Diabetes Complication Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established models for evaluating the efficacy of treatments targeting these diabetes complications. These models cover various complications, including cardiovascular, renal, neurological, and ocular issues, enabling comprehensive preclinical research on the effects of potential therapeutic candidates. Our team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your research needs.
Introduction
Diabetes complications arise from the chronic effects of poorly managed or uncontrolled diabetes and can impact multiple organ systems. One of the most common complications is cardiovascular disease, as high blood sugar damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Diabetic neuropathy is another frequent complication, where nerve damage leads to symptoms like pain, numbness, and weakness, particularly in the limbs. Kidney damage, known as diabetic nephropathy, can eventually result in kidney failure, while diabetic retinopathy affects the eyes and can lead to blindness if not properly managed. Furthermore, diabetes can cause significant foot complications, such as ulcers and infections, often due to poor circulation and nerve damage, sometimes requiring amputations in severe cases.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a broad range of well-established rodent models for evaluating diabetes complications, including models for cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and diabetic foot ulcers. These models are carefully designed to replicate key aspects of human diabetes-related complications, providing an accurate platform for preclinical assessment of therapeutic candidates. We offer comprehensive evaluations of various parameters, including blood glucose levels, vascular health, nerve function, kidney function, and retinal damage, to ensure precise and reliable results. Our team of skilled scientists will collaborate closely with you throughout the research process, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring that your project receives the highest quality support. To learn more about the rodent diabetes complication models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
| Diabetes Complications Models | Simulates | Drug Evaluation | Animal species |
| Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Model | Type 1 Diabetes, Skin Defects, Wound Healing Impairment | Wound healing agents, Insulin therapies (e.g., insulin glargine), Topical treatments for skin defects, Anti-inflammatory drugs | Rat |
| Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model | Type 1 Diabetes, Foot Ulcers, Diabetic Complications | Wound healing agents, Insulin therapies, Antimicrobial agents, Topical treatments, Anti-inflammatory drugs | Rat |
| Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Peripheral Vascular Disease Model | Type 1 Diabetes, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Blood Flow Impairment | Vasodilators, Insulin therapies, Antithrombotic drugs, Anti-inflammatory drugs, Drugs targeting endothelial function | Rat |
| Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Cataract Model | Type 1 Diabetes, Cataract Formation | Anti-cataract agents, Insulin therapies, Antioxidants, Inflammation modulators, Proteinase inhibitors | Rat |
| High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Diabetic Nephropathy, Kidney Dysfunction | Anti-diabetic drugs (e.g., GLP-1 agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors), Renal protectants (e.g., angiotensin inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors), Anti-inflammatory drugs, Antioxidants | Mouse |
| db/db Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Diabetic Nephropathy, Kidney Dysfunction | Anti-diabetic drugs (e.g., metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors), Renal protectants (e.g., angiotensin inhibitors), Anti-inflammatory agents, Diuretics | Mouse |
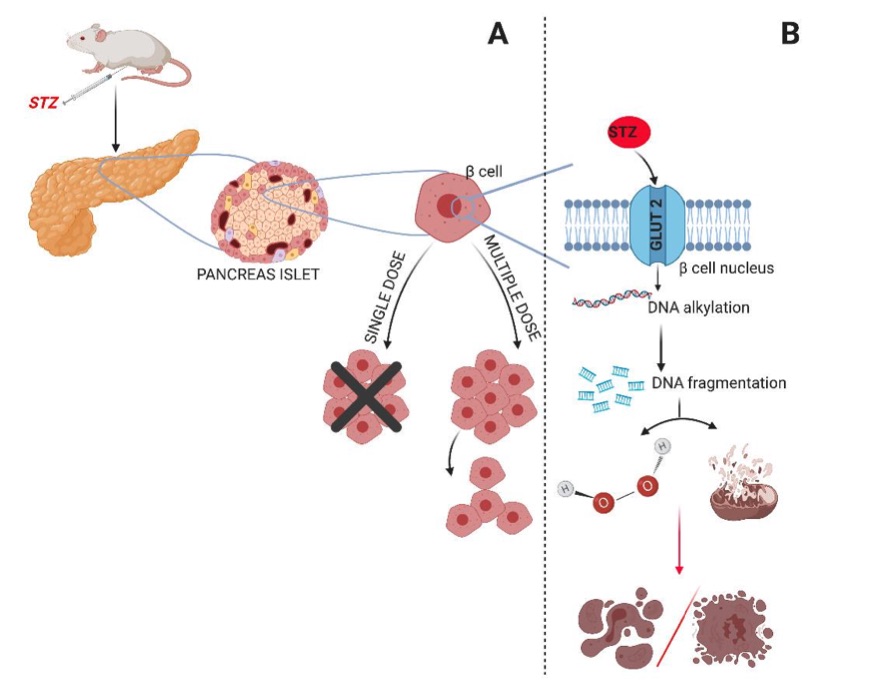 Fig. 1 Diabetes induction model with STZ. 1
Fig. 1 Diabetes induction model with STZ. 1
Measurements
We offer a comprehensive range of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in rodent diabetes complications models, utilizing advanced technologies to assess the effects of potential therapeutic candidates. Our evaluations include, but are not limited to:
-
General Observations:
- Body weight: Regular monitoring to assess changes in body weight due to metabolic disturbances.
