3D Bio-printed Tissue Model
With the popularity of the 3Rs principle and the increasing demand for cost reduction, in vitro models are increasingly favored by researchers. The 3D bio-printed tissue model is a new and promising model for studying disease mechanisms and drug effects. Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in drug research, we have abundant modeling experience and in vitro and in vivo model libraries, and can provide comprehensive drug evaluation services.
3D Bio-printed Tissue Models
Evaluation of drugs in animals is often considered as an important and reliable means of obtaining information on the availability, toxicity, and metabolism of the drug. However, in reality, data obtained from animals is often not reflected correctly in the human body due to differences between animals and humans. In addition, animal testing is cumbersome and costly, so there is an urgent need for an effective and convenient alternative model. The 2D cell line is also a commonly used drug screening and evaluation model, but there are also problems such as the inability to simulate actual tissue behavior or its inability to be properly aligned in the human body, and 3D printing technology makes it possible to construct a 3D tissue or organ model similar to the real tissue environment. Therefore, it has great potential as an alternative of animal model. There are several ways to achieve 3D cell culture, such as microcontact printing, photolithography, 3D printing, and soft-lithography. It is worth noting that 3D printing is one of the most critical and attractive methods. It is only necessary to use a variety of biocompatible materials and cells and utilize a 3D model, the technology can construct complex 3D living tissue.
According to the principle that cells are released from the print head, 3D printing technology can be divided into three types: inkjet, microextrusion, and laser-assisted printing and stereolithography methods.
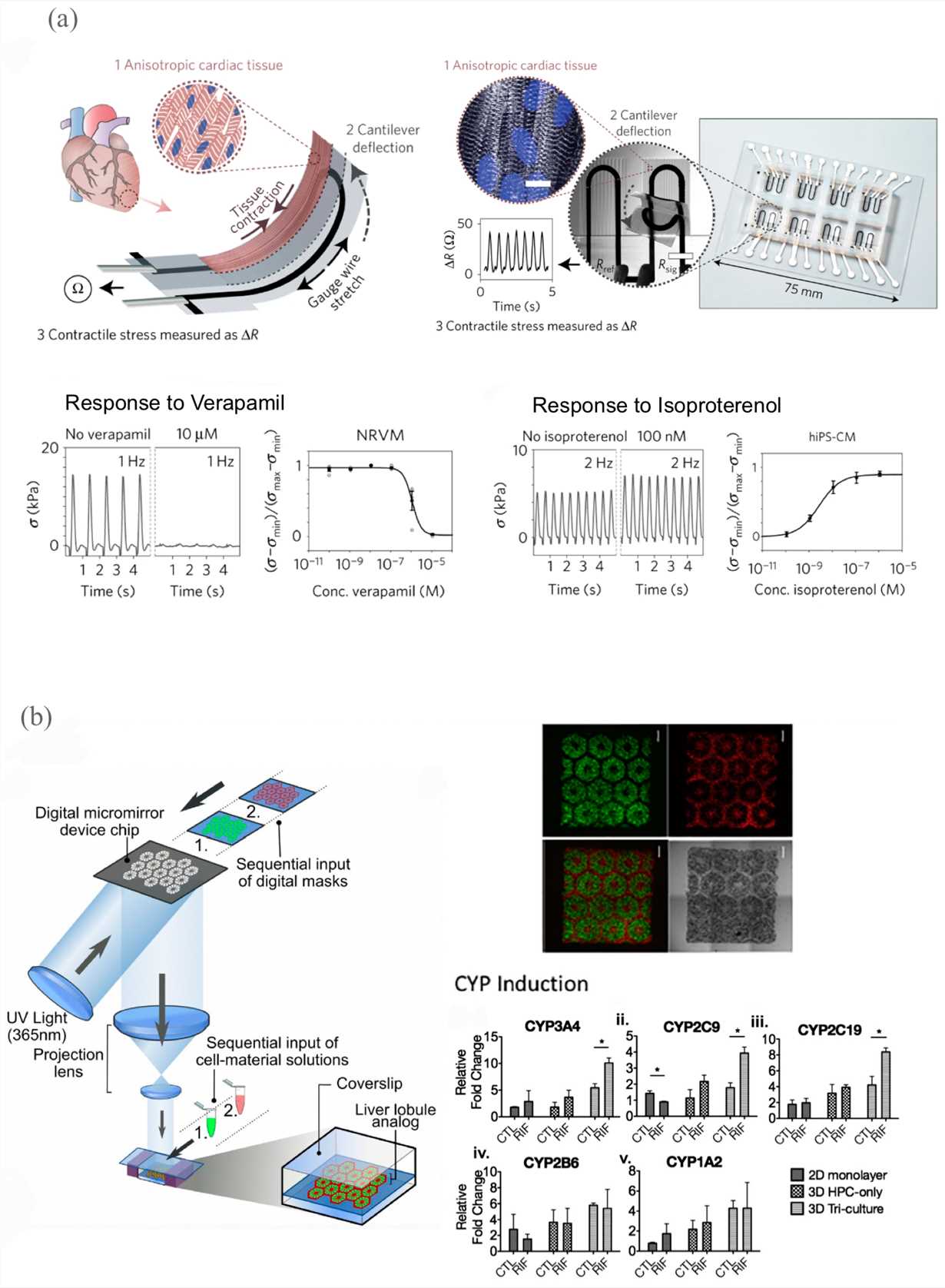 Fig.1 Bioprinted cardiovascular and liver models for drug development.1
Fig.1 Bioprinted cardiovascular and liver models for drug development.1
An important factor in achieving 3D tissue printing is biocompatible materials. In the printing process, a material in the form of a hydrogel called bioink is usually required to encapsulate the cells to protect the cells from external forces. These bioinks should satisfy the characteristics of suitable viscosity, sufficient mechanical strength and the like. Biocompatible materials are also used to build polymeric frameworks to create 3D structures. The most commonly used in 3D bioprinting technology are synthetic polymers and natural polymers. In general, synthetic polymers are often used to make mechanically stronger models with lower bioaffinity, while natural polymer produced models have stronger biological activity and higher similarity to natural tissues, but its mechanical properties are weaker.
3D Printed in vitro Tissue Models
| Embryonic carcinoma | Colon cancer | Skin tissue | Ovarian cancer | Breast cancer |
| Liver cancer | Cervical cancer | Liver lobule analog | Liver tissue | etc. |
Based on a rich library of 3D printed tissues models, we have established a series of drug development services, including drug screening, drug pharmacodynamics and ADME evaluation, drug toxicity testing, and various customized drug evaluation services.
Screening and evaluation of drugs using in vitro models is currently a trend in drug development. The 3D bio-printed tissue model is an emerging and promising technology in numerous in vitro models. As a CRO company with more than 10 years of experience in drug research and development, Creative Biolabs continues to absorb cutting-edge technologies and creatively apply them to drug screening and evaluation services, and is committed to providing the most reliable, most worry-free and cost-saving services for the pharmaceutical researchers with unremitting efforts.
References
- Lam, Ethan Hau Yin, et al. "3D bioprinting for next-generation personalized medicine." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.7 (2023): 6357. under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
