Epinephrine induced Ventricular Tachycardia Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a severe cardiac arrhythmia originating in the heart's lower chambers, posing a significant risk for sudden cardiac death. Its unpredictable nature and potential for rapid progression underscore the urgent need for effective therapeutic strategies and thorough safety assessments of new compounds.
At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to advancing cardiovascular research, providing a variety of well-established in vivo models to evaluate anti-arrhythmic drug efficacy and assess pro-arrhythmic risk.
Epinephrine-Induced VT Model
The epinephrine-induced VT model is a widely recognized in vivo preclinical tool, particularly valuable for assessing the pro-arrhythmic potential of novel compounds and evaluating the efficacy of anti-arrhythmic agents. This model effectively mimics conditions of heightened sympathetic tone, a common physiological trigger for arrhythmias in clinical settings, including stress, exercise, and certain pathological states. It is also highly relevant for investigating arrhythmias linked to underlying genetic predispositions, such as catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT).
Model Construction Steps
The construction of this model involves inducing sympathetic overactivity through controlled epinephrine administration, followed by meticulous cardiac monitoring. The general strategy focuses on creating a reproducible arrhythmic substrate to test drug effects.
01Animal Preparation
Healthy animals (e.g., rats, mice, depending on study needs) are selected and acclimated to the laboratory environment.
02Anesthetic Consideration
Animals are often anesthetized, though conscious models can also be employed. The choice of anesthetic is critical, as certain agents can modulate epinephrine's arrhythmogenic effects, requiring careful selection to ensure model consistency and relevance.
03Epinephrine Administration
A carefully calibrated dose of epinephrine (adrenaline) is administered, typically via intravenous infusion or bolus injection. The dose and route are optimized to reliably induce ventricular arrhythmias.
04ECG/Telemetry Monitoring
Continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) recording is performed using surface electrodes or implantable telemetry devices. This allows for real-time monitoring of cardiac rhythm, heart rate, and various ECG parameters (e.g., QT interval).
05Data Collection and Analysis
Arrhythmia onset, duration, type (e.g., coupled beats, bigeminy, polymorphic VT, ventricular fibrillation), and burden are meticulously recorded and analyzed. Hemodynamic parameters, such as blood pressure, may also be monitored.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- Physiological Relevance: Accurately mimics sympathetic activation, a major clinical trigger for arrhythmias.
- Reproducibility: Established protocols ensure consistent and reliable arrhythmia induction.
- Sensitivity: Detects subtle pro-arrhythmic effects, even those unmasking genetic predispositions.
- Translational Potential: Findings often correlate well with human clinical outcomes, aiding in risk assessment and drug development.
Limitations:
- Acute Model: Primarily an acute model, which may not fully capture chronic or progressive arrhythmia mechanisms without further experimental modifications.
- Anesthetic Influence: The choice of anesthetic can impact results, necessitating stringent control and validation.
Evaluation Platform
Our advanced evaluation platform integrates comprehensive biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, and imaging capabilities with precise physiological monitoring. This allows for a holistic assessment of drug effects and disease mechanisms, ensuring robust and reliable data generation for your research.
Key Test Indicators:
- Electrocardiographic (ECG) Parameters: Heart Rate, PR interval, QRS duration, QT interval, QTc (corrected QT interval).
- Arrhythmia Quantification: Incidence, duration, and burden of ventricular arrhythmias (e.g., VT, VF, coupled beats, bigeminy).
- Hemodynamic Parameters: Systolic, Diastolic, and Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (BP).
- Cardiac Tissue Analysis: Histopathology (e.g., fibrosis, hypertrophy), immunohistochemistry (e.g., ion channel expression), molecular assays (e.g., gene expression, protein levels related to calcium handling).
Applications
- Disease Simulation: Drug-induced arrhythmias, stress-induced arrhythmias, exercise-induced arrhythmias, and arrhythmias associated with familial syndromes like CPVT.
- Drug Evaluation: Novel anti-arrhythmic compounds, compounds undergoing pro-arrhythmic risk assessment (safety pharmacology) for potential off-target effects, and drugs targeting sympathetic nervous system modulation.
- Treatments Development: Pharmacological interventions aimed at preventing, reducing, or terminating ventricular arrhythmias, as well as mechanistic studies of novel therapeutic targets.
Related Ventricular Tachycardia Models
Our Advantages
- Seasoned Scientific Team: Years of specialized expertise in in vivo arrhythmia models, ensuring meticulous study design and execution.
- State-of-the-Art Facilities: Equipped with advanced telemetry, high-resolution ECG recording, and sophisticated data analysis platforms for precise results.
- Robust, GLP-Compliant Protocols: Adherence to the highest scientific and regulatory standards, ensuring data integrity for global acceptance.
- Comprehensive Data Analysis & Interpretation: We provide insightful analysis and expert interpretation to guide your strategic decisions.
- Tailored Solutions: Customized study designs to precisely meet your unique research objectives and timelines.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs is committed to advancing cardiovascular science through our robust epinephrine-induced VT model. We offer comprehensive preclinical services tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can accelerate your drug development journey.
FAQs
-
Q1: How do you ensure the reproducibility of arrhythmia induction in this model?
