Cardiovascular Medicine related Glycan Introduction
Accelerate Your Glycan-Based Discoveries!
Are you currently facing challenges in understanding the intricate molecular mechanisms of cardiovascular diseases or identifying novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets? Creative Biolabs offers cutting-edge solutions in Glycan in Cardiovascular Medicine. We help you accelerate scientific discovery and enhance diagnostic precision through advanced glycomics analysis and targeted antibody development. Leveraging innovative glycoprotein profiling techniques and comprehensive bioinformatic analysis, we provide unparalleled insights into cardiac and vascular health.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) represents the leading global mortality cause and encompasses conditions affecting the heart or vasculature, such as coronary artery diseases (CAD) like angina and myocardial infarction. CVDs constitute a broad category comprising stroke, heart failure, hypertensive heart disorder, rheumatic heart condition, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, congenital heart defect, valvular heart issue, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disorder, thromboembolic condition, and venous thrombosis. Underlying mechanisms vary across these pathologies.
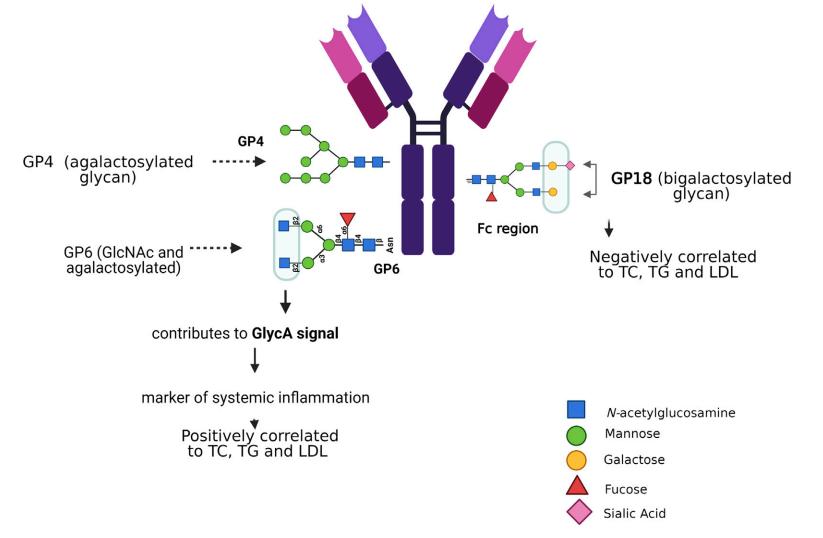 Fig.1 N-glycosylation associated with risk factors for dyslipidemia.1,3
Fig.1 N-glycosylation associated with risk factors for dyslipidemia.1,3
The Role of Glycans in Cardiovascular Medicine
Cardiovascular pathologies correlate with elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and diminished high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. These conditions heighten atherosclerotic plaque risk in major arteries. During lesion initiation (fatty streak formation), monocytes infiltrate vascular subendothelial zones. This mechanism entails endothelial P- and/or E-selectin expression, binding properly glycosylated/sulfated P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) or sialyl Lewis x on circulating monocytes. Generally, murine P-selectin deficiency retards atherosclerotic plaque advancement. Oxidized lipids within LDL particles or inflammatory cascades induce endothelial P-selectin in early atheromas. LDL retention in nascent plaques likely involves proteoglycan recognition. This interplay causes irreversible LDL structural modifications, enhancing oxidation and macrophage/smooth muscle cell uptake. Additionally, apolipoprotein B's basic amino acid clusters (LDL's protein component) bind proteoglycan glycosaminoglycans' negative charges. Diminished LDL sialylation occurs in coronary artery disease patients, potentially facilitating desialylated LDL uptake into atheromatous plaques.
Published Data
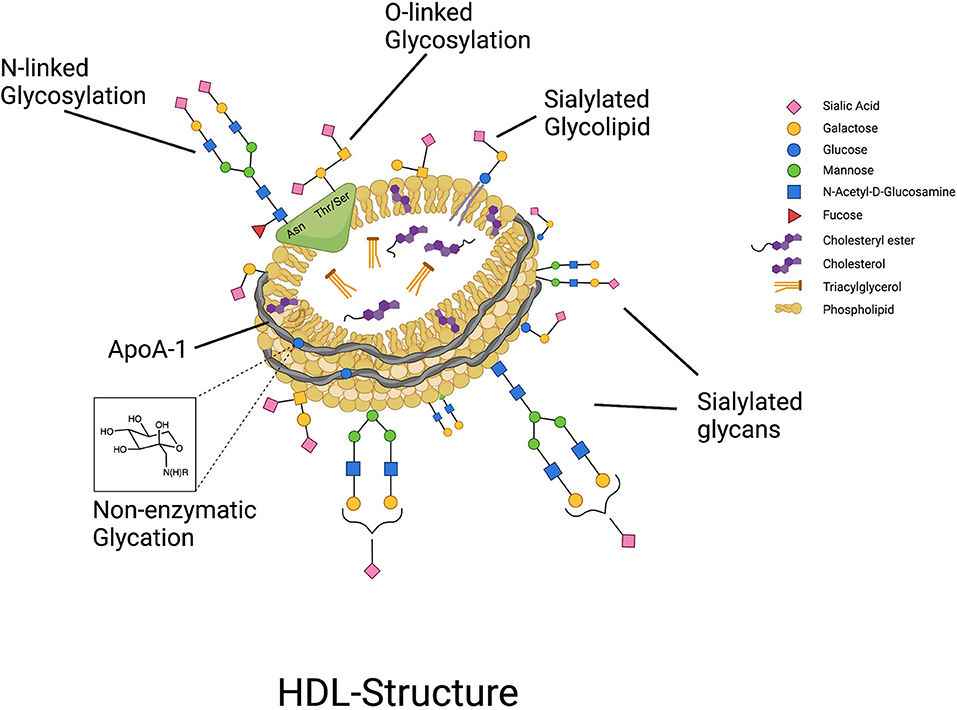 Fig.2 Highly glycosylated HDL particles.2,3
Fig.2 Highly glycosylated HDL particles.2,3
The literature indicates that early investigations into the glycosylation of HDL-associated proteins have revealed differential glycan patterns in various pathological conditions related to cardiovascular disease. Specifically, small pilot studies, referenced within the review, have demonstrated a promising correlation between unique HDL glycosylation profiles and cardiovascular outcomes. While the review itself does not present new experimental data from the authors, it consolidates findings from existing research where experimental approaches involved profiling HDL-associated protein glycosylation using methods such as mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography. These experiments aimed to identify specific glycan alterations on HDL proteins that could serve as indicators of disease etiology, progression, or risk stratification. The results from these collective studies suggest that modifications in HDL glycosylation are present in different CVD states, thereby supporting the potential for these glycoprofiles to act as valuable biomarkers, although the need for larger, well-controlled cohort studies for robust validation is consistently highlighted.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs delivers a complete portfolio of offerings engineered to advance your investigations in Glycan Cardiovascular Medicine:
- Comprehensive Glycan Profiling Services
- Glycoprotein Analysis & Site-Specific Glycosylation
- Anti-Glycan Antibody Development
- Functional Glycan Studies
- Custom Glycoconjugate Synthesis
Discover the Creative Biolabs Edge – Obtain Your Pricing Now
