O-Linked Glycan Introduction
Accelerate Your Glycan-Based Discoveries!
Are you currently facing challenges in precisely characterizing complex glycoproteins, understanding their biological roles, or identifying novel biomarkers in the biochemistry and biopharmaceutical field? Our O-Linked Glycan Product and Service helps you accelerate drug discovery and deepen biological insights through advanced mass spectrometry and comprehensive bioinformatics. Creative Biolabs provides the expertise and technology to unravel the intricate world of O-glycosylation, guiding your research to new frontiers.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
O-Linked Glycan
O-Glycosidic modifications predominantly target serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues in polypeptide backbones. O-glycosylated proteins frequently constitute substantial biomolecules exhibiting predominantly biantennary architectures with reduced branching complexity relative to N-glycans. Unlike N-linked modifications, O-glycosidic attachment represents a genuine post-translational modification lacking consensus motifs and requiring no oligosaccharide precursor for protein conjugation. These glycoconjugates exhibit substantial structural diversity, necessitating classification schemes based on core configurations.
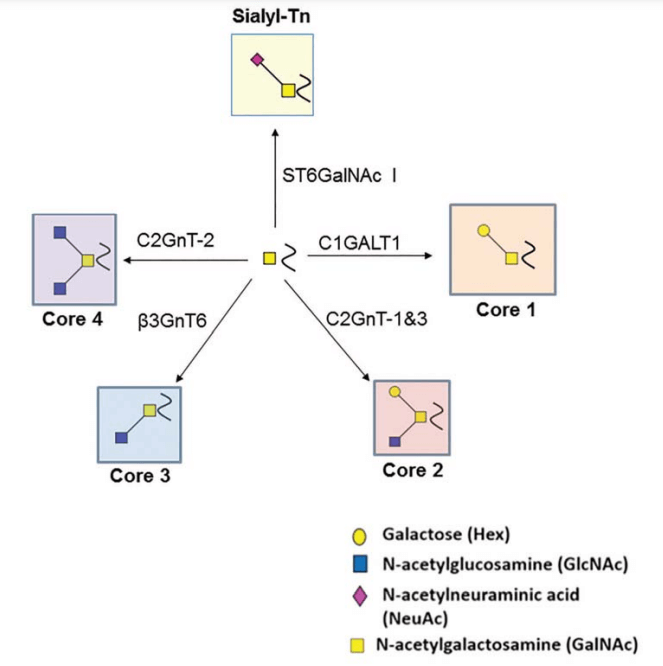 Fig.1 Illustrates enzymatic pathways extending O-glycan structures through biosynthetic enzymes.1,4
Fig.1 Illustrates enzymatic pathways extending O-glycan structures through biosynthetic enzymes.1,4
The predominant O-glycan variant initiates with a GalNAc moiety (Tn antigen), designated mucin-type glycosylation. Alternative O-linked structures feature initial glucosamine, galactose, fucose, mannose, or xylose units anchored to Ser/Thr sites. Recent evidence implicates unmodified O-GlcNAc modifications in phosphorylation interplay and signaling dynamics within cellular environments.
O-Glycosylated structures abound throughout secretory tissues and cell types. They concentrate abundantly within mammalian oocyte zona pellucida matrices, potentially serving as sperm recognition sites. Furthermore, O-glycans mediate hematopoietic regulation, inflammatory processes, and ABO blood group determinant biosynthesis.
O-Linked Glycosylation
Protein glycosylation modifies amino acid side chains through diverse sugar-amino acid linkages. Four types exist: N-glycosylation targets asparagine (Asn) amide groups; O-glycosylation modifies hydroxyl-containing residues including serine (Ser), threonine (Thr), hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine, and tyrosine (Tyr); C-mannosylation occurs at tryptophan (Trp); and S-glycosylation attaches to cysteine (Cys). Among these, N- and O-linked modifications predominate in mammalian proteins, with common O-glycosylated examples being glycophorin, mucin, notch regulators, cell fate determinants, thrombospondin, factor VII, and factor IX.
The predominant O-glycosylation form involves GalNAc transfer to Ser/Thr hydroxyls via O-glycosidic bonds, yielding mucin-type O-glycans (O-GalNAc). Additional O-linked variants occur, among which O-fucose and O-mannose participate in protein folding processes.