A: Reproducibility is paramount in our studies. We achieve this through rigorously standardized protocols, precise calibration of epinephrine doses, and consistent administration routes. Our experienced scientific team meticulously controls experimental variables, including animal strain, age, and environmental conditions, to minimize variability and ensure reliable and repeatable arrhythmia induction across all study cohorts.
-
Q2: Can this model differentiate between pro-arrhythmic mechanisms (e.g., EADs vs. DADs)?
A: While the epinephrine-induced VT model primarily assesses the overall pro-arrhythmic potential, our comprehensive evaluation platform allows for deeper mechanistic insights. By combining ECG analysis with advanced techniques such as ex vivo cardiac tissue studies, calcium imaging, or molecular analyses, we can infer potential underlying mechanisms like early afterdepolarizations (EADs) or delayed afterdepolarizations (DADs) and their contribution to arrhythmia initiation.
-
Q3: How do you account for the influence of anesthetics on the model's outcomes?
A: The choice of anesthetic is a crucial consideration in this model. We employ specific anesthetic protocols known to have minimal impact on cardiac electrophysiology or sympathetic tone, or we carefully select anesthetics whose effects are well-characterized and consistent. Our team meticulously controls anesthetic depth and continuously monitors physiological parameters to ensure that any observed arrhythmogenic effects are primarily attributable to epinephrine and the test compound, rather than the anesthetic agent.
-
Q4: Can this model be adapted to investigate arrhythmias related to specific genetic conditions like CPVT?
A: Absolutely. The epinephrine-induced VT model is highly adaptable for investigating arrhythmias linked to genetic conditions, particularly those exacerbated by sympathetic activation, such as CPVT. We can utilize specific genetically modified animal models (e.g., knock-in mice) in conjunction with epinephrine challenge to explore disease mechanisms, test novel therapies, and understand how compounds interact with underlying genetic predispositions.
-
Q5: Can I provide my own test compounds, and what are the requirements for compound submission?
A: Yes, clients can certainly provide their own test compounds for evaluation. We require detailed information regarding the compound's chemical structure, purity, solubility, stability, and any known safety data. Our team will work closely with you to determine the appropriate formulation and administration route to ensure optimal delivery and accurate assessment within the model.
Published Data
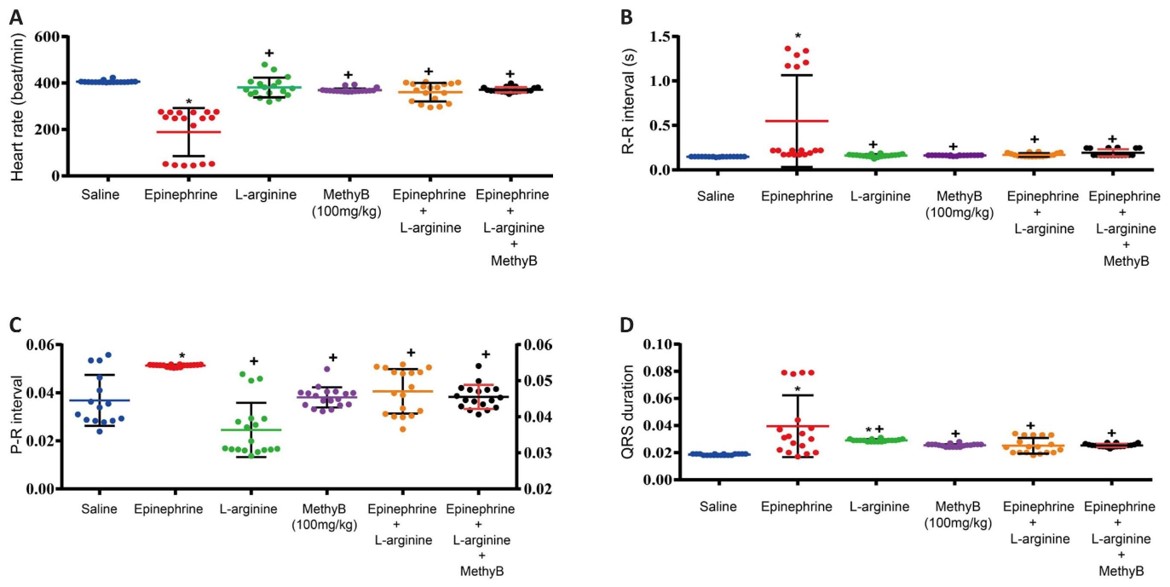 Fig.1 Effects of L-arginine on the Epinephrine-Induced ventricular arrhythmias.1
Fig.1 Effects of L-arginine on the Epinephrine-Induced ventricular arrhythmias.1
This research utilized the epinephrine-induced arrhythmia model in rats to investigate the protective effects of L-arginine, a nitric oxide precursor. The study's results demonstrated that L-arginine significantly shortened the duration of epinephrine-induced arrhythmias and decreased the number of extrasystoles, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent to mitigate sympathetic overactivity-induced cardiac dysfunction and myocardial injury.
Reference
- Abdel-Salam, Omar ME, et al. "Protection by L-arginine against epinephrine-induced arrhythmia and cardiotoxicity." Innov Discov 1 (2024). Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. DOI: 10.53964/id.2024012
For Research Use Only.
