Anti-Fungal Glycan Antibody Development Service
The fungal cell wall is a sophisticated, multi-layered armor that is essential for fungal viability, morphogenesis, and protection against environmental stress. Unlike mammalian cells, fungi possess a unique cell wall architecture composed of complex polysaccharides, including beta-glucans, chitin, mannoproteins, and galactomannans. These components are not only critical for structural integrity but also serve as primary pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) recognized by the host innate immune system. Consequently, the fungal cell wall represents an ideal reservoir of targets for the development of diagnostic biomarkers and antifungal therapeutics, such as echinocandins which target beta-1,3-glucan synthase.
However, the structural complexity and dynamic nature of fungal glycans pose significant challenges for research. The inner skeletal layer, primarily composed of a branched beta-1,3-glucan network cross-linked with chitin, is often masked by an outer layer of densely packed mannoproteins in yeasts (e.g., Candida albicans) or alpha-glucans and galactomannans in filamentous fungi (e.g., Aspergillus fumigatus). Understanding the precise organization, masking/unmasking dynamics, and biosynthesis of these glycans requires high-precision research tools.
Creative Biolabs leverages decades of expertise in carbohydrate chemistry and antibody engineering to offer a comprehensive anti-fungal glycan antibody development service. We provide researchers with high-affinity, linkage-specific antibodies capable of differentiating subtle structural variations in fungal cell wall components, supporting advanced studies in fungal biology, drug mechanism of action, and biomarker discovery.
Challenges in Fungal Glycan Immunology
Weak Immunogenicity
Fungal polysaccharides are T-cell independent antigens. Traditional immunization typically elicits only low-affinity IgM responses without memory B-cell formation, making the generation of high-affinity IgG antibodies difficult.
Structural Similarity
Many fungal glycans share repeating units. For example, distinguishing between a linear beta-1,3-glucan backbone and a beta-1,6-glucan side chain requires antibodies with exquisite epitope specificity to avoid cross-reactivity.
Epitope Masking
In intact cells, key structural components like beta-glucan are often "masked" by the outer mannan layer. Antibodies must be validated to recognize both exposed epitopes in mutants/drug-treated cells and native structures.
Contamination Risks
Commercially available polyclonal sera are often contaminated with antibodies against other cell wall components (e.g., anti-mannan antibodies in an anti-glucan preparation), leading to confounding experimental results.
Comprehensive Anti-Fungal Glycan Antibody Services
We address these pain points through a rigorous development platform that combines precise antigen design with high-throughput screening. Our service portfolio covers the major structural and antigenic components of the fungal cell wall.
Anti-Beta-Glucan Antibody Development
Beta-glucans constitute the core skeletal framework of the fungal cell wall. The biological function and immunogenicity of beta-glucans are heavily dependent on their linkage type. We offer the development of antibodies that specifically recognize:
- beta-1,3-glucan antibody: Targets the linear backbone, essential for visualizing the main structural scaffold.
- beta-1,6-glucan antibody: Targets the side chains that often serve as attachment points for GPI-anchored proteins.
- beta-1,3-1,6-glucan branching point antibody: Specialized for detecting the cross-linking nodes critical for cell wall rigidity.
These reagents are invaluable for studying the "unmasking" phenomenon, where antifungal treatment exposes the inner beta-glucan layer to immune recognition.
Anti-Chitin Antibody Development
Chitin, a linear polymer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) linked by beta-1,4 bonds, forms the crystalline microfibrils that provide tensile strength to the cell wall. While chitin is found in many organisms, fungal chitin is often uniquely cross-linked to glucans. Our anti-chitin antibody development focuses on generating reagents that can bind to crystalline chitin in the fungal bud neck (septum) and the lateral cell wall. These antibodies are essential for researching cytokinesis, cell separation, and the compensatory upregulation of chitin synthesis in response to cell wall stress.
Anti-Mannan and Mannoprotein Antibody Development
The outer layer of yeast cell walls is enriched with mannoproteins modified by extensive N-linked and O-linked mannosylation. These structures are the first point of contact with the host. We provide:
- Anti-N-linked mannan antibody: Targeting the alpha-1,6-mannose backbone or alpha-1,2/alpha-1,3-mannose side chains.
- Anti-O-linked mannan antibody: Targeting short linear mannose chains attached to serine/threonine residues.
- Phosphomannan antibody: Recognizing the charged phosphodiester bridges crucial for cell wall porosity and antigenicity.
