Glycosphingolipids Analysis Service
What Are Glycosphingolipids?
Glycosphingolipids (GSLs) are structurally diverse amphipathic lipids in the outer plasma membrane. They have a ceramide backbone with carbohydrate parts attached. GSLs are rich in lipid rafts, which helps organize membrane areas, control receptor grouping, and assist signal transmission. GSLs are made in the Golgi apparatus. The process starts with glucosylceramide formation, then adds galactose, branched sugars, and terminal residues like sialic acid or fucose. These changes give GSLs unique properties, such as blood group determinants. GSLs do many crucial jobs in the body. They affect insulin receptor signaling, bind to toxins and viruses, and adjust immune responses. Clearly, GSLs play a big role in cell communication, pathogen access, and immune balance. Creative Biolabs offers accurate and reliable glycolipids analysis service, studying GSL structure, function, and interactions. Our advanced methods and expert team ensure detailed insights, helping you understand GSLs better for your research or projects.
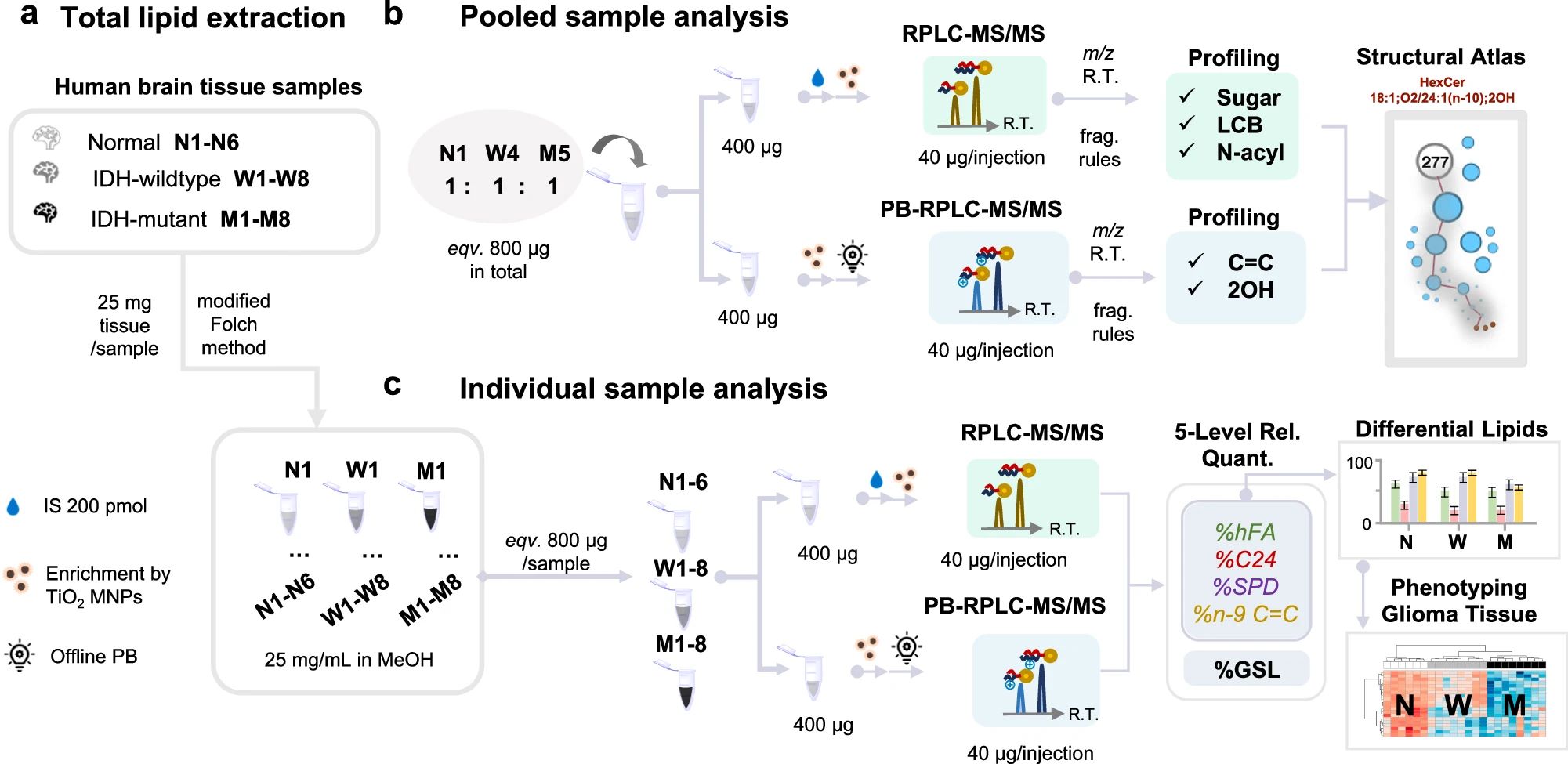 Fig.1 GSLs profiling workflow in human glioma tissue samples.1
Fig.1 GSLs profiling workflow in human glioma tissue samples.1
Structure of Glycosphingolipids
Glycosphingolipids are a subclass of glycolipids where glycan headgroups are attached to a ceramide lipid anchor. GSLs are lipids composed of:
- Ceramide: A sphingosine base amidated with a fatty acid.
- Carbohydrate chain: One or more sugar residues linked to ceramide via a β-glycosidic bond.
Types of Glycosphingolipids
GSLs are structurally categorized by their glycan headgroup and ceramide variation. The major types include neutral glycosphingolipids and acidic glycosphingolipids (gangliosides). The glycan moiety determines the bioactivity and specificity of GSL-protein interactions, including recognition by lectins and toxins.
