Acute Myocardial Ischemia (AMI) induced Left Heart Failure Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to advancing cardiovascular research by providing a variety of well-established, physiologically relevant animal models to evaluate the efficacy of novel HF therapies.
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) represents a progressive and debilitating condition where the heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body's demands. Often a long-term consequence of acute myocardial ischemia (AMI), it leads to significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. Understanding and addressing the complex mechanisms driving HF is crucial for developing effective treatments.
Acute Myocardial Ischemia (AMI)-Induced Left HF Model
Our AMI-induced left HF model is a cornerstone of preclinical cardiovascular research, meticulously developed to mimic the clinical progression of human heart attack, leading to chronic HF. This robust model allows for precise investigation into the underlying pathophysiology and the rigorous evaluation of potential therapeutic interventions.
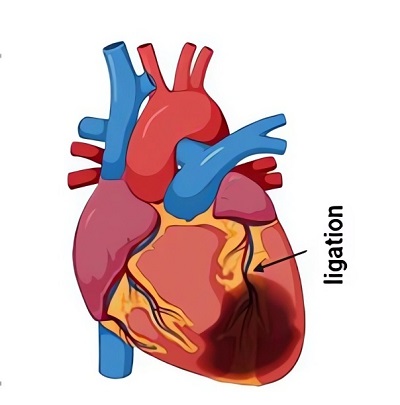 Fig.1 Surgical techniques for coronary artery ligation MI rat model of HF.1
Fig.1 Surgical techniques for coronary artery ligation MI rat model of HF.1
Model Construction Steps
The construction of our AMI-induced left HF model primarily involves the permanent or temporary ligation of the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery in small rodents (Mouse, Rat) and non-rodent large animals (Rabbit, Dog, NHPs). This surgical procedure induces a controlled myocardial infarction, leading to ischemic injury and subsequent cardiac remodeling that progresses to HF.
01Anesthesia and Thoracotomy
Animals are anesthetized, intubated, and mechanically ventilated. A left thoracotomy is performed to expose the heart.
02LAD Coronary Artery Ligation
The LAD coronary artery is carefully identified and permanently ligated using fine sutures. For reperfusion models, the ligature may be released after a defined ischemic period.
03Infarct Confirmation (Initial)
Animals are anesthetized, intubated, and mechanically ventilated. A left thoracotomy is performed to expose the heart.
04Chest Closure and Recovery
The chest cavity is closed, and the animal is carefully monitored during recovery, with appropriate post-operative analgesia and care provided.
05Longitudinal Monitoring
Animals are then allowed to recover over a period, during which cardiac remodeling and HF develop. Serial assessments are performed to track the progression of the disease.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Clinical Relevance: Closely mimics the most common cause of HF in humans – post-MI remodeling.
- Reproducibility: Standardized surgical techniques ensure consistent infarct size and predictable progression to HF.
- Comprehensive Phenotyping: Allows for detailed functional, structural, and molecular characterization of HF.
- Translational Predictability: Responses to pharmacological interventions in this model often correlate well with clinical outcomes.
- Adaptability: Suitable for acute cardioprotection studies as well as chronic HF evaluations over an extended period.
Limitations:
- Invasiveness: Requires advanced surgical skills and specialized equipment.
- Technical Skill Required: The success and reproducibility of the model are highly dependent on the expertise of the surgical team.
- Post-Operative Care: Requires diligent post-operative monitoring and care to ensure animal welfare and minimize mortality.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive evaluation platform to thoroughly characterize the effects of therapeutic interventions in our AMI-induced Left HF model. Our state-of-the-art facilities are equipped with advanced instruments for biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, and imaging analyses, ensuring robust and reliable data generation.
Key Evaluation Parameters Include:
- Cardiac Function (Imaging): Echocardiography (LVEF, FS, LV dimensions, wall motion), MRI (for more detailed structural and functional assessment).
- Hemodynamics (Invasive): Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), dP/dt max/min, cardiac output, systemic blood pressure.
- Histopathology: Infarct size quantification, myocardial fibrosis (e.g., Masson's Trichrome, Sirius Red staining), cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, inflammatory cell infiltration, capillary density.
- Biochemical Markers: Plasma and tissue levels of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP), cardiac troponins (cTnI/T), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6).