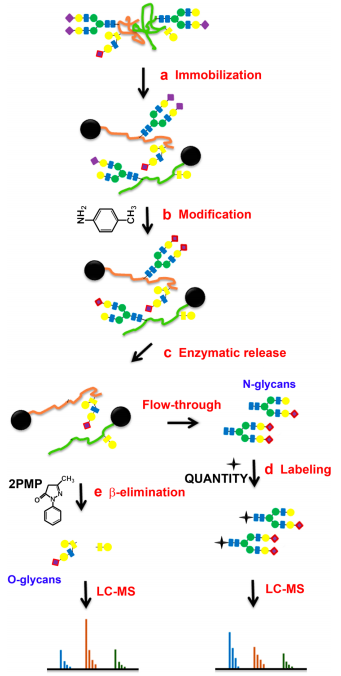 Fig.2 Schematic diagram of sequential releases and analyses of N-linked and O-linked glycans via chemoenzymatic method.2,4
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of sequential releases and analyses of N-linked and O-linked glycans via chemoenzymatic method.2,4
O-Linked Glycosylation Profiling
Simultaneous analysis of O-glycans and N-glycans from glycoproteins is advantageous. Advancing methodologies for this purpose represents a primary focus in glycomics, with glycan cleavage achievable through distinct reactions. N-glycans are enzymatically cleaved from glycoproteins, contrasting with chemical liberation methods for O-glycans.
O-Glycosylation plays crucial roles in biological systems, influencing protein conformation and activity. Nevertheless, structural determination of O-glycans persists as a significant obstacle in proteomic studies. Contemporary mass spectrometry (MS) now provides robust capabilities for high-resolution characterization of O-glycan structures.
Three principal MS-based strategies are employed for mucin-type O-glycan investigation: (a) O-glycan profiling (structural assessment of liberated glycans), (b) a "bottom-up" methodology (analyzing glycopeptides with attached O-glycans), and (c) a "top-down" technique (examining intact glycoproteins with bound glycans). These MS approaches constitute substantial advancements for O-glycosylation research, proving invaluable for comprehensive identification of O-glycan variants, branching architectures, and glycosylation site occupancy.
Published Data
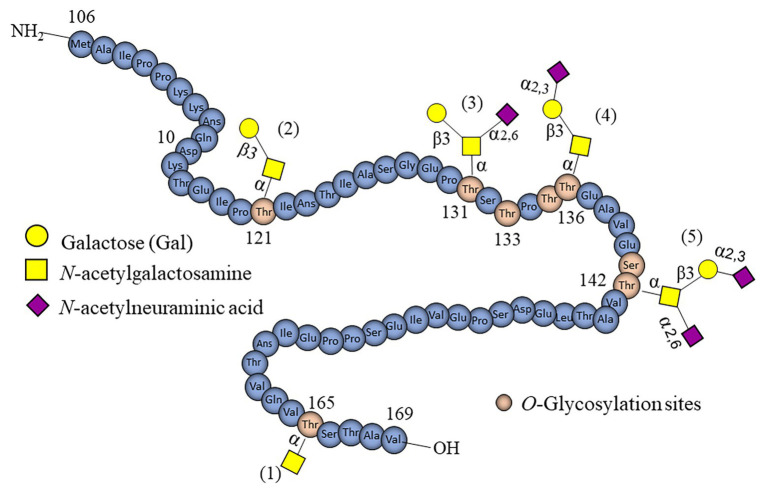 Fig.3 Depicts structural diversity of O-glycans present in casein-derived glycomacropeptide.3,4
Fig.3 Depicts structural diversity of O-glycans present in casein-derived glycomacropeptide.3,4
The study investigated microbial enzymatic processing of mucin-type O-GalNAc glycans in intestinal environments. For instance, Akkermansia muciniphila, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron were shown to possess specialized enzymes crucial for glycan breakdown. Specifically, the study identified the involvement of α-fucosidases and α-sialidases, which target specific sugar linkages. A key finding was the demonstration of endo-α-N-acetylgalactosaminidases, enzymes that directly cleave galacto-N-biose (GNB) from peptide backbones, facilitating access to these O-linked glycans. These experimental results highlight the precise enzymatic machinery gut microbes employ, suggesting that O-linked glycan utilization is a finely tuned process contributing to microbial predominance and subsequent host immune modulation.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing cutting-edge solutions for comprehensive O-linked glycan analysis. Leveraging our deep expertise and state-of-the-art analytical platforms, we offer a suite of services designed to meet the diverse needs of your research and development projects:
- Global O-Glycan Profiling
- Site-Specific O-Glycosylation Analysis
- Comparative O-Glycomics
- O-Glycopeptide Analysis
- O-GlcNAc Profiling
- Custom Glycoengineering Support
Leveraging proven expertise in antibody science, Creative Biolabs delivers premium-grade anti-carbohydrate antibody development services featuring cost-effective solutions. Aided by our state-of-the-art technology and professional scientists, we are able to help global customers produce anti-carbohydrate antibodies, including monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal antibodies.