| Neutral GSLs | No sialic acid; composed of glucose or galactose residues | e.g., Lactosylceramide, Globotriaosylceramide |
| Acidic GSLs (Gangliosides) | Contain one or more sialic acids | e.g., GM1, GM3, GD1a |
Glycosphingolipids in Skin and Skincare
GSLs are abundant in the stratum corneum and contribute to skincare.
- Their ceramide anchor reinforces lipid lamellae integrity.
- GSL metabolism products influence natural moisturizing factor (NMF) levels.
- Some GSLs participate in keratinocyte signaling.
- Topical GSLs or GSL precursors can help restore barrier function in dry or aged skin.
- GM3 and other glycosphingolipids have been proposed as active ingredients in cosmeceuticals for barrier repair.
Blood Group Determinants
Certain GSLs carry terminal sugar motifs identical to ABO blood group antigens:
- Globo-series GSLs like Gb3 and Gb4 can bear blood group determinants.
- Gangliosides can also act as blood group antigens (e.g., GM1 with terminal galactose residues).
GSL Analysis Technologies
Analyzing GSLs is technically demanding due to their hydrophobicity and glycan diversity. To address the analytical complexity of GSLs, Creative Biolabs offers a versatile suite of cutting-edge technologies tailored to distinct research applications. Whether the goal is to define intact GSL structures, quantify disease-associated biomarkers, map lipid distribution in tissues, or explore glycan–protein interactions, our platform integrates validated workflows to ensure accuracy, sensitivity, and biological relevance. The table below outlines recommended analytical approaches based on specific GSL research objectives, enabling clients to select the most appropriate technologies for their experimental needs.
