HBV Transgenic Mouse Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established, optimized models to assess the efficacy of antiviral and liver protective treatments for Hepatitis B, ensuring reliable preclinical results for your research and drug development efforts.
Introduction
Hepatitis B (HBV) is a serious viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic diseases. The virus is transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, and other body fluids. Chronic HBV infection can lead to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, and an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). Approximately 296 million people worldwide are living with chronic HBV, making it a significant global health burden. The infection can progress slowly, often without symptoms, for years, which makes it difficult to diagnose early. People with chronic HBV are at a higher risk of developing cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Current treatments include antiviral drugs that suppress viral replication, but there is no complete cure. Understanding the virus's behavior and evaluating new drug candidates is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and preventing the progression of liver disease. Animal models, such as the HBV transgenic mouse model, play a vital role in advancing research and developing new therapies.
Disease Models and Applications
The HBV Transgenic Mouse Model is an essential tool for studying the molecular mechanisms of HBV infection and evaluating therapeutic interventions. This model is created by introducing HBV genes into mouse embryonic stem cells, leading to the expression of HBV antigens in their liver cells. These mice exhibit key characteristics of HBV infection, including the production of HBV surface antigens and the establishment of chronic infection. A significant advantage of this model is its ability to mimic the persistent infection seen in humans, making it ideal for testing antiviral drugs and immune modulators. However, the model has limitations, such as the fact that it does not fully replicate the human immune system's response to the virus, and the severity of the disease can vary. Despite these challenges, it remains a powerful tool for preclinical research on HBV therapies.
- Simulates: This model simulates chronic Hepatitis B infection in humans by expressing HBV antigens in mouse liver cells. It provides insights into the disease's progression, immune response, and liver damage.
- Evaluates Drugs: The HBV Transgenic Mouse Model is used to evaluate the efficacy of antiviral drugs, immune modulators, and liver protectants. It allows for the assessment of therapeutic interventions in reducing viral load, improving liver function, and preventing liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.
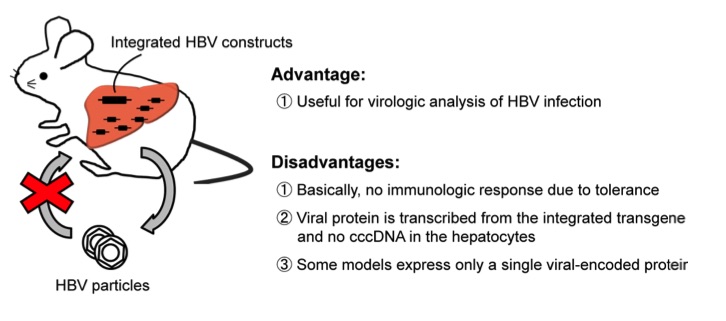 Fig.1 Hepatitis B virus (HBV) transgenic mouse model.1
Fig.1 Hepatitis B virus (HBV) transgenic mouse model.1
Measurements
We offer a comprehensive range of measurements to evaluate drug efficacy in the HBV Transgenic Mouse Model, using advanced techniques that include, but are not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight, mortality rate, and serum HBV marker levels (e.g., HBsAg, HBeAg).
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of HBV antigen expression in liver tissues, along with immune cell infiltration (e.g., T-cells, macrophages).
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IFN-γ to assess immune response.
- Liver function biomarkers: Serum levels of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), bilirubin, and albumin to evaluate liver injury and functionality.
- Gene/protein expression analysis: RT-qPCR and Western blot techniques to examine HBV gene expression and host responses to infection.
Additionally, our expert team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data interpretation, providing you with a tailored and effective approach for your research.
Related Services
Beyond the HBV Transgenic Mouse Model, we also offer other methods to induce HBV infection in rodents, such as hydrodynamic injection and humanized liver mouse models. These alternative approaches may be suitable for specific research requirements, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of potential therapies.
- AAV/HBV induced Chronic HBV Infection Model
- Hydrodynamic Injection HBV Model
- Hepatitis B Humanized Mouse Model
- Chronic Hepatitis B Woodchuck Model
Advantages
- Expertise: Extensive experience in providing customized animal models tailored to your specific research needs.
- Advanced Technologies: Access to cutting-edge technologies for assessing drug efficacy, including molecular biology techniques and imaging tools.
- Comprehensive Support: Full project management support, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring successful outcomes.