- Molecular Analysis: Gene and protein expression of remodeling markers (e.g., collagen I/III, α-SMA, ANP, β-MHC), signaling pathway components (e.g., MAPK, Akt), and apoptosis markers.
Applications
- Evaluate Cardioprotective Agents: Assess compounds aimed at reducing initial myocardial injury during ischemia or reperfusion.
- Test Anti-Remodeling Therapies: Investigate drugs designed to prevent or reverse adverse ventricular remodeling, fibrosis, and hypertrophy.
- Assess Function-Enhancing Treatments: Study interventions that improve overall cardiac contractility and pumping efficiency in the context of established HF.
- Analyze Regenerative Approaches: Evaluate the efficacy of cell-based therapies (e.g., stem cells), gene therapies, or exosome-based treatments in restoring myocardial function.
- Investigate Mechanistic Pathways: Elucidate the complex molecular and cellular pathways involved in the transition from MI to chronic HF.
Related Heart Failure Models
PA Constriction induced Right HF Model
Ascending Aortic Arch Constriction induced Post-Pressure Overload Heart Failure Model
Abdominal Aortic Stenosis induced Left HF Model
DOCA & Salt induced Left HF Model
Adriamycin induced Left HF Model
Our Advantages
- Deep Expertise: Over decades of specialized experience in cardiovascular pharmacology and animal model development.
- Unrivaled Reproducibility: Our highly standardized protocols ensure consistent and reliable experimental outcomes, critical for robust data interpretation.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: We provide a holistic assessment platform, combining functional, structural, and molecular analyses for in-depth insights.
- Tailored Study Design: Flexible and customizable study designs to precisely meet your unique research objectives.
- Ethical Compliance: Strict adherence to international ethical guidelines and regulatory standards, ensuring the highest animal welfare.
- Dedicated Support: A collaborative partnership approach, offering expert guidance and transparent communication throughout your project.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
We invite you to connect with our scientific team to discuss your specific research needs and explore how our advanced AMI-induced left HF model can be strategically integrated into your cardiovascular drug development pipeline. Our experts are ready to assist you in designing studies that deliver clear, actionable results.
FAQs
-
Q1: What measures do you take to ensure the reproducibility and consistency of the AMI-induced HF model across different cohorts?
A: Reproducibility is paramount to our model's integrity. We achieve this through highly standardized surgical protocols performed by experienced surgeons, focusing on precise ligation and consistent anesthetic management. Strict inclusion/exclusion criteria, based on initial functional assessments, minimize animal variability, ensuring high data reliability for clients.
-
Q2: Can you customize the severity of the myocardial infarction to match specific research requirements?
A: Yes, our model offers flexibility in MI severity. While our standard protocol ensures highly reproducible infarcts leading to HF, we can adjust the ligation technique for varying infarct sizes as required. This customization is thoroughly discussed with clients during study design to align model characteristics with experimental goals.
-
Q3: What are the key indicators Creative Biolabs uses to confirm the successful induction of HF in the AMI model?
A: HF induction is confirmed through a multi-modal approach. Key indicators include reduced LVEF and FS (echocardiography), elevated LVEDP (invasive hemodynamics), increased heart and lung weight, and histological evidence of myocardial fibrosis and hypertrophy. Elevated circulating biomarkers like BNP or NT-proBNP also serve as crucial biochemical confirmations.
-
Q4: What types of therapeutic agents can be evaluated using this model, including different routes of administration?
A: Our versatile AMI-induced HF model evaluates a broad spectrum of therapeutic agents, including small molecules, biologics, cell-based therapies, and gene therapies. We support various administration routes, such as oral, intravenous, subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, and direct myocardial injection, ensuring flexibility for your compound's delivery strategy.
-
Q5: Can you perform studies investigating the acute cardioprotective effects during the ischemia-reperfusion phase?
A: Yes, our model can adapt to investigate acute cardioprotection during ischemia-reperfusion injury. This involves temporary LAD ligation followed by reperfusion to assess interventions limiting infarct size, mitigating inflammation, or preserving function. Such studies often include early time point assessments and specific biomarkers of acute injury.
-
Q6: How do you ensure the translational relevance of the AMI-induced HF model to human HF?
