Glycosyltransferase & Glycosidase Substrate Microarray
A glycan microarray is a tool that can analyze many different types of glycan structures at once. These arrays allow for the screening of glycosyltransferase and glycosidase specificities. They do this by testing enzyme activities against a large collection of glycan substrates at the same time. At Creative Biolabs, our glycosyltransferase & glycosidase substrate microarray service starts with a detailed discussion to make sure you get the right glycan substrates, enzymes, and conditions for your experiment. We handle all aspects of the process, from preparing the microarrays to enzyme incubation and data analysis, to deliver high-quality, reproducible results.
Background
Glycan Microarrays for Screening Sialyltransferase Specificities
Glycosyltransferases (GTs) are essential enzymes. They attach sugar molecules from activated donors onto larger molecules like proteins or lipids. This action creates glycosidic bonds, which are important for building critical glycans. GTs are very specific. They recognize certain sugars and the molecule being modified. This specificity leads to the amazing structural variety seen in glycans. Scientists divide GTs into different categories based on the sugar they transfer. Some of the main types include sialyltransferases, galactosyltransferases, fucosyltransferases, and glucosyltransferases. They play a key role in keeping cells healthy, helping them communicate with each other, and protecting the body against diseases.
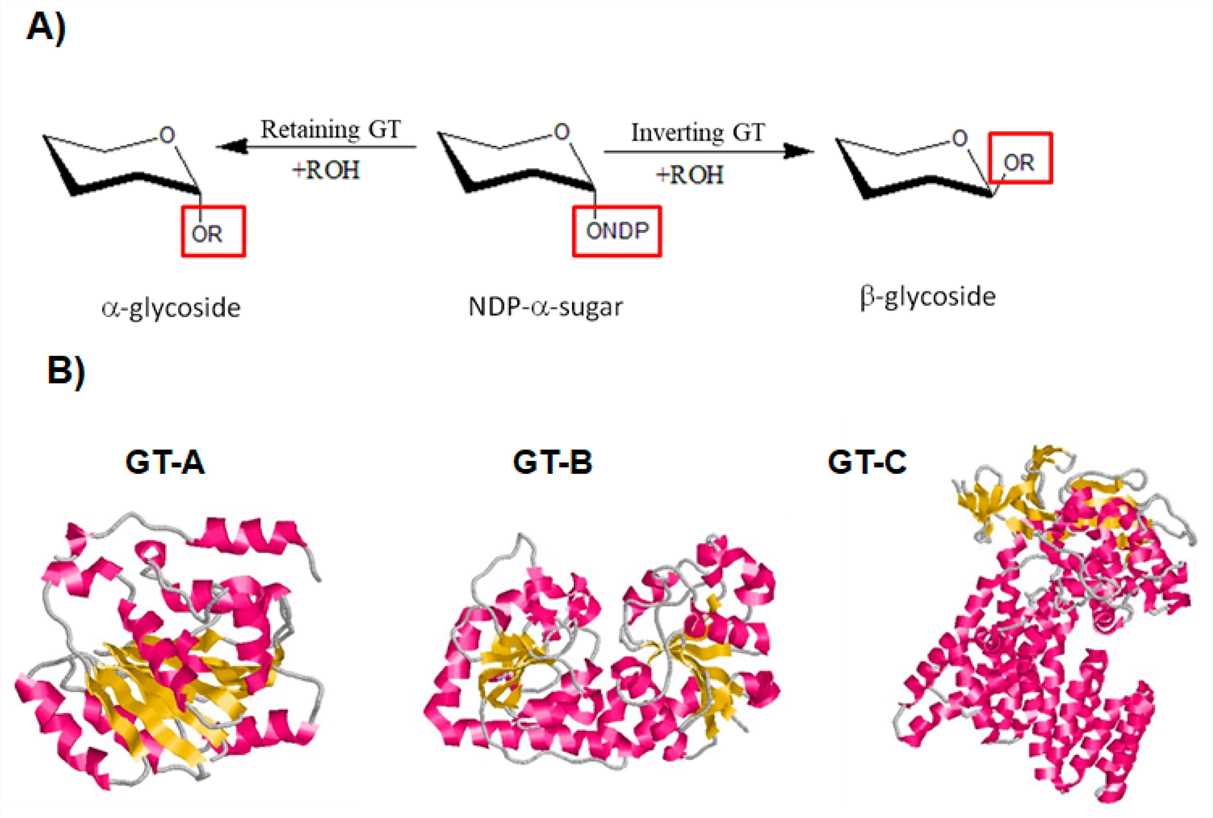 Fig.1 Different types of GTs classified by catalytic mechanisms and 3D structures.1
Fig.1 Different types of GTs classified by catalytic mechanisms and 3D structures.1
Glycan microarrays are a great tool for studying sialyltransferase specificity. These enzymes add sialic acid, which affects how cells interact with each other and the immune system. The microarray technique lets researchers test many potential glycan structures at the same time. For example, we can test a recombinant human α2-6 sialyltransferase. It's put on the array with a biotin-conjugated sialic acid donor. Fluorescently labeled streptavidin then shows where the enzyme has acted. This directly reveals the enzyme's preferences for what it accepts, even spotting new substrates that older methods missed. Glycan microarrays are now vital tools for exploring GT activities.