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of glycomics research, offering unparalleled expertise and a distinct competitive edge in the field of Glycan in Cardiovascular Medicine. Our commitment to scientific rigor, coupled with a deep understanding of biological systems, ensures superior outcomes for your research and development needs.
- Deep Scientific Expertise: Over years of specialized experience in glycobiology and cardiovascular research, enabling nuanced interpretation of complex glycomic data.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Access to advanced mass spectrometry platforms, high-throughput glycan analysis systems, and proprietary bioinformatics tools for comprehensive and accurate profiling.
- Customized Solutions: Tailored project design to meet unique research objectives, from biomarker discovery to therapeutic target validation.
- High-Affinity Antibody Development: Demonstrated expertise in producing high-specificity anti-glycan antibodies vital for diagnostics and therapeutics.
- Integrated Workflow: A seamless process from sample preparation to data interpretation and functional validation, ensuring coherent and actionable results.
- Collaborative Partnership: We act as an extension of your research team, providing dedicated support and expert consultation throughout the project lifecycle.
FAQs
Here are some common questions from researchers interested in the role of glycans in cardiovascular medicine:
Q: What are the primary types of glycans relevant to cardiovascular health, and how do they differ in their biological roles?
A: The primary types of glycans relevant to cardiovascular health include N-linked glycans, O-linked glycans (including mucin-type O-glycans and O-GlcNAc), and glycolipids. N-linked glycans are typically found on secreted and cell surface proteins, influencing protein folding, stability, and cell-cell recognition. Mucin-type O-glycans support protective mucus barriers and cellular signaling. O-GlcNAc is a dynamic modification on intracellular proteins, regulating signaling pathways and gene expression in response to metabolic changes. Glycolipids function as key membrane components, engaged in cellular recognition and signal transduction. Each type plays distinct yet interconnected roles in maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis and contributing to disease pathogenesis.
Q: How can glycan analysis contribute to the development of new therapeutic strategies for cardiovascular diseases?
A: Glycan analysis can identify aberrant glycosylation patterns that are directly linked to disease progression. By pinpointing these specific glycan structures or the enzymes that create them (glycosyltransferases) or remove them (glycosidases), researchers can identify novel therapeutic targets. For example, inhibiting or enhancing specific glycosyltransferases could modify disease-associated glycans, potentially reversing pathological processes or improving drug delivery and efficacy. This opens avenues for developing highly specific glycan-targeting drugs or antibodies.
Q: Can glycan biomarkers differentiate between different stages or subtypes of a cardiovascular disease, such as early-stage vs. advanced atherosclerosis?
A: Emerging research suggests that glycan biomarkers hold significant promise for differentiating between various stages or subtypes of cardiovascular diseases. Specific alterations in glycan structures can reflect subtle changes in cellular metabolism, inflammation, or tissue remodeling that occur at different points in disease progression. For instance, distinct N-glycan patterns might be associated with early inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis, while more complex or branched glycans could indicate advanced plaque formation, offering a more refined diagnostic and prognostic tool than traditional markers.
Related Products and Services
To further advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a portfolio of solutions:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Loaeza-Reyes, Karen Julissa et al. "An Overview of Glycosylation and its Impact on Cardiovascular Health and Disease." Frontiers in molecular biosciences vol. 8 751637. 16 Nov. 2021, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.751637
- Romo, Eduardo Z, and Angela M Zivkovic. "Glycosylation of HDL-Associated Proteins and Its Implications in Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis, Metabolism and Function." Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine vol. 9 928566. 27 May. 2022, https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.928566
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