- Reliability: High reproducibility and consistency in our animal models, providing robust and reliable data for preclinical studies.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What is the main advantage of using the HBV Transgenic Mouse Model?
This model closely mimics chronic HBV infection in humans, making it ideal for preclinical testing of antiviral therapies and liver protectants.
-
2. How does the HBV Transgenic Mouse Model compare to other animal models?
While it offers valuable insights into HBV infection, alternative models like hydrodynamic injection or humanized liver mice may provide different perspectives, particularly regarding immune responses.
-
3. Can the model be used for testing combination therapies?
Yes, the HBV Transgenic Mouse Model is suitable for evaluating the efficacy of combination therapies, including antiviral drugs and immune modulators.
-
4. Are there any limitations to this model?
The model may not fully replicate the complexity of the human immune system, which could influence the generalizability of results in certain therapeutic contexts.
-
5. What types of measurements are taken in the HBV Transgenic Mouse Model?
We assess body weight, viral load, immune response markers, liver function, and tissue pathology, providing a comprehensive evaluation of drug effects.
Published Data
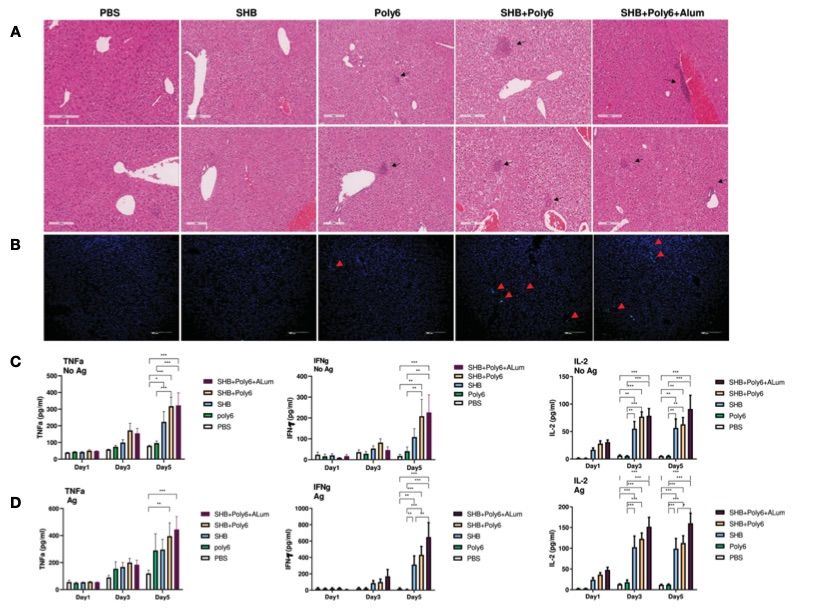 Fig. 2 Vaccinations containing Poly6 induced potent stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines.2
Fig. 2 Vaccinations containing Poly6 induced potent stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines.2
The potential of Poly6 in combination with HBsAg as a therapeutic vaccine against hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection was evaluated in this study. The immunotherapeutic effects of Poly6 combined with HBsAg vaccination were tested in C57BL/6 mice and an HBV transgenic mouse model. Vaccination with the Poly6/HBsAg combination resulted in significant lymphocyte infiltration in the livers of the mice, as compared to the PBS or SHB groups (Figure 2A). Additionally, CD8+ T cell infiltration was observed in the liver of mice vaccinated with the Poly6/HBsAg combination, but not in the other groups (Figure 2B). Th1 cytokine levels (IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α) were measured in the culture supernatants of splenocytes from the vaccinated HBV transgenic mice (Figure 2). The groups receiving the Poly6/HBsAg combination exhibited significantly higher secretion levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-2 compared to the other groups (Figure 2C). Stimulation with HBs and HBc proteins further enhanced the magnitude of these responses (Figure 2D), suggesting that Poly6 enhances Ag-specific Th1 responses.
References
- Inuzuka, Tadashi et al. "Mouse models of hepatitis B virus infection comprising host-virus immunologic interactions." Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 3,2 377-89. 23 Apr. 2014, DOI:10.3390/pathogens3020377. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Choi, Yu-Min et al. "A hepatitis B virus-derived peptide combined with HBsAg exerts an anti-HBV effect in an HBV transgenic mouse model as a therapeutic vaccine." Frontiers in immunology vol. 14 1155637. 2 Jun. 2023, DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155637. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
