (Gal-beta-1,3-GalNAc-Ser/Thr) antigens directly on the MUC5AC peptide core.
This phenomenon creates a distinct class of neo-epitopes known as MUC5AC glycopeptides. Unlike the native mucin found in healthy tissues or the generic carbohydrate antigens found on various proteins, these glycopeptides represent a unique molecular signature of cancer cells. For instance, the expression of a tumor specific MUC5AC antibody target is often undetectable in normal pancreatic tissue but is highly upregulated in early pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Similarly, an aberrant glycosylation antibody targeting MUC5AC can distinguish malignant gastric tissue from normal gastric mucosa with remarkable precision. These characteristics make MUC5AC glycopeptides ideal candidates for the development of a gastric cancer MUC5AC antibody or a pancreatic cancer MUC5AC antibody that can serve as a potent tool for tumor detection, prognosis, and potential therapeutic targeting in a research setting.
Challenges in Developing Anti-Glycopeptide Antibodies
Despite the immense potential of MUC5AC glycopeptides as targets, the development of robust antibodies against them is fraught with technical challenges that often stymie standard antibody generation campaigns.
Immune Tolerance and Low Immunogenicity
One of the primary hurdles is the low immunogenicity of carbohydrate antigens. Glycans are typically T-cell independent antigens, meaning they fail to recruit the T-cell help necessary for isotype switching and affinity maturation in B cells. Furthermore, because MUC5AC is a self-antigen expressed in normal tissues (albeit with different glycosylation), the host immune system is often tolerant to the peptide backbone. Breaking this tolerance to generate a high-affinity anti-MUC5AC antibody that specifically recognizes the tumor-associated glycoform requires sophisticated immunogen design and potent adjuvant systems.
Structural Complexity and Cross-Reactivity
Mucins share significant sequence homology. For example, MUC5AC shares structural similarities with MUC5B, another secreted mucin. A standard antibody raised against the peptide portion might cross-react with MUC5B, leading to false positives in lung or salivary research samples. Conversely, an antibody raised against the glycan alone (e.g., anti-sTn) will bind to sTn on any protein, lacking tumor specificity. The goal is to create a glycosylation site specific antibody that recognizes the combined epitope—the specific glycan attached to the specific MUC5AC peptide sequence. This requires precise synthesis of glycopeptide antigens and rigorous screening strategies to filter out binders that recognize only the peptide or only the glycan.
Antigen Presentation and Synthesis
Reproducing the exact tumor glycoform in an immunogen is chemically demanding. Simply mixing peptides and sugars is insufficient. Successful custom glycopeptide antibody development relies on the synthesis of defined glycopeptides where the glycan is covalently linked to the correct serine or threonine residue in the MUC5AC tandem repeat, mimicking the native conformation found on the tumor cell surface.
Our Comprehensive Solution: Anti-MUC5AC Glycopeptide Antibody Development
To overcome these barriers, Creative Biolabs has integrated advanced chemical synthesis, immunology, and high-throughput screening into a seamless service pipeline. We provide a complete solution for researchers seeking to generate novel reagents against MUC5AC glyco-epitopes.
Precision Immunogen Design
We begin by designing and synthesizing custom glycopeptides that replicate the aberrant glycosylation found in your target cancer type. Whether you are interested in a MUC5AC Tn antibody, a MUC5AC sTn antibody, or a target involving the Lewis antigens, we can synthesize MUC5AC tandem repeats carrying these specific structures. These glycopeptides are then conjugated to immunogenic carrier proteins like KLH or BSA to enhance immune response.
Specialized Immunization Protocols
We utilize proprietary adjuvant systems and specialized immunization schedules optimized for glycopeptide antigens. For targets that are highly conserved, we can employ autoimmune mouse strains or knockout mice to overcome tolerance issues. This ensures the generation of a diverse B-cell repertoire capable of producing high-affinity anti-glycopeptide antibodies.
Dual-Screening Strategy
Our screening process is the core of our specificity guarantee. We employ a dual-binding assay strategy. Clones are selected based on their ability to bind the MUC5AC glycopeptide but are counter-screened against the naked MUC5AC peptide and irrelevant proteins carrying the same glycan. This rigorous negative selection removes non-specific binders, isolating only those clones that act as a true tumor specific glyco-epitope antibody.
