pMCAO Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Stroke, particularly ischemic stroke, represents a devastating global health challenge, leading to significant long-term disability and mortality worldwide. Effective therapeutic development hinges on robust preclinical models that accurately mimic human disease pathophysiology.
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to advancing stroke research by providing a comprehensive suite of meticulously validated models, empowering your quest for groundbreaking therapies.
Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Models
The permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) model is a widely recognized and indispensable preclinical tool for simulating focal cerebral ischemia, a common form of human ischemic stroke. By inducing a sustained reduction in blood flow to critical brain regions supplied by the middle cerebral artery (MCA), such as the striatum and cerebral cortex, this model faithfully recapitulates the complex pathophysiology of ischemic injury, including excitotoxicity, inflammation, and neuronal cell death.
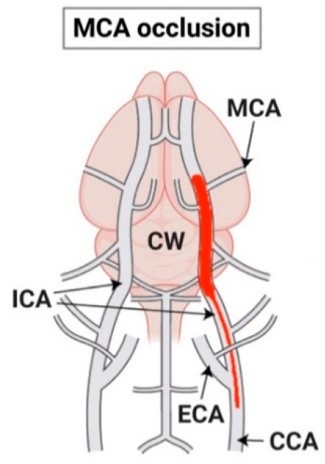 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the MCAO stroke model.1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the MCAO stroke model.1
Model Construction Steps
The construction of the pMCAO model involves a precise surgical procedure to permanently occlude the MCA, most commonly through an intraluminal filament approach or direct electrocoagulation. Our standardized methods ensure reproducible, reliable data.
01Anesthesia and Preparation
Animals are carefully anesthetized, with body temperature meticulously maintained using a feedback-controlled heating system. This minimizes physiological stress and reduces variability in infarct size.
02Surgical Exposure
A midline cervical incision provides access to the common carotid artery (CCA), external carotid artery (ECA), and internal carotid artery (ICA). All branches of the ECA are ligated, with the exception of the superior thyroid artery, which is temporarily occluded.
03MCA Occlusion (Intraluminal Filament)
For the intraluminal method, a nylon monofilament with a rounded, often coated, tip is gently inserted into the ECA, advanced into the ICA, and carefully guided cranially to occlude the MCA's origin. Proper positioning is confirmed by a slight resistance, and the filament is then secured by ligating the ECA stump.
04MCA Occlusion (Electrocoagulation)
As an alternative, direct electrocoagulation involves performing a small craniotomy above the MCA's trajectory. The distal MCA is then precisely exposed and permanently occluded using fine bipolar electrocoagulation, ensuring complete and irreversible vessel closure.
05Wound Closure and Recovery
Following occlusion, the incision is meticulously closed in layers. Animals are then allowed to recover in a controlled environment, with close monitoring for any signs of distress or neurological deficits. Post-operative analgesia is administered as needed to ensure animal welfare.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Translational Relevance: Closely mimics focal cerebral ischemia and large vessel occlusion without reperfusion seen in a significant subset of human stroke cases.
- Suitable for Chronic Studies: Enables robust investigation of long-term neurological deficits, chronic inflammation, and the efficacy of neurorestorative and regenerative therapies over extended periods.
- Robust and Reproducible: With our stringent standardized protocols and highly skilled surgeons, the model yields consistent infarct volumes and predictable neurological outcomes, minimizing inter-animal variability.
Limitations:
- Potential for Variability: Despite standardization, factors such as the extent of collateral circulation or minor differences in filament placement can subtly influence infarct size and neurological outcome.
- Limited Reperfusion Study: Not inherently suitable for investigating therapies dependent on reperfusion, such as thrombolytics, unlike transient MCAO models.
Evaluation Platform
Our state-of-the-art platform integrates biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, behavioral, and advanced imaging techniques. This provides a holistic assessment of therapeutic efficacy, quantifying infarct size, neurological function, and delving into stroke pathology and recovery mechanisms.
Test Indicators:
- Infarct Volume: Quantification via TTC staining or MRI.
- Neurological Deficit Scores: Standardized scales like modified neurological severity score (mNSS) or Bederson score.
- Behavioral Assessments: Rotarod, Cylinder Test, Corner Turn Test, Grip Strength, and Open Field test.
- Histopathological Analysis: H&E staining, Nissl staining for neuronal viability, and neuronal counts.
- Immunohistochemistry: Markers for neuronal survival (e.g., NeuN), glial activation (e.g., GFAP, Iba1), inflammation (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β), angiogenesis (e.g., CD31), and neurogenesis (e.g., DCX, BrdU).
- Molecular Biomarkers: qPCR, Western Blot, and ELISA for gene/protein expression and inflammatory mediators.
- Neurotransmitter Levels: Quantification of glutamate and GABA.
- Oxidative Stress Markers: Measurement of malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity.
- Synaptic Plasticity Markers: Assessment of proteins such as PSD-95 and synaptophysin.
Applications
- Simulate Diseases: Primarily focal cerebral ischemia, chronic ischemic stroke, and stroke complicated by relevant co-morbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, or aging.
- Evaluate Drugs: Comprehensive assessment of neuroprotective agents, anti-inflammatory compounds, immunomodulators, neurorestorative therapies, and various combination treatments.
- Investigate Treatments: Efficacy testing of pharmacological interventions, advanced cell-based therapies (e.g., mesenchymal stem cell transplantation), gene therapies, and physical rehabilitation strategies aimed at improving functional recovery and long-term outcomes.