Aspergillus Galactomannan Antibody Development
Invasive Aspergillosis is characterized by the release of galactomannan (GM) into the bloodstream. This molecule contains a mannan backbone with beta-1,5-galactofuranose side chains—a sugar ring form absent in humans. We develop high-affinity monoclonal aspergillus fumigatus antibody clones specifically against the galactofuranose epitopes. These antibodies are optimized for sandwich ELISA and Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) formats, supporting the creation of sensitive research-grade diagnostic kits.
Cryptococcus GXM Antibody Development
The virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans is largely governed by its polysaccharide capsule, primarily composed of Glucuronoxylomannan (GXM). The capsule structure is highly dynamic and varies between serotypes. We offer custom generation of GXM antibody and glucuronoxylomannan antibody reagents capable of differentiating between serotypes (A, B, C, D) or recognizing conserved structural motifs. These antibodies are widely used to visualize capsule growth (quellung reaction), study capsule shedding, and detect cryptococcal antigen (CrAg) in biological fluids.
Workflow for Anti-Fungal Glycan Antibody Generation
Get a Quote for Anti-Fungal Glycan Antibody Development
Applications in Fungal Research
Our linkage-specific antibodies enable a wide variety of experimental approaches:
Cell Wall Architecture Imaging
Using immunofluorescence microscopy, researchers can use our antibodies to map the spatial distribution of cell wall components. For example, a beta-1,3-glucan antibody can reveal the exposure of the inner cell wall at the bud scar, while a mannan antibody stains the outer periphery. This is crucial for phenotyping cell wall mutants.
Drug Mechanism of Action Studies
Antifungal drugs like Caspofungin (an echinocandin) inhibit beta-glucan synthesis, leading to cell wall stress and remodeling. Our antibodies allow researchers to quantify the "unmasking" of beta-glucan and chitin that occurs as a compensatory response, providing a direct readout of drug efficacy and cellular response pathways.
Biomarker Discovery and Validation
Circulating fungal glycans (like galactomannan and (1,3)-beta-D-glucan) are key markers for invasive fungal disease. Our high-affinity monoclonal antibodies are ideal for developing and validating sandwich ELISAs to detect these antigens in serum or BAL fluid models in animals.
Why Choose Our Linkage-Specific Antibodies?
Precise Epitope Definition
We use defined synthetic oligosaccharides as immunogens to ensure antibodies target specific linkages without cross-reacting to similar structures.
High Affinity
Through proprietary adjuvant technologies and optimized immunization protocols, we overcome weak immunogenicity to produce high-affinity IgG antibodies.
Validated Performance
Antibodies are validated using glycan arrays and fungal cell models to ensure they work in real biological contexts, not just against synthetic antigens.
Custom Engineering
We offer format switching (e.g., IgM to IgG), chimerization, and conjugation services to adapt the antibody to your specific assay platform.
How to Start Your Project
Starting a collaboration with us is simple. Contact our team with your target of interest—whether it is a specific fungal species like Aspergillus fumigatus or a conserved structure like beta-glucan. Our scientists will work with you to design a custom antibody development plan that meets your specific research needs and timelines.
Inquire Now
Published Data
A study demonstrated the feasibility and utility of generating monoclonal antibodies against complex fungal carbohydrates.
In this research, investigators addressed the need for specific diagnostic reagents for invasive aspergillosis. They synthesized a pentasaccharide mimic of Aspergillus galactomannan containing the immunodominant beta-1,5-galactofuranose side chains. By using this defined antigen for immunization and screening, they successfully isolated monoclonal antibodies (clones 7B8 and 8G4) that specifically bound to the galactofuranose residues. Crucially, the study employed glycan microarray technology to map the fine specificity of these antibodies, showing that they could distinguish between the full-length pentasaccharide and smaller trisaccharide fragments. This level of discrimination is vital for avoiding cross-reactivity with other environmental glycans and ensures high specificity in diagnostic assays. The figure below illustrates the specificity profile of these antibodies, confirming their selective binding to the fungal-specific galactomannan structure.