Validation and Application Testing
We go beyond simple ELISA binding. We validate candidate antibodies using relevant tumor cell lines (e.g., gastric or pancreatic cancer cells) and tissue microarrays. We can verify performance in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and western blotting, ensuring the antibody recognizes the native antigen in a biological context.
Service Workflow
Start Your MUC5AC Project
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
Unrivaled Specificity
Our antibodies distinguish between normal and tumor MUC5AC, and do not cross-react with other mucins like MUC2 or MUC5B.
Versatile Platforms
We offer hybridoma development, phage display, and B-cell sorting to generate full IgG, Fab, or scFv formats.
Deep Expertise
Our scientists have decades of experience in glyco-immunology, ensuring optimal antigen design for your specific needs.
Comprehensive Data
We provide extensive validation data, including glycan array profiles and IHC images, to prove antibody performance.
Published Data
Recent research has validated MUC5AC as a potent target for imaging metastatic pancreatic cancer. In a proof-of-concept study utilizing a patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) model, a fluorescent anti-MUC5AC antibody conjugate (MUC5AC-IR800) was evaluated for its ability to detect liver metastases. As shown in Fig.1, the probe demonstrated exceptional specificity. While the liver metastasis was barely distinguishable under white light (A, B), fluorescence imaging revealed a strong, distinct signal localized specifically to the tumor tissue at the liver edge (A', B'). The study reported a high tumor-to-background ratio (TBR) of 1.787, confirming that the antibody could effectively discriminate between the MUC5AC-expressing tumor and the surrounding normal liver parenchyma.
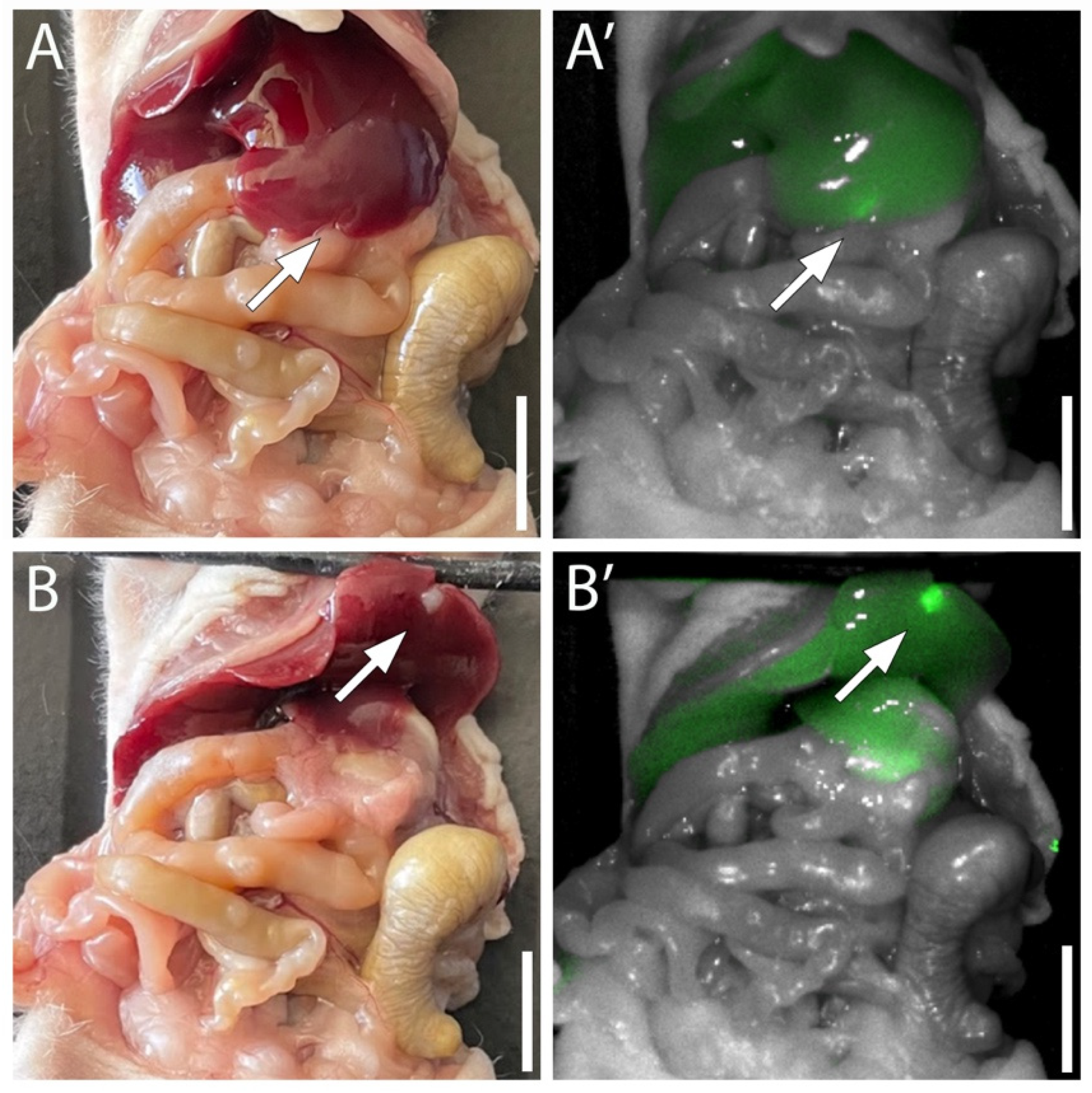 Fig.1 Fluorescence labeling of orthotopic pancreatic cancer liver metastasis by MUC5AC-IR800.1
Fig.1 Fluorescence labeling of orthotopic pancreatic cancer liver metastasis by MUC5AC-IR800.1
FAQs
How does your service distinguish between MUC5AC and MUC5B?
Distinguishing between mucins is critical due to their sequence homology. We achieve specificity by selecting immunogens from unique tandem repeat regions of MUC5AC that are absent in MUC5B. Furthermore, our screening protocol includes a negative selection step where we test candidate antibodies against MUC5B peptides. Only clones that bind MUC5AC but do not cross-react with MUC5B are advanced to the validation stage.
Can you develop antibodies against rare glycoforms like MUC5AC-sTn?
