GlycoRNA Insights: Latest Research and Applications
What is GlycoRNA?
In the rapidly advancing field of molecular biology, GlycoRNA (glycoconjugated RNA; often written glycorna) has emerged as a significant area of research with great potential. GlycoRNAs represent a class of RNA molecules modified with sugar residues, contributing to a wide array of cellular functions, including immune response modulation, cell signaling, and the regulation of gene expression. GlycoRNAs were first reported in 2021 as small non-coding RNAs bearing sialylated N-glycans that localize predominantly to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. The discovery suggested RNAs can form a third scaffold for glycosylation (beyond proteins and lipids) and bind Siglec receptors implicated in immune regulation. Subsequent work refined the chemistry: the modified nucleoside acp³U (3-amino-3-carboxypropyl-uridine) is an attachment site for N-glycans on RNA; detection leveraged rPAL (RNA-optimized periodate oxidation and aldehyde ligation) with mass spectrometry to read out native glycoRNA linkages.
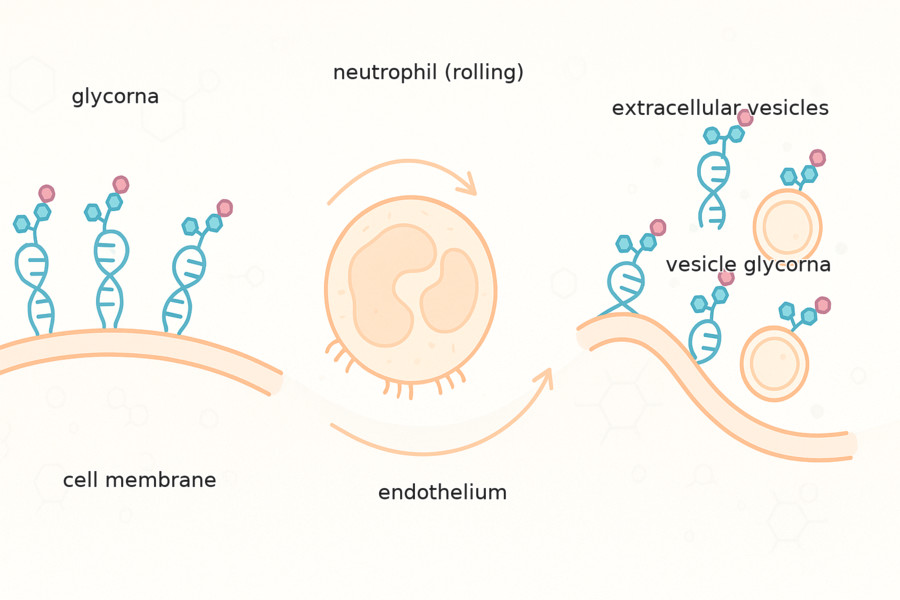 Fig.1 GlycoRNA-mediated neutrophil interaction and vesicle signaling.
Fig.1 GlycoRNA-mediated neutrophil interaction and vesicle signaling.
GlycoRNA Latest Research
The field of glycoRNAs began in 2021 with the foundational discovery that these sugar-coated RNAs exist on cell surfaces, which really kicked off the research effort. By 2024, scientists started figuring out their function. A key study revealed that glycoRNAs are crucial for attracting immune cells (neutrophils) to where they're needed, likely by interacting with a protein called P-selectin. That same year, a new imaging tool called ARPLA was developed, allowing researchers to actually see where glycoRNAs are located. 2025 saw even more progress. A technique known as drFRET enabled the detection of glycoRNAs on tiny particles in biofluids, opening the door for potential use in diagnostics. As the field grew, researchers began connecting glycoRNAs to broader areas like cancer and immune regulation. However, an important preprint also emerged, cautioning that some results could be skewed by contaminating glycoproteins, highlighting the need for extremely careful lab work.
