Glycoglycerolipids Analysis Service
What Are Glycoglycerolipids?
Glycoglycerolipids (GGLs) are a unique class of membrane glycolipids predominantly found in the chloroplast membranes of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Glycoglycerolipids consist of:
- A glycerol backbone,
- One or two sugar residues (commonly galactose or sulfoquinovose),
- Two fatty acyl chains esterified at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Unlike sphingolipids or phospholipids, GGLs comprise a glycerol backbone linked to sugar headgroups and fatty acid chains, contributing both to the structural integrity of thylakoid membranes and to diverse biological functions—including photosynthesis, cellular signaling, immune modulation, and apoptosis. Recent evidence also highlights their potential roles in human health and disease, prompting growing demand for accurate and comprehensive GGL profiling. Creative Biolabs offers a cutting-edge glycoglycerolipids analysis service, enabling the precise characterization of GGLs across a wide spectrum of biological samples. Our platform supports research into plant biology, microbial lipidomics, food science, and biomedical applications, particularly the anticancer potential of specific GGLs.
Major Types of GGLs
These glycolipids are largely localized in the chloroplast thylakoid membrane, accounting for over 70% of the membrane lipid content in photosynthetic organisms.
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Typical Sugar Moiety | Known Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG | Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol | Galactose | Membrane structure, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory |
| DGDG | Digalactosyldiacylglycerol | Di-galactose | Photosynthesis, membrane stabilization |
| SQDG | Sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol | Sulfoquinovose | DNA polymerase inhibition, anti-viral |
Why Analyze Glycoglycerolipids?
- MGDG and DGDG are essential for thylakoid membrane stacking and photosynthetic protein complex stabilization.
- Although not traditionally classified with sphingolipids or cholesterol-based rafts, some glycoglycerolipids have been found in membrane microdomains in bacteria and chloroplast membranes, potentially contributing to localized signaling or metabolite exchange.
- Cyanobacteria-derived GGLs rich in γ-linolenic acid (GLA) have shown apoptotic effects on breast cancer cells, activating caspase pathways without cytotoxicity to normal fibroblasts.
- GGLs in edible plants like spinach, seaweed, and arugula are being studied for their anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities.
Our Analytical Workflow for Glycoglycerolipids
We offer a multi-step analytical platform for comprehensive profiling of glycoglycerolipids, adaptable to various sample types including microbial extracts, plant tissues, purified organelles, and formulated products.
1. Sample Preparation
Optimized extraction using the methyl-tert-butyl ether extraction.
2. Lipid Fractionation
- Normal-phase HPLC or TLC for class-based separation.
- Column chromatography for target GGL isolation.
3. Identification & Structural Analysis
- NMR spectroscopy (1H and 13C) for glycosidic linkages and fatty acid chain configuration.
- MS/MS (LC-MS or MALDI-TOF) to elucidate acyl chain composition and positional isomers.
4. Quantification
- HPLC–UV or ELSD quantification using calibration with purified standards.
- Accurate IC50 estimation in bioactivity assays
Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount | Preparation Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh plant tissue | ≥ 200 mg | Flash-freeze in liquid nitrogen immediately after collection |
| Dried plant material | ≥ 20 mg | Dry completely under vacuum or lyophilization before shipping |
| Cyanobacterial or algal cultures | ≥ 100 mL | Harvest by centrifugation, rinse with PBS or deionized water |
| Lipid extracts | ≥ 100 µg total lipid | Dissolve in chloroform/methanol (2:1 v/v) in amber vials |
| Purified GGL fractions | ≥ 50 µg | Provide solvent type and expected GGL composition if known |
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
- Deep experience in glycolipidomics with tailored protocols for plant, microbial, and synthetic lipid sources
- Proven capability in isolating minor lipid fractions, including chloroplast GGLs and sulfoquinovosyl lipids
- Comprehensive analytical tools include NMR, HPLC–UV/ELSD, LC-MS/MS, and high-resolution mass spectrometry
- Integrated services from structural elucidation to biological validation (e.g., apoptosis, cytotoxicity, IC₅₀ testing)
- Fast turnaround, flexible pricing, and publication-ready reports
- Strict quality control and data reproducibility for regulatory and academic settings
Whether you're investigating chloroplast biogenesis, validating dietary GGL content, or screening anti-proliferative natural products, Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive glycolipid analysis services, including specialized glycoglycerolipid profiling, to accelerate your research. Our end-to-end solutions ensure precision and efficiency across all glycolipid classes. Contact us now to discuss your project and receive a custom quote tailored to your specific needs.