A: Translational relevance is central to our model design. Our AMI-induced HF model closely mimics human post-MI HF, including cardiac remodeling, ventricular dysfunction, and neurohumoral activation. The measured endpoints (e.g., LVEF, LVEDP, fibrosis, BNP) highly correlate with human clinical parameters, maximizing the likelihood of successful clinical translation.
Published Data
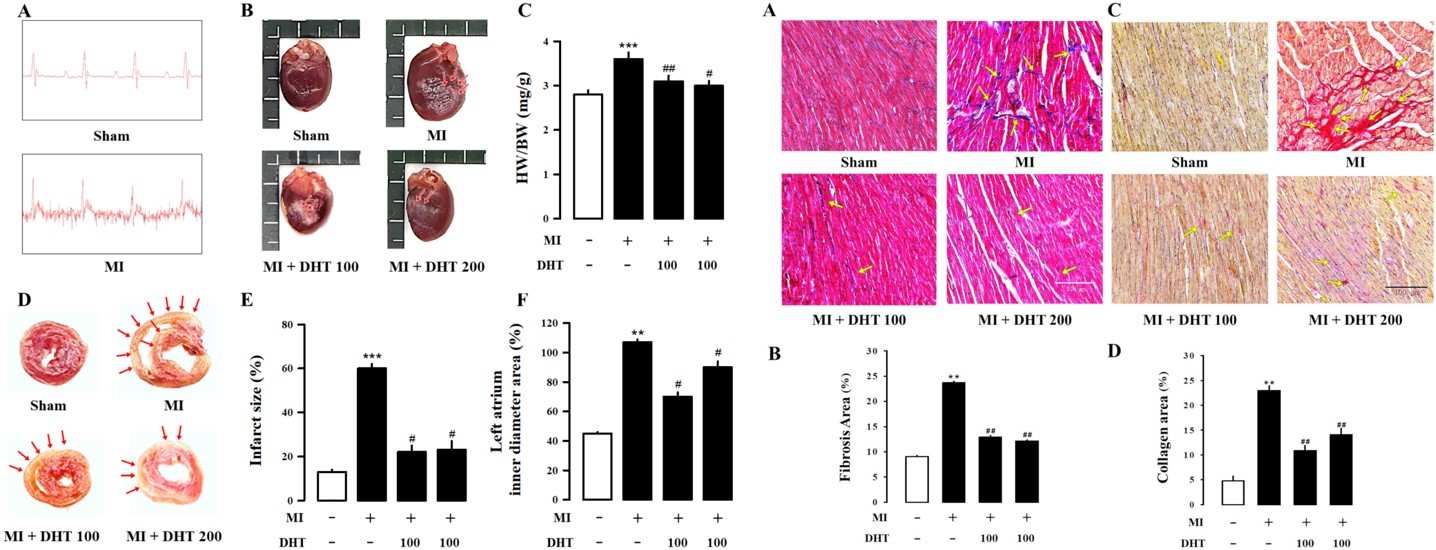 Fig.2 Effect of DHT on cardiac morphology and fibrosis in MI-induced HF rats.2
Fig.2 Effect of DHT on cardiac morphology and fibrosis in MI-induced HF rats.2
A compelling example of the model's utility is demonstrated in a study evaluating the cardioprotective potential of traditional herbal formulas. In a rat model of MI-induced HF, researchers assessed the effects of Dohongsamul-tang (DHT) on cardiac function and remodeling. The study reported that DHT significantly reduced infarct size by approximately 63.3% and heart weight by 16.7%. Furthermore, levels of crucial HF biomarkers such as LDH and CK-MB were notably decreased by 37.6% and 47.6% respectively, alongside improvements in cardiac function. These findings highlight the model's ability to precisely identify therapeutic agents that can mitigate myocardial damage and improve outcomes in HF.
References
- Farag, Ahmed et al. "A review on experimental surgical models and anesthetic protocols of heart failure in rats." Frontiers in veterinary science vol. 10 1103229. 27 Mar. 2023. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1103229
- Jang, Youn-Jae et al. "The Cardioprotective Potential of Herbal Formulas in Myocardial Infarction-Induced Heart Failure through Inhibition of JAK/STAT3 Signaling and Improvement of Cardiac Function." Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 17,9 1132. 27 Aug. 2024. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091132
For Research Use Only.
