Anti-Heparan Sulfate (HS) Antibody Development Service
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear, heavily sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) found on the cell surface and in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It plays a pivotal role in regulating physiological processes such as cell signaling, angiogenesis, and viral entry. However, developing high-affinity anti-heparan sulfate antibodies remains a significant challenge due to the complex, heterogeneous nature of HS sulfation patterns and its low immunogenicity. Creative Biolabs leverages decades of expertise in glycan immunology to offer comprehensive services for the development of highly specific anti-HS antibodies, supporting researchers in decoding the "sulfation code" of this intricate molecule. We offer specialized antibody development for this target as part of our broader capabilities in glycosaminoglycan (GAG) research. If you're exploring other GAG-related projects or need reagents for additional targets, our main Anti-Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Antibody Development page provides a full overview of available services to support your glycobiology research.
Introduction to Heparan Sulfate and Its Biological Significance
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) consist of a core protein to which linear HS chains are covalently attached. The HS chain is a polymer of repeating disaccharide units comprising glucuronic acid (GlcA) or iduronic acid (IdoA) and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). The functional diversity of HS arises from extensive enzymatic modifications during biosynthesis, including N-deacetylation/N-sulfation, epimerization of GlcA to IdoA, and O-sulfation at specific positions (2-O, 3-O, and 6-O).
These distinct sulfation motifs serve as high-affinity binding sites for a myriad of ligands, including growth factors (FGF, VEGF), chemokines, morphogens, and viral envelope proteins. Consequently, HS is integral to:
- Tumor Microenvironment: HS remodeling by enzymes like Sulfs and Heparanase regulates tumor growth and cell migration.
- Viral Infection: HS acts as the initial attachment receptor for numerous viruses, including HSV, HPV, and SARS-CoV-2.
- Developmental Biology: HS gradients coordinate morphogen signaling during embryogenesis.
Despite its importance, the availability of reliable reagents is limited. Traditional immunization often yields antibodies with broad cross-reactivity (e.g., reacting with heparin or other GAGs). Our anti-HS antibody development service specifically addresses these hurdles by utilizing advanced phage display and optimized hybridoma technologies to target defined sulfation epitopes for research applications.
Project Workflow
Request a Quote
Comprehensive Anti-HS Antibody Development Services
Creative Biolabs offers a flexible platform tailored to the unique properties of glycosaminoglycans. Our service portfolio includes:
Phage Display Antibody Generation
Phage display is the gold standard for generating anti-glycan antibodies. We utilize vast human scFv/Fab libraries to select binders against specific HS motifs. This method avoids the tolerance mechanisms of the host immune system, allowing for the generation of antibodies against self-antigens found on human tissues.
Custom Hybridoma Development
For clients preferring full-length IgGs or IgMs, we offer optimized immunization protocols using GAG-protein conjugates or cell-surface targets. We employ specialized adjuvants and screening strategies to boost the immune response against the weakly immunogenic carbohydrate chains.
Targeting Specific Sulfation Motifs
We can develop antibodies that discriminate between subtle structural differences, such as:
- N-sulfated domains (GlcNS): Markers of mature HS chains.
- 6-O-sulfated epitopes: Critical for growth factor binding.
- 2-O-sulfated motifs: Often involved in viral attachment.
- Non-sulfated regions (NA domains): Useful for studying HS biosynthesis.
Antibody Engineering & Formatting
Once a binder is identified, we can reformat scFv fragments into full-length human or mouse IgG/IgM for better stability and ease of detection. We also provide biotinylation and fluorophore conjugation services for direct use in flow cytometry or imaging.
Service Highlights
Defined Specificity
Validated against comprehensive glycan arrays to ensure no cross-reactivity with Chondroitin Sulfate (CS), Dermatan Sulfate (DS), or Hyaluronic Acid (HA).
High Affinity
Selection of binders with nanomolar affinity, suitable for detecting low-abundance HS epitopes in complex tissues.
Versatile Applications
Proven performance in IHC, Dot Blot, ELISA, and Flow Cytometry for cancer research and diagnostics.
Custom Formats
Flexible delivery options including scFv, Fab, IgM, IgG, or recombinant formats to fit your assay needs.
Start Your Anti-HS Project
To initiate a project, please provide us with details regarding your target specificity (e.g., broad HS binding vs. specific sulfation motif), intended application, and any preferred host species. Our team will design a customized proposal within 24 hours. We are committed to accelerating your research in oncology, neuroscience, and virology with high-quality GAG-specific antibody tools.
Contact Us to Discuss Your Project
Published Data
In recent years, phage display has emerged as a powerful technology for identifying antibodies against tumor-specific glycoforms. A 2023 study published in Cancers utilized phage display to screen a large human single-chain variable fragment (scFv) library against Multiple Myeloma (MM) cells. The researchers successfully isolated several antibody candidates that specifically recognized a heavily sulfated, MM-associated glycoform of Syndecan-1 (CD138), a major heparan sulfate proteoglycan. As illustrated in Fig.1, flow cytometry analysis confirmed that these phage-display derived antibodies bound strongly to MM cell lines expressing the specific HS sulfation motifs, while showing minimal binding to control cells lacking the target glycan. This data underscores the capability of phage display to generate highly specific reagents for detecting complex, tumor-associated GAG structures, providing valuable tools for researching novel therapeutic targets.