Published Data
A recent in vitro study evaluated the anti-proliferative effect of monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) extracted from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 on breast cancer cell lines. This cyanobacterial MGDG, enriched with γ-linolenic acid (GLA) at the sn-1 position, significantly inhibited cell growth in HER2-positive BT-474 and triple-negative MDA-MB-231 cells. At 60 ng/ml, it induced apoptosis in 70% of BT-474 cells, while 200 ng/ml yielded 58% apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells. Caspase-3/7 activity increased up to 3-fold, confirming caspase-dependent apoptosis. Importantly, the same treatment had negligible cytotoxicity in human dermal fibroblasts, and commercial plant-derived MGDG failed to induce similar effects, highlighting the therapeutic relevance of lipid structure specificity.
NMR is a powerful tool for verifying MGDG isolation. The following figure shows how NMR analysis confirmed the isolation of MGDG from Synechocystis sp. In the experiment, 1H NMR was used to examine the fractions obtained with 40% chloroform and 60% acetone. The NMR peaks of fraction I matched those of a standard MGDG, proving high purity. NMR analysis successfully confirmed the high-purity extraction of MGDG from the cyanobacterial lipid extract.
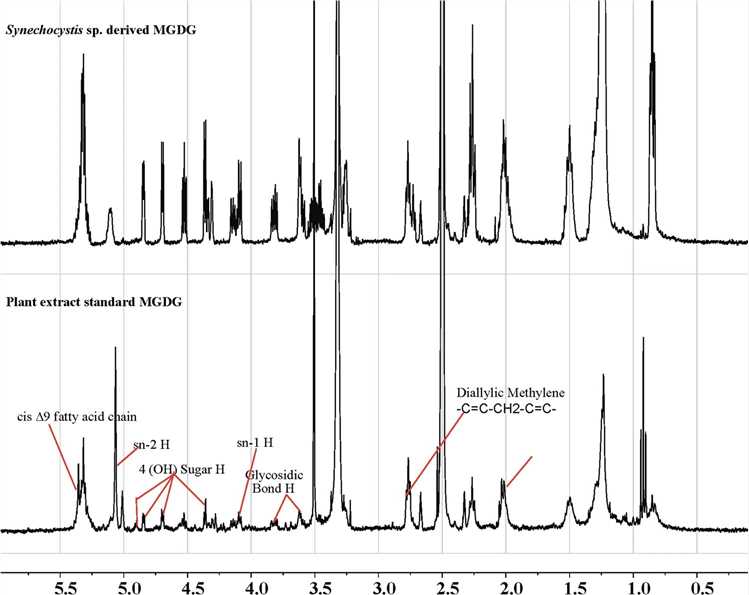 Fig.1 NMR-based structural identification of MGDG.1
Fig.1 NMR-based structural identification of MGDG.1
FAQs
What types of glycoglycerolipids can your platform analyze?
Our platform is optimized to detect and characterize major classes of glycoglycerolipids (GGLs), including monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG), digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG), and sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol (SQDG), across diverse biological sources such as plants, cyanobacteria, algae, and microbial extracts. Structural resolution is achieved at both the glycan and lipid levels.
What are the sample submission requirements for glycoglycerolipid analysis?
We accept a variety of sample types, including:
- Fresh or lyophilized plant tissues
- Algal and cyanobacterial pellets
- Total lipid extracts
- Purified GGL fractions
Recommended quantities and handling instructions are detailed in our Sample Requirements section.
How do you ensure data reproducibility and quality in your analysis reports?
We maintain stringent internal QC protocols:
- Technical triplicates for each sample run
- Internal standards for quantitation and retention time calibration
- Cross-validation with both MS and NMR where needed
- Raw and processed data included in the final report
Upon request, we also provide publication-ready figures and data tables formatted for scientific journals.
Reference:
- Abedin, Muhammad Raisul, and Sutapa Barua. "Isolation and purification of glycoglycerolipids to induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells." Scientific Reports 11.1 (2021): 1298. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80484-x