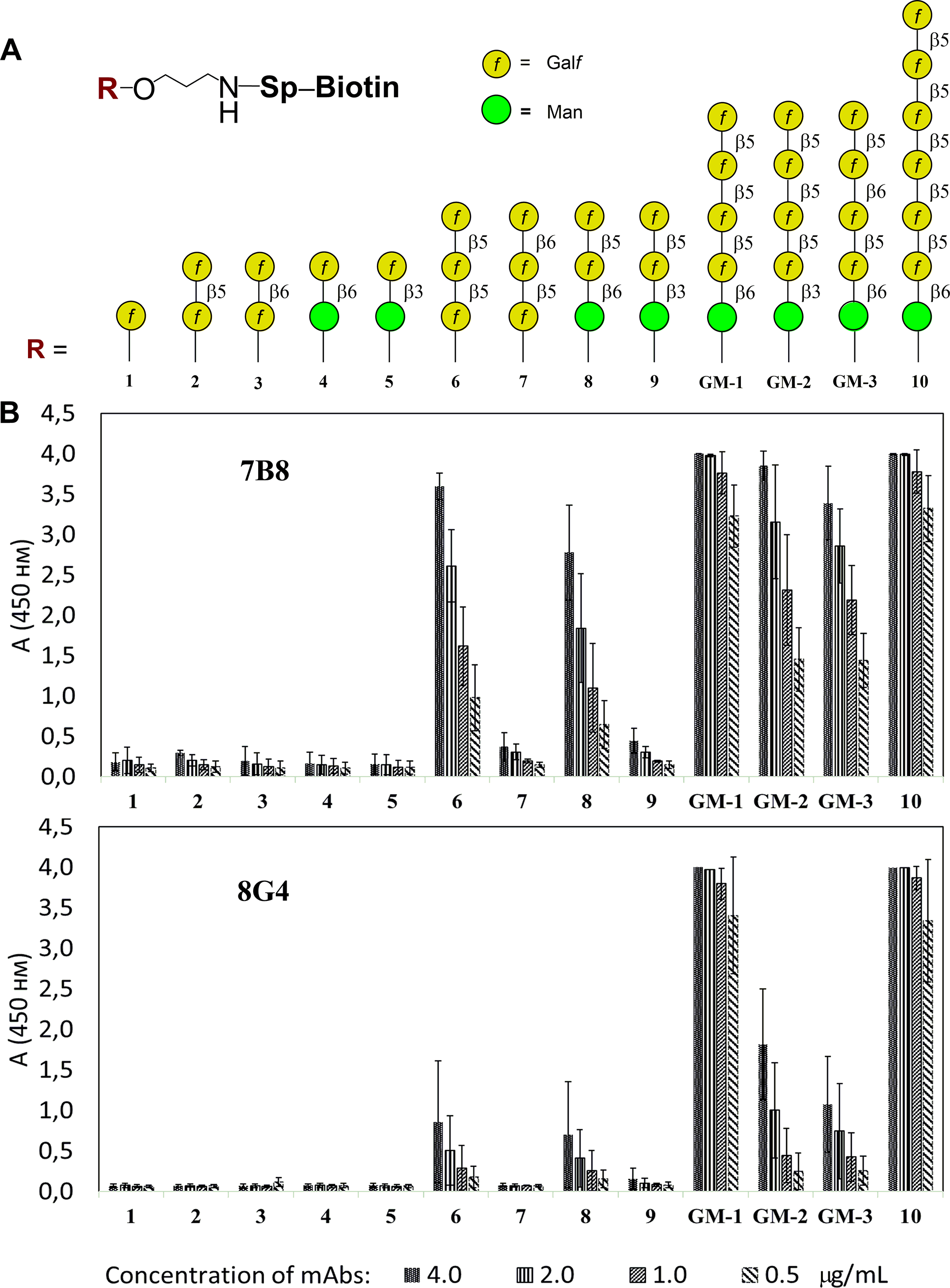 Fig.1 Investigation of oligosaccharide specificity of mAbs 7B8 and 8G4 using ELISA.1
Fig.1 Investigation of oligosaccharide specificity of mAbs 7B8 and 8G4 using ELISA.1
FAQs
Can you distinguish between beta-1,3 and beta-1,6 glucans?
Yes. By using defined synthetic oligosaccharides as immunogens and employing a rigorous counter-selection strategy during screening, we can isolate clones that bind exclusively to the beta-1,3 or beta-1,6 linkage, minimizing cross-reactivity.
Do your antibodies work on live fungal cells?
Many of our antibodies are validated for flow cytometry and immunofluorescence on live or fixed fungal cells. However, accessibility depends on the cell wall architecture; some inner layer targets (like chitin) may require permeabilization or unmasking treatments to be accessible.
Are these antibodies suitable for diagnostic development?
Our antibodies are developed as Research Use Only (RUO) reagents. However, they are manufactured with high quality and consistency, making them excellent candidates for the early-stage research and development of diagnostic assays (e.g., LFA, ELISA).
What formats can you provide?
We can provide full-length IgG, IgM, or recombinant fragments (scFv, Fab). For carbohydrate targets, IgM is common, but we can also engineer class-switched IgG variants for easier handling and detection.
Reference:
- Matveev, Artem L., et al. "Novel mouse monoclonal antibodies specifically recognize Aspergillus fumigatus galactomannan." PLOS ONE 13.3 (2018): e0193938. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193938