- Blood glucose levels: Measurement of fasting blood glucose and postprandial glucose to assess glycemic control.
- Mortality rate: Tracking of survival rates throughout the study to evaluate the severity of complications.
- Food intake and water consumption: Monitoring to detect early signs of diabetes-related complications such as polyphagia or polydipsia.
-
Immunohistochemistry:
- Tissue-specific damage: Infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in organs affected by diabetes complications, such as the kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
- Tissue fibrosis or damage: Detection of fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy models or retinal changes in diabetic retinopathy.
-
Cytokine Profiling (e.g., ELISA):
- Inflammatory mediators: Expression levels of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β to evaluate inflammation associated with diabetes complications like nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy.
- Oxidative stress markers: Assessment of biomarkers like malondialdehyde (MDA) or advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that indicate oxidative damage.
-
Hematology Analysis and Serum Biomarkers:
- Kidney function biomarkers: Measurement of serum creatinine, urea, and urine albumin to assess diabetic nephropathy.
- Liver enzymes and lipid profiles: Analyzing liver function (e.g., AST, ALT) and lipid metabolism (e.g., cholesterol, triglycerides) in models with co-occurring metabolic dysfunction.
- Endothelial function biomarkers: Levels of nitric oxide or markers of endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular complications linked to diabetes.
-
Gene/Protein Expression Profiling via RT-qPCR and Western Blot:
- Insulin resistance markers: Expression of genes and proteins such as IRS-1, GLUT4, and PPARγ in muscle or adipose tissue to study insulin resistance.
- Angiogenesis and fibrosis markers: Expression of VEGF, TGF-β, and collagen in retinal or kidney tissues to assess diabetic retinopathy or nephropathy.
- Nerve damage markers: Expression of neuroinflammatory markers (e.g., GFAP, TNF-α) and neurotrophic factors to study diabetic neuropathy.
In addition to established diabetes complications models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models specifically designed to address unique research needs. Guided by scientific literature and prior studies, our team is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach for your research at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to diabetes complications models, we also offer a wide range of models for other diseases. These models enable comprehensive evaluation across diverse therapeutic areas.
Advantages
- State-of-the-Art Technologies: We employ cutting-edge technologies for accurate and reliable data collection. From gene and protein expression profiling to advanced immunohistochemistry and cytokine analysis, our methods ensure the highest quality results for evaluating drug efficacy and disease mechanisms.
- Comprehensive Support: From experimental design to data interpretation, our team provides full support throughout your project. We guide you in choosing the right models, designing experiments, and analyzing data to ensure that your research progresses smoothly and delivers actionable insights.
- Quality Assurance and Reliability: We prioritize the integrity of your results. Our models undergo rigorous validation and quality control to ensure they are reliable, reproducible, and scientifically sound. This commitment to quality allows us to provide trustworthy data that drives the success of your research.
- Timely Delivery: We understand the importance of meeting deadlines in research and development. Our efficient approach ensures timely results, so you can make informed decisions at each stage of your project without unnecessary delays.
- Collaborative Approach: We believe in working closely with our clients, maintaining open communication, and fostering strong collaborations. Our team is always ready to discuss challenges, suggest improvements, and provide scientific advice to help you achieve your research goals.