| What to Study | Technologies We Recommend | Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Elucidation (Intact GSLs) | LC-MS/MS (HILIC or Reversed-Phase), UVPD, CID with glycan-specific fragmentation | High-resolution profiling of glycan and ceramide structures |
| Quantitative Biomarker Analysis | LC-MS/MS with MRM or PRM, Stable Isotope-labeled Internal Standards, Permethylation with Differential Labeling | Absolute or relative quantification of disease-associated GSLs |
| Tissue Localization / Spatial Mapping | MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry, LC-MS/MS with regional dissection | Visualization of GSLs in specific anatomical or pathological regions |
| GSL–Protein Interaction Analysis | Glycan Microarray, Lectin-binding Assays, Pull-down Enrichment + LC-MS/MS | Identification of interactions with Siglecs, galectins, antibodies |
| Microbial Toxin or Virus Binding Studies | TLC + Toxin or Lectin Overlay, LC-MS for GSL receptor identification | Determining host GSL receptors for bacterial toxins or viral entry |
| Blood Group Antigen Typing | LC-MS/MS, TLC + Antibody Overlay, Lectin-based Detection | Profiling of ABO, Lewis, and P blood group antigens on GSLs |
Our Analytical Solutions for Glycosphingolipid
Our glycosphingolipid analysis service delivers:
- Ultra-sensitive LC-MS/MS quantitation
- Isomeric and compositional profiling
- Blood group antigen mapping on glycolipids
- Custom GSL-protein interaction studies using glycan arrays
Analyzable Glycosphingolipids
Our platform supports the detection, structural annotation, and quantification of a wide array of glycosphingolipid subclasses across diverse biological matrices. Representative categories include:
| Glycosphingolipid Class | Analyzable Glycosphingolipids Examples |
|---|---|
| Cerebrosides | Glucosylceramide (GlcCer), Galactosylceramide (GalCer) |
| Globosides | Gb3 (CD77), Gb4, Forssman antigen |
| Lactosylceramides | LacCer |
| Gangliosides | GM1, GM2, GM3, GD1a/b, GT1b, GQ1b |
| Sulfatides | SHexCer, SLacCer |
| Fucosylated GSLs | Lewisx, sLex |
| Lyso-GSLs | Lyso-GlcCer, Lyso-Gb3 |
Sample Requirements for Glycosphingolipids Analysis
To ensure accurate structural annotation and quantitative performance, sample integrity and preparation are critical. There are the general requirements based on sample type. We also offer customized extraction services for clients unable to process their samples. Please inquire about compatible buffers and shipping instructions.
| Sample Type | Recommended Amount | Notes & Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | 20–100 mg | Fresh-frozen preferred; snap-freezing in liquid N₂ |
| Cells | ≥1 × 10⁶ cells | Washed pellet in PBS; avoid serum contamination |
| Serum/Plasma | ≥100 µL | Non-hemolyzed; collected in EDTA or heparin tubes |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | ≥200 µL | For ganglioside and sulfatide profiling |
| Urine | ≥1 mL | Early morning or pooled samples for biomarker studies |
| Purified Lipid Extract | ≥50 µg total lipid | Provide extraction protocol if submitting lipid extracts |
Applications in Biomedicine
- Cancer: Altered GSL expression (e.g., GM2, GD3) marks malignant transformation.
- Neurological disorders: Gangliosides are key players in myelin stability and neuroinflammation.
- Infectious disease: GSLs are exploited by viruses and toxins for cell entry.
- Autoimmunity: Anti-GSL antibodies are found in diseases like Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Anti-Glycan Antibody Detection Services
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
- Specializing in glycosphingolipidomics with advanced LC-MS/MS platforms.
- Flexible workflows tailored for complex glycolipid structures.
- High-throughput capacity with strict quality control.
- Expert support from sample prep to data interpretation.
At Creative Biolabs, we are passionate about helping you uncover the structural and functional complexities of glycosphingolipids. With our advanced analytical platforms and deep expertise in glycolipid biology, we support everything from biomarker discovery to therapeutic development. Whether you're working on cancer, neurology, or immunology, we’re here to provide accurate, insightful, and publication-ready data. Contact our team to explore how we can support your next breakthrough.
References:
- Wang, Zidan, et al. "Illuminating the dark space of neutral glycosphingolipidome by selective enrichment and profiling at multi-structural levels." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 5627. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50014-8
- Schindler, Ryan L., et al. "Profiling Intact Glycosphingolipids with Automated Structural Annotation and Quantitation from Human Samples with Nanoflow Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry." Analytical Chemistry 96.15 (2024): 5951-5959. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.4c00077