Yes, generating antibodies against specific glycoforms is a core competency of our platform. We chemically synthesize MUC5AC peptides carrying the specific glycan of interest (e.g., sTn, Tn, or Lewis antigens). We then screen for antibodies that require both the specific glycan and the peptide backbone for binding, ensuring the resulting antibody is a true glycosylation site specific antibody.
What types of validation data do you provide?
We provide a comprehensive data package to ensure the antibody meets your requirements. This typically includes ELISA data showing binding affinity, glycan array profiling to demonstrate epitope specificity, and Western blot analysis. Upon request, we can also perform immunohistochemistry (IHC) on relevant tumor tissue microarrays or flow cytometry on specific cancer cell lines to validate performance in biological samples.
Is this service suitable for developing therapeutic candidates?
While our primary deliverables are for research use, the quality and specificity of the antibodies we generate make them excellent candidates for early-stage therapeutic development. We offer antibody engineering services, including humanization and affinity maturation, to support the transition from a research tool to a potential preclinical therapeutic candidate (e.g., for ADC or CAR-T development).
What is the typical timeline for a custom project?
The timeline varies depending on the complexity of the target and the specific services requested. A standard monoclonal antibody development project, from immunogen synthesis to hybridoma screening, typically takes about 4-6 months. We provide a detailed project schedule during the initial consultation and keep you updated with regular progress reports throughout the development process.
Reference:
- Turner, Michael A., et al. "Highly Selective Targeting of Pancreatic Cancer in the Liver with a Near-Infrared Anti-MUC5AC Probe in a PDOX Mouse Model: A Proof-of-Concept Study." Journal of Personalized Medicine 13.5 (2023): 857. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050857
Supports
- Anti-MUC1 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC4 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC16 (CA-125) Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC5AC Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-MUC2 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-Podocalyxin (PODXL) Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Anti-CD43 Glycopeptide Antibody Development
- Custom Glycopeptide Target Antibody Development
