Thrombin induced Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Thrombotic diseases, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), pose significant global health challenges, leading to substantial morbidity and mortality. Developing effective antithrombotic therapies and understanding the intricate mechanisms of thrombus formation are crucial for improving patient outcomes.
At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to advancing this vital research by providing a variety of well-established and highly reliable in vivo models to rigorously evaluate the efficacy of novel antithrombotic agents.
Thrombin-Induced IVC Thrombosis Model
The thrombin-induced inferior vena cava (IVC) thrombosis model is a robust and widely utilized preclinical tool for investigating venous thrombosis and assessing the efficacy of antithrombotic compounds. This model precisely mimics key aspects of human venous thrombosis pathophysiology by combining localized blood flow stasis with induced hypercoagulability, reflecting Virchow's Triad.
Model Construction Steps
The construction strategy for the Thrombin-Induced IVC Thrombosis Model involves a controlled surgical intervention to induce both mechanical stasis and a procoagulant stimulus within the IVC. This dual approach ensures consistent and physiologically relevant thrombus formation, making it an ideal system for evaluating novel antithrombotic therapies.
01Surgical Exposure and Preparation
A suitable rodent model (e.g., rat or mouse) is anesthetized and carefully positioned on a heated platform to maintain physiological temperature throughout the procedure. A midline abdominal incision is performed to expose the IVC.
02Vessel Ligation
Two ligatures are strategically placed distal to the left renal vein around the posterior IVC, forming a snare-like configuration. All IVC side branches distal to the left renal vein and proximal to the bifurcation are meticulously ligated to ensure isolated blood flow.
03Thrombin Infusion
A precise dose of thrombin, a potent procoagulant enzyme (typically ranging from 100–2,000 µg/kg), is directly injected into the isolated IVC segment, often via the right femoral vein.
04Stasis Induction
Following a brief, precise interval (e.g., 10 seconds) after thrombin infusion, the pre-placed ligatures are tightened around the IVC to induce complete blood stasis within the segment. This combined stimulus rapidly initiates the formation of a stable thrombus.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Reproducibility: The controlled induction method ensures consistent thrombus formation, leading to reliable and reproducible experimental outcomes.
- Physiological Relevance: By incorporating both stasis and hypercoagulability, the model accurately reflects the multifactorial nature of human venous thrombosis.
- Quantitative Assessment: Thrombus characteristics, such as size, weight, and composition, can be precisely quantified, enabling robust evaluation of therapeutic interventions.
- Translational Potential: Data generated from this model frequently correlate well with clinical trial outcomes, enhancing its predictive value for drug development.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Utilizing rodent models offers a more economical approach for early-stage drug screening compared to larger animal models.
Limitations:
- Species Differences: As a rodent model, there are inherent physiological differences from humans that must be considered when extrapolating results.
- Acute Nature: The model typically induces acute thrombosis, which may not fully capture the complexities of chronic or recurrent thrombotic events seen in some clinical scenarios.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive evaluation platform for in-depth analysis of thrombus formation and therapeutic efficacy. Our state-of-the-art facilities support biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, and behavioral analyses, plus advanced imaging. This enables investigation of underlying mechanisms, detailed thrombus characterization, and visualization of development and resolution in vivo or ex vivo.
Key test parameters include:
- Thrombus weight, length, and volume.
- Histological assessment of thrombus composition (e.g., fibrin, red blood cells, platelets).
- Evaluation of vessel wall integrity and recanalization.
- Analysis of relevant biomarkers associated with coagulation, inflammation, and fibrinolysis.
Applications
- Disease Simulation: This model effectively simulates venous thromboembolism (VTE), including DVT and PE. By accurately recreating conditions leading to these critical events, it offers a crucial in vivo environment for studying disease progression and identifying therapeutic interventions.
- Drug Evaluation: As the gold standard, the model rigorously assesses novel anticoagulants (e.g., DOACs, heparins, vitamin K antagonists), thrombolytic agents for clot dissolution, and antiplatelet therapies. Its utility in demonstrating preventative or therapeutic potential is vital for advancing drug candidates.
- Mechanism Elucidation: The platform enables deep investigation into thrombus formation and resolution mechanisms, including roles of coagulation factors, platelet-endothelial interactions, inflammatory mediators, and fibrinolytic processes. This enhances understanding of thrombotic