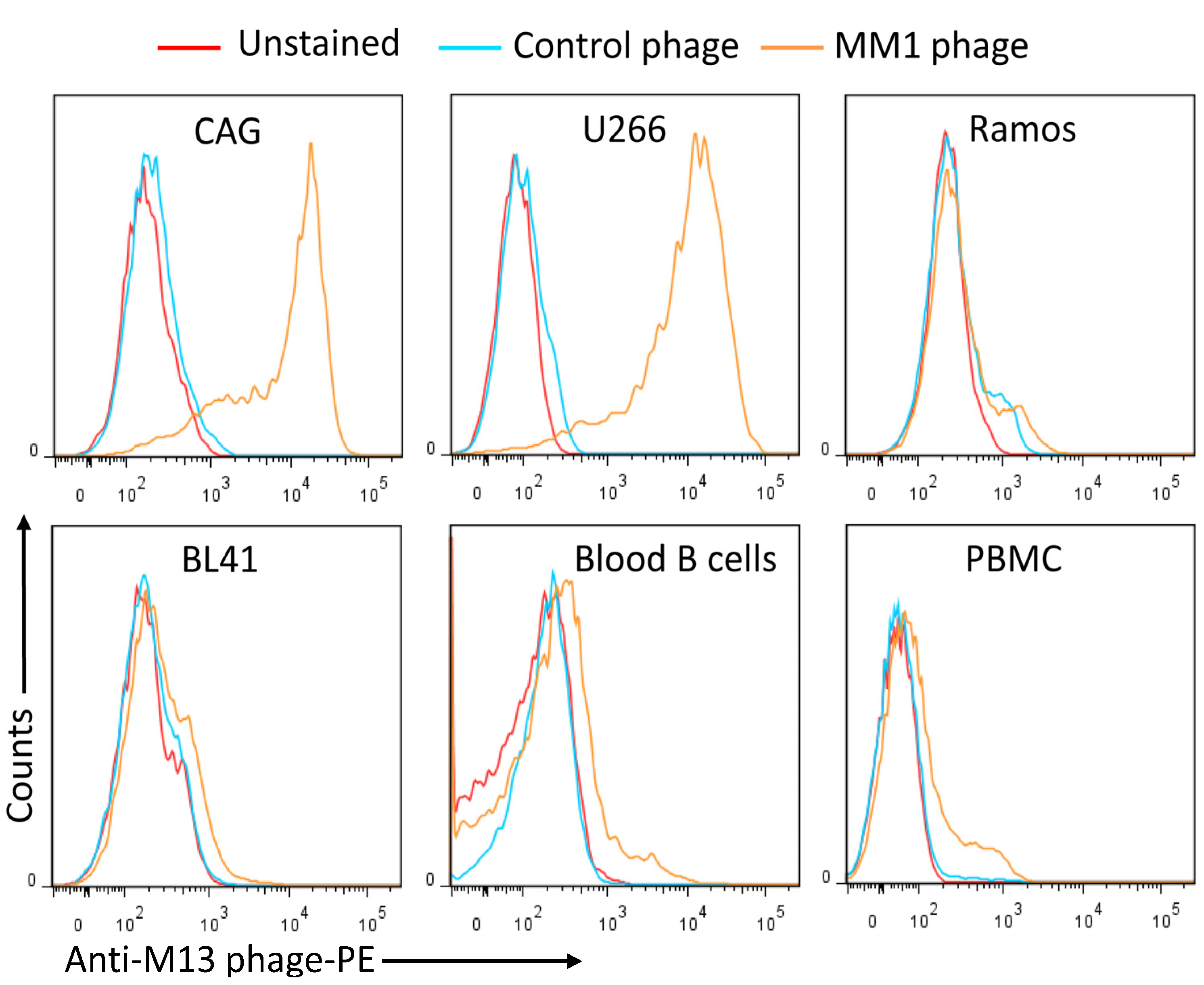 Fig.1
Flow cytometry analysis of anti-HS antibody binding specificity.1
Fig.1
Flow cytometry analysis of anti-HS antibody binding specificity.1
FAQs
How do you ensure the antibody does not cross-react with other GAGs like Chondroitin Sulfate?
We employ a rigorous screening process using a comprehensive GAG glycan array. Positive clones are counter-screened against Chondroitin Sulfate (CS), Dermatan Sulfate (DS), Keratan Sulfate (KS), and Hyaluronic Acid (HA) to ensure that the selected antibody binds exclusively to Heparan Sulfate (HS) epitopes.
Can you generate antibodies against a specific sulfation pattern (e.g., 6-O-sulfated HS)?
Yes. By using defined synthetic oligosaccharides or enzymatically modified HS preparations as immunogens/panning targets, we can enrich for antibodies that specifically recognize distinct sulfation motifs, such as 6-O-sulfated or 2-O-sulfated domains.
What is the advantage of using phage display for anti-HS antibody development?
Phage display allows for the selection of antibodies from vast libraries without relying on an animal's immune system, which is often tolerant to self-antigens like HS. This technology enables the isolation of high-affinity binders against conserved or weakly immunogenic GAG structures that are difficult to target with traditional hybridoma methods.
Do you offer the antibodies in specific formats like IgM or IgG?
Yes. While many anti-glycan antibodies naturally occur as IgMs, we can engineer and reformat the variable regions (scFv) obtained from phage display into full-length IgG (mouse or human) or retain them as IgM, depending on your downstream application needs.
Reference:
- Sioud, M.; Olberg, A. Antibody Surface Profiling Identifies Glycoforms in Multiple Myeloma as Targets for Immunotherapy: From Antibody Derivatives to Mimetic Peptides for Killing Tumor Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 1934. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071934
Supports
- Anti-Heparan Sulfate (HS) Antibody Development Service
- Anti-Chondroitin Sulfate (CS) Antibody Development Service
- Anti-Dermatan Sulfate (DS) Antibody Development Service
- Anti-Keratan Sulfate (KS) Antibody Development Service
- Anti-Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Antibody Development Service
- Anti-GAG Sulfation Motif (Neo-epitope) Antibody Development Service
- Tumor-Associated GAG Antibody Development Service
