Brain Tissue Binding
Estimation of the unbound fraction of drug in brain provides a valuable tool for identifying new therapies for central nervous system (CNS) diseases. Creative Biolabs performs tailored brain tissue binding assay to evaluate brain tissue binding of drugs and predict their disposition into brain.
Although the brain receives about one-sixth of cardiac output, drug penetration to brain cannot be measured by plasma protein binding assay. It is because the composition of brain and plasma are very different; therefore free drug fraction in plasma cannot replace unbound brain concentrations.
The main reason for different drug penetration characters is blood-brain barrier (BBB). BBB is a highly selective semipermeable membrane that separates blood circling from CNS and the brain extracellular fluid. It consists of the endothelium of brain capillaries and astrocyte. The endothelial cells of brain capillaries are more tightly joined than most capillaries in other tissues, resulting in slower passive diffusion of water-soluble drugs. Furthermore, it selectively transports of lipophilic compounds by way of active transport. The astrocytic sheath consists of a layer of glial connective tissue cells (astrocytes) close to the basement membrane of the capillary endothelium and plays an important role in secretion and absorption of neural transmitters.
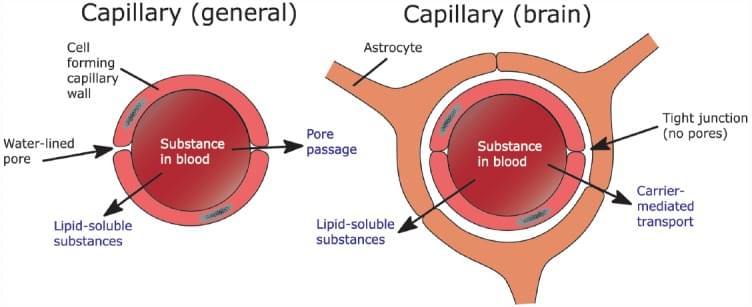 Fig. 1 The difference between general capillaries and brain capillaries.1
Fig. 1 The difference between general capillaries and brain capillaries.1
Another unique system for drug distribution into brain is that a drug may extend into brain tissue from CSF via the choroid plexus by passive diffusion or active transport. The drug penetration rate into CSF is determined mainly by the extent of protein binding, degree of ionization, and lipid-water partition coefficient of the drug.
Assessment of brain unbound concentration (Cu, brain) is crucial in understanding the PK and PD of CNS drugs, as only the unbound drug is free to diffuse across the BBB into the action sites. In case of that, Creative Biolabs provides a high throughput brain tissue binding assay to deliver a value of fraction of compound unbound to brain tissue (fu, brain). Our brain tissue binding assay is fully developed to use a 96-well equilibrium dialysis unit for quickly and accurately determining the unbound fraction of drugs in brain tissue. The results are calculated by LC-MS/MS. Also, we employed brain to plasma ratio (Kp) or log ratio of blood to brain (logBB) to indicate whether a drug has good brain penetration. For compounds which undergo drug transport, differences between the unbound plasma-to-brain fraction ratios and brain-to-plasma exposure can be observed.
Data Analysis
The drug unbound fraction (fu, brain) is calculated from diluted brain tissue homogenates to yield an estimate of unbound fraction using the following formula:
 fu,brain: The unbound fraction in brain tissue
fu,brain: The unbound fraction in brain tissue
fu,homogenate: The unbound fraction in brain homogenate
Dilution is the dilution factor for the brain homogenate
If the compound demonstrates available by in vitro assay, we are able to provide in vivo assessment to determine the pharmacokinetics and the brain to plasma ratio of the compound.
For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
Reference
- Boonstra, Evert, et al. "Neurotransmitters as food supplements: the effects of GABA on brain and behavior." Frontiers in psychology 6 (2015): 167121. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