- Validate Targets: Confirming the therapeutic potential and mechanistic role of novel molecular targets implicated in stroke pathophysiology and recovery processes.
- Discover Biomarkers: Identification and validation of potential biomarkers for early diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of therapeutic response in ischemic stroke.
Related Stroke Models
- tMCAO Model
- Photochemically induced Ischemic Stroke Model
- Collagenase induced Hemorrhagic Stroke Model
- Sodium Laurate induced Cerebral Microvascular Injury Model
Our Advantages
- Decades of Expertise: Years of specialized experience in neurobiology, stroke modeling, and preclinical drug development.
- Standardized Protocols: Rigorous, validated methodologies ensuring unparalleled reproducibility and data consistency across all studies.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: A broad spectrum of phenotypic, histological, and molecular endpoints for in-depth, multi-faceted analysis.
- Customized Solutions: Flexible model design and integration of comorbidities to precisely meet your unique research objectives.
- Collaborative Partnership: Expert scientific consultation from initial study design through to comprehensive data interpretation.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Leverage Creative Biolabs' extensive expertise and advanced pMCAO models to accelerate your stroke research. We are dedicated to providing precise, high-quality preclinical services tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and explore how our capabilities can support your therapeutic development goals.
FAQs
-
Q1: How does the pMCAO model differ from transient MCAO (tMCAO) models, and which is more suitable for my research?
A: pMCAO involves permanent MCA occlusion, mimicking human large vessel occlusions without reperfusion. tMCAO involves temporary occlusion followed by reperfusion. Choose pMCAO for chronic injury and long-term recovery studies, especially for therapies not reliant on reperfusion. Select tMCAO for acute reperfusion injury and thrombolytic agent evaluation.
-
Q2: Can you incorporate specific comorbidities like diabetes or hypertension into the pMCAO model?
A: Yes, we offer specialized pMCAO models integrating comorbidities like diabetes or hypertension. These models provide a more physiologically accurate and translationally relevant platform, enhancing the predictive power of your preclinical data.
-
Q3: How do you ensure the reproducibility and consistency of your pMCAO models?
A: Reproducibility is paramount. We achieve this through strict adherence to standardized surgical protocols by experienced surgeons, continuous physiological monitoring, meticulous post-operative care, and consistent animal housing. This minimizes variability, ensuring reliable outcomes.
-
Q4: Can I provide my own compounds for testing, and how do you handle drug administration?
A: Yes, clients can provide compounds. We have expertise in various administration routes (IV, IP, oral, subcutaneous) and osmotic pump implantation. Our team collaborates to determine the optimal, safest method for your therapeutic agent.
-
Q5: Can you assist with study design for my pMCAO project?
A: Absolutely. Our experienced scientific team collaborates from the outset to define objectives, select model variants, determine dosing, choose endpoints, and establish statistical plans. Our goal is to ensure your study is scientifically sound and efficient.
Published Data
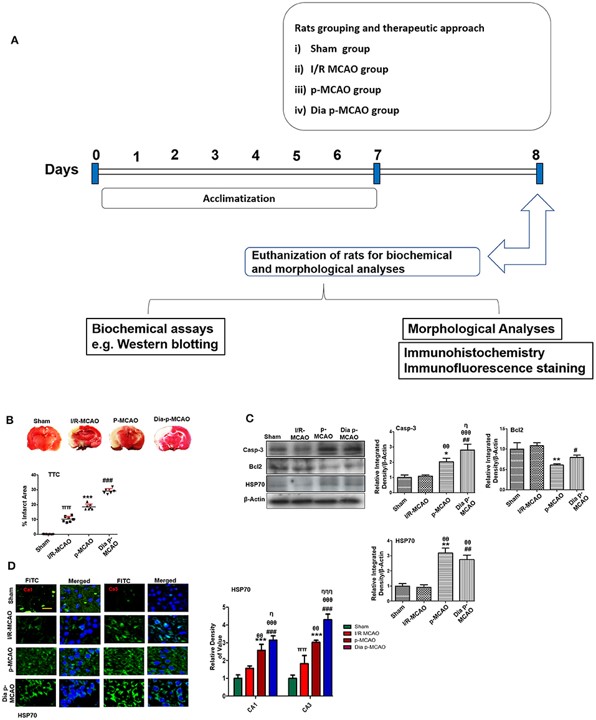 Fig.2 Relative effect of ischemia on brain infarction and cell apoptosis.2
Fig.2 Relative effect of ischemia on brain infarction and cell apoptosis.2
This research conducted a comprehensive pathological comparison of hippocampal changes in tMCAO and pMCAO rat models, including pMCAO with diabetic conditions. The study revealed distinct discrepancies in numerous pathological processes across these models, including neuronal apoptosis, glutamate excitotoxicity, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and neurotrophic changes. This highlights that pMCAO, especially when combined with comorbidities like diabetes, significantly impacts key molecular pathways, underscoring the model's importance for understanding complex stroke pathophysiology and for tailored therapeutic development.
References
- Lunardi Baccetto, Sarah, and Christian Lehmann. "Microcirculatory Changes in Experimental Models of Stroke and CNS-Injury Induced Immunodepression." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 20,20 5184. 19 Oct. 2019. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205184
- Shah, Fawad Ali et al. "Pathological Comparisons of the Hippocampal Changes in the Transient and Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Rat Models." Frontiers in neurology vol. 10 1178. 14 Nov. 2019. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.01178
For Research Use Only.