Screening Glycosidase Specificities Using Glycan Microarrays
Glycosidases (or glycanases) do the opposite of glycosyltransferases. They cleaveglycosidic bonds in glycans. This process breaks down the sugars into simpler forms. These enzymes are vital for recycling glycans and controlling their structure. Glycosidases are enzymes that change how glycans work. They do this by snipping specific sugars, like galactose or sialic acid. This directly impacts how the body responds to pathogens, how cells communicate with each other, and how the body recognizes pathogens. Some of the key types include β-galactosidase, sialidases, and fucosidases. Each one targets different bonds. It's important to note that glycosidases and transferases often balance each other. They work together to manage the creation and removal of glycans in health and disease. This includes things like infections and inflammation. Scientists now use glycan microarrays to quickly test glycosidase activity. For example, a microarray can show exactly which galactose links to the cuts made by β-galactosidase. This clarifies its role in metabolism and identifies targets for therapies.
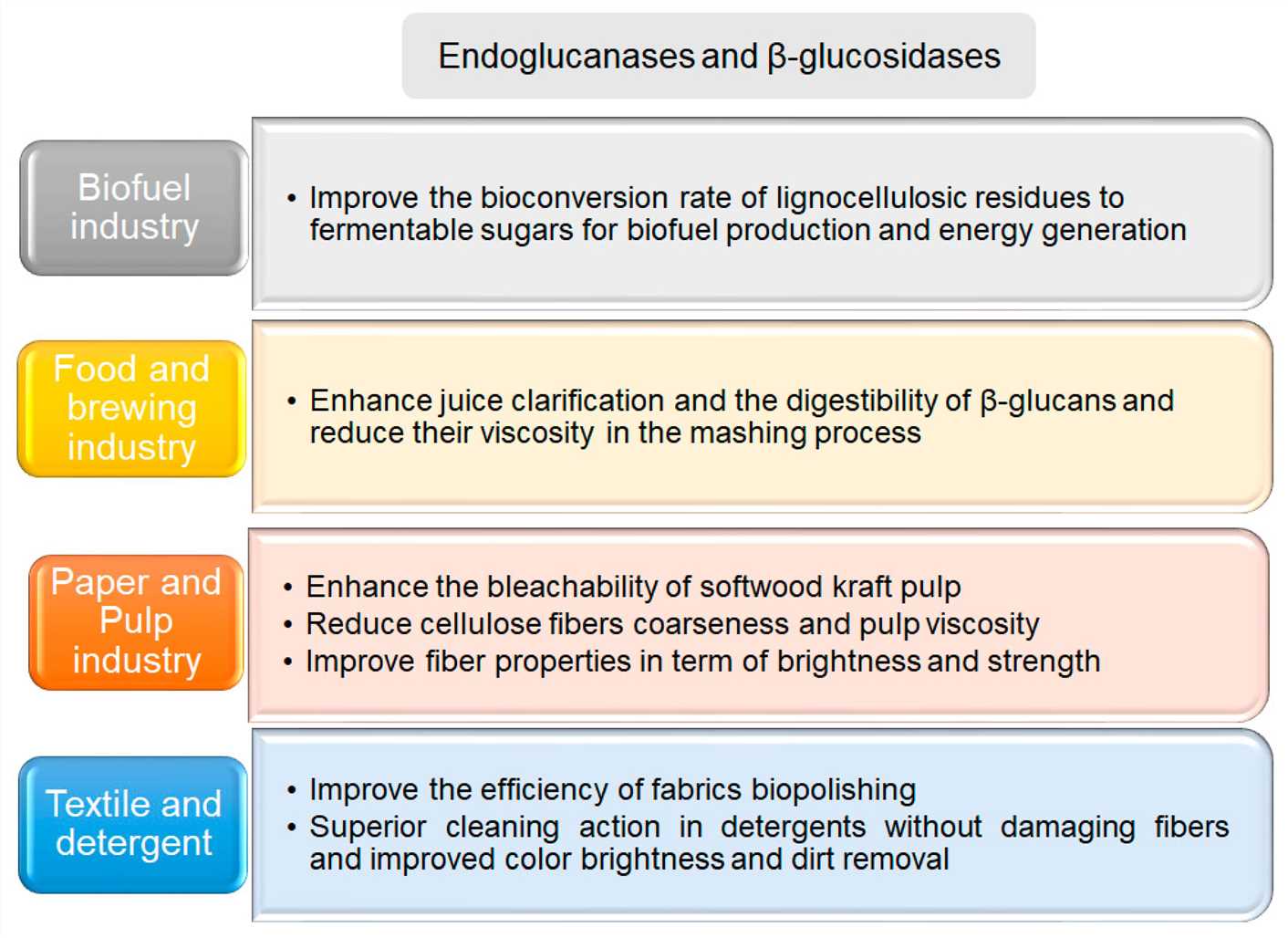 Fig.2 Applications of endoglucanases and β-glucosidases in various industries.1
Fig.2 Applications of endoglucanases and β-glucosidases in various industries.1
Our Service Overview
Step 1: Get the glycan microarray ready
Our team will prepare glycan microarrays with many different types of glycan substrates. These arrays are printed on special glass slides using a method called the NHS method. This method can immobilize glycans (sugars) in a very precise and consistent way. We will make the microarrays to fit your specific research needs. We will include glycans that are important for your enzyme studies.
Step 2: Incubating with enzymes
Recombinant glycosyltransferases or glycosidases will be incubated with their respective donor substrates on the microarray surface. This allows the enzymes to interact with the immobilized glycans. This results in the transfer or hydrolysis of sugar residues, depending on the enzyme type. We provide two methods for detecting enzyme activity: label-based and label-free. This gives you the flexibility to choose the method that best fits your experiment.
Step 3: Detection and analysis