| Objective | Recommended Approach | Recommended Services |
|---|---|---|
| Localize glycoRNAs | ARPLA, spatially resolved detection | GlycoRNA Imaging Service |
| Profile EV glycoRNAs | drFRET for small extracellular vesicle detection/quantification | GlycoRNA Profiling Service |
| Couple identity to function | rPAL/drFRET integrated with small RNA-seq to link composition and phenotype | GlycoRNA Functional Analysis Service |
GlycoRNA in Cancer1
One of the most exciting areas of research for glycorna is its role in cancer. Glycosylation is a well-known mechanism in cancer biology, with altered glycosylation patterns often correlating with tumor progression and metastasis. GlycoRNA may be a key player in these processes. Recent studies suggest that glycorna cancer may serve as a biomarker for early cancer detection or as a potential target for novel therapeutic interventions. Cancer cells are known to have altered glycosylation patterns, and glycorna molecules could be part of these changes, influencing the tumor microenvironment, cell-cell communication, and immune system evasion. Research has shown that glycorna cell modifications could impact the behavior of tumor-associated cells, such as cancer stem cells, which are notorious for their resistance to conventional therapies. By targeting glycorna cancer pathways, researchers hope to develop more effective, precision-based cancer therapies that can specifically target these modified molecules, potentially enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
| Study | Findings | Impact on Cancer Research |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer Glycosylation Study (2023) | Altered glycorna glycosylation in breast cancer cells. | Potential for glycorna cancer as a biomarker for early detection. |
| Tumor Microenvironment Research (2022) | Glycorna modifications in immune cells correlate with tumor progression. | Targeting glycorna could disrupt cancer cell communication and metastasis. |
| GlycoRNA and Cancer Stem Cells (2021) | Glycorna cell changes observed in cancer stem cells resistant to therapy. | GlycoRNA-targeted therapies could reduce resistance and improve treatment efficacy. |
GlycoRNA and Immune Function
Another crucial application of glycorna is its involvement in immune system regulation, particularly in neutrophils. Neutrophils are the first line of defense in the immune system, responding quickly to infections and tissue damage. Recent studies have uncovered a fascinating link between glycorna neutrophils and their ability to modulate immune responses. In glycorna neutrophils, glycosylation changes can alter the function of these cells, influencing their migration to infection sites, activation, and the secretion of cytokines. Understanding the glycosylation patterns of RNA in neutrophils could lead to more targeted approaches in treating autoimmune diseases and inflammatory conditions. The glycosylation of RNA molecules within neutrophils can also impact their ability to communicate with other immune cells, potentially enhancing or suppressing inflammatory responses. Targeting glycorna neutrophils could, therefore, provide new therapeutic avenues for controlling chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders.
| Research Area | GlycoRNA Findings | Potential Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil Migration | Altered glycosylation patterns in neutrophils impact their movement. | Targeting glycorna neutrophils could improve wound healing and infection response. |
| Immune Response Modulation | Glycorna neutrophils can influence the activation of other immune cells. | New treatments for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. |
| Cytokine Secretion | Changes in glycorna glycosylation affect cytokine release in neutrophils. | Targeting glycorna may modulate inflammatory responses. |
Service Spotlight—Integrate GlycoRNA into Your Pipeline
To translate insights into reproducible data, Creative Biolabs offers an end-to-end GlycoRNA Analysis Service, supported by specialized modules. We align each module with the latest methodological guidance and embed rigorous controls responsive to ongoing glycorna controversy discussions. Services include:
For teams exploring glycorna cell biology, glycorna cancer hypotheses, or EV-based markers, the imperative is clear: adopt orthogonal assays with robust enzymatic and depletion controls to produce results that stand up to scrutiny and accelerate consensus. Creative Biolabs is ready to support that journey with standardized, control-rich platforms spanning imaging, profiling, and functional testing. Contact our experts to get more latest information.
FAQs
What exactly is GlycoRNA and why does it matter to my program?
GlycoRNA refers to small RNAs that carry glycan moieties and can appear on the cell surface and extracellular vesicles. Emerging studies link these structures to adhesion and immune communication, positioning glycoRNAs as a potential third glycan scaffold alongside proteins and lipids. For research teams, they offer new readouts to probe cell–cell interactions, trafficking, and microenvironment signaling without invoking clinical claims.
Where is the field going?
Rapidly evolving toolkits (rPAL, ARPLA, lectin-based assays, EV-compatible FRET readouts) are enabling spatial mapping, quantitation, and target discovery with growing implications in cancer and immunology.
What types of samples can you evaluate for glycorna signals?
We typically work with cultured cells, primary cell preparations, and tissue sections when fixation and retrieval conditions are validated for the chemistry. For acellular materials, we analyze extracellular vesicles and selected biofluids under particle-normalized workflows. When sample matrices are complex, we begin with a small feasibility panel to tune background, probe specificity, and enzymatic controls before expanding.
What practical outputs will I receive if I start a study with Creative Biolabs?
You receive a study plan, annotated SOPs, predefined acceptance criteria, and a feasibility report summarizing controls and optimization results. For production runs, we deliver raw and processed datasets, quantification tables, representative images or traces, and an interpretive memo highlighting caveats and next steps. We can also align deliverables to your internal assay review templates for easier adoption.
How do you image glycorna in situ, and what readouts do I get?
We use proximity-based chemistries that require simultaneous recognition of glycan features and RNA sequence elements. Outputs include puncta density per cell, membrane-biased distribution scores, and colocalization indices with markers of interest. High-content imaging enables field-of-view averaging and ROI-level statistics. We provide raw images, QC logs, segmentation masks, and quantified tables suitable for downstream statistics.
Reference:
- Kim, Hyung Seok. "GlycoRNA: A new player in cellular communication." Oncology Research 33.5 (2025): 995. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. http://dx.doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.060616
Supports
- GlycoRNA Analysis Technologies
- GlycoRNA-seq: High-Throughput Sequencing of Glycosylated RNAs
- Novel GlycoRNA Imaging: Visualizing GlycoRNAs in Single Cells
- Clier-qPCR: Quantitative Validation of GlycoRNAs