Discover the Creative Biolabs Advantage—Contact Us to Get a Quote Today
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of glycomics research, offering a distinct advantage in O-linked glycan products and services. Our commitment to scientific rigor, advanced technology, and client success makes us the preferred partner for your most challenging projects.
- Unparalleled Expertise: Our team comprises glycobiology specialists with decades of experience in complex glycan analysis and interpretation, ensuring robust and accurate results.
- Cutting-Edge Mass Spectrometry Platforms: We utilize the latest high-resolution mass spectrometers and advanced fragmentation techniques for comprehensive and precise O-glycan characterization, including isomeric differentiation.
- Customized Analytical Strategies: Recognizing the unique nature of each project, we develop tailored strategies for O-glycan release, separation, and analysis, optimizing for your specific sample type and research goals.
- Comprehensive Data Interpretation: Beyond raw data, we provide in-depth bioinformatics analysis and expert interpretation, translating complex glycomics data into clear, actionable biological insights.
- Site-Specific Resolution: Our methodologies are capable of providing site-specific O-glycosylation information, critical for understanding functional impact and structural roles.
- Quality Assurance: Adherence to stringent quality control measures at every stage ensures the highest data integrity and reproducibility.
FAQs
Here are some common questions prospective clients ask about O-linked glycan product and service:
Q: Why is O-linked glycan analysis more challenging than N-linked glycan analysis?
A: O-linked glycans are inherently more heterogeneous due to the lack of a strict consensus sequence for their attachment, and their biosynthesis is less templated compared to N-linked glycans. This makes their prediction and structural elucidation more complex. Our advanced mass spectrometry techniques and bioinformatics pipelines are specifically optimized to overcome these challenges, providing highly accurate and detailed characterization.
Q: What types of samples can you analyze for O-linked glycans?
A: We are equipped to analyze a wide range of biological samples, including purified proteins, recombinant biotherapeutics, cell lysates, and various biological fluids such as serum, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid. Our experienced team can guide you on optimal sample preparation for your specific project to ensure the best possible results.
Q: How can understanding O-linked glycosylation benefit my drug discovery project?
A: Understanding O-linked glycosylation can reveal critical information about protein function, stability, immunogenicity, and receptor binding. This knowledge is invaluable for target validation, lead optimization, and developing biotherapeutics with improved efficacy and safety profiles. By precisely characterizing O-glycans, you can accelerate your drug development process and reduce costly uncertainties.
Related Products and Services
To advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a comprehensive product portfolio:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
Creative Biolabs offers a series of anti-glycan antibody-related services for worldwide customers. To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Gupta, Rohitesh et al. "A Systematic Review on the Implications of O-linked Glycan Branching and Truncating Enzymes on Cancer Progression and Metastasis." Cells vol. 9,2 446. 14 Feb. 2020, DOI:10.3390/cells9020446.
- Yang, Shuang et al. "Simultaneous analyses of N-linked and O-linked glycans of ovarian cancer cells using solid-phase chemoenzymatic method." Clinical proteomics vol. 14 3. 13 Jan. 2017, DOI:10.1186/s12014-017-9137-1
- González-Morelo, Kevin J et al. "Molecular Insights Into O-Linked Glycan Utilization by Gut Microbes." Frontiers in microbiology vol. 11 591568. 5 Nov. 2020, DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2020.591568
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