After some time, the products of the reaction are found. For label-based detection, we use biotinylated donor substrates and fluorescent streptavidin conjugates to visualize enzyme activity. For label-free detection, we use special proteins called lectins. These lectins can identify changes to sugar structures. Then, the microarray slides are scanned using special microscopes to take pictures of the fluorescence or lectin binding patterns.
Step 4: Understanding the data
We use special computer programs to study the data and create detailed profiles of how well the enzymes work and what they do. The results provide quantitative data on how the enzymes interact with their substrates, highlighting the preferred substrates and how well the enzymes perform under various conditions. The data can be presented as heatmaps, bar charts, or detailed tables, depending on what you prefer.
Ask for Sample Preparation Tips
Ordering Our Service
To order the glycosyltransferase & glycosidase substrate microarray service, simply contact our customer support team or submit a request via our website. Provide us with details about the glycosyltransferase or glycosidase you wish to study, along with any specific glycan substrates or assay conditions you would like to include. Once we receive your order, our team will work closely with you to ensure the microarray is customized to meet your exact specifications. We will also provide you with the final analysis report, which includes a comprehensive overview of the enzyme-substrate interactions tested.
The glycosyltransferase & glycosidase substrate microarray service from Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive, high-throughput platform for studying glycosyltransferases and glycosidases. By screening of hundreds of glycan substrates simultaneously, our service accelerates enzyme characterization, facilitates enzyme inhibitor discovery, and enhances the understanding of glycan biology in health and disease. Whether you are a researcher in academia or the pharmaceutical industry, our service offers the tools you need to advance your glycosylation research and therapeutic development. For more information or to place an order, contact Creative Biolabs today and take the next step in your glycosylation research.
Reference:
- Amin, Khadija, et al. "Glycoside hydrolases and glycosyltransferases from hyperthermophilic archaea: Insights on their characteristics and applications in biotechnology." Biomolecules 11.11 (2021): 1557. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111557