- Customer-Centric Focus: At every step of your project, we are dedicated to your success. We work hard to ensure customer satisfaction, offering personalized service, expert advice, and responsive support to address any needs or concerns that arise throughout the research process.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What types of disease models do you offer?
A: We offer a wide range of rodent disease models, including models for obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, liver diseases, and other metabolic disorders. These models are specifically designed to simulate human disease conditions for preclinical drug testing.
-
Q: How do I choose the right model for my research?
A: Our scientific team works closely with you to understand your research goals and recommend the most suitable model for your study. We consider factors such as the type of disease, therapeutic target, and specific evaluation metrics to ensure that the model meets your needs.
-
Q: What are the key parameters measured in your models?
A: We measure a variety of parameters depending on the disease model, including body weight, glucose levels, food intake, tissue composition, inflammation markers, cytokine profiles, organ function biomarkers, and molecular expression levels to assess drug efficacy and disease progression.
-
Q: Do you provide customized models for specific research needs?
A: Yes, we specialize in developing custom animal models tailored to specific research needs. If you have a particular disease condition or therapeutic approach in mind, our team can help design and implement a model that aligns with your study objectives.
-
Q: What technologies do you use for data analysis?
A: We use state-of-the-art technologies for data analysis, including RT-qPCR, Western blotting, ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and high-throughput sequencing. These techniques allow us to provide comprehensive insights into gene/protein expression, inflammation, metabolic changes, and other key markers.
-
Q: How long does it take to receive results?
A: The timeline for receiving results depends on the complexity of the study. However, we prioritize efficiency and aim to provide reliable results within a timeframe that meets your research goals, ensuring high-quality outcomes without unnecessary delays.
Published Data
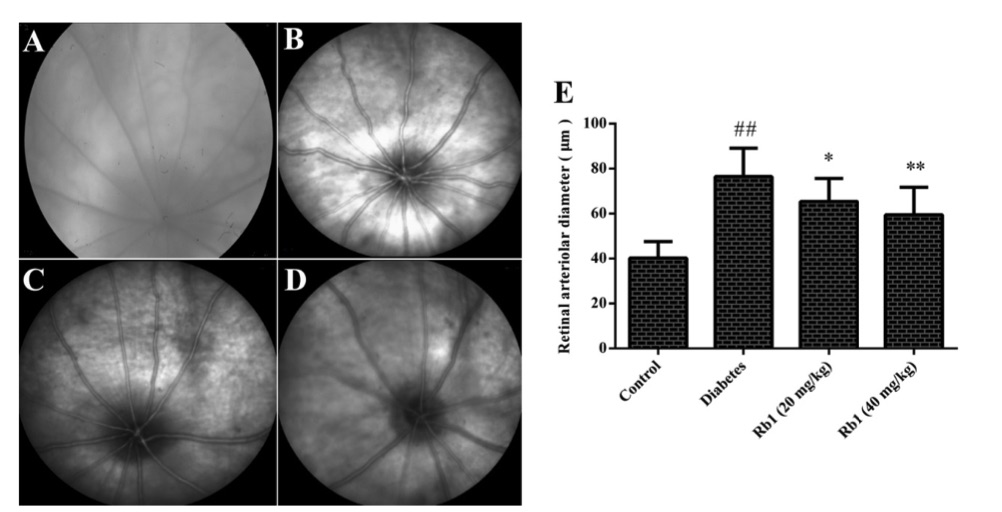 Fig. 2 Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the diameter of retinal vessels and fundus photography.2
Fig. 2 Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the diameter of retinal vessels and fundus photography.2
This study aimed to investigate the effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on diabetic retinopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The results showed that the diameter of retinal vessels in the diabetes group was significantly larger compared to the control group. However, treatment with ginsenoside Rb1 (20 and 40 mg/kg) led to a noticeable reduction in the retinal vessel diameter in the diabetic rats, indicating a potential therapeutic effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on diabetic retinopathy.
References
- Wszola, Michal et al. "Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in a Mouse Model (BALB/c) Is Not an Effective Model for Research on Transplantation Procedures in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes." Biomedicines vol. 9,12 1790. 29 Nov. 2021, DOI:10.3390/biomedicines9121790. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Dong, Changxia et al. "Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates diabetic retinopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats1." Acta cirurgica brasileira vol. 34,2 e201900201. 28 Feb. 2019, DOI:10.1590/s0102-8650201900201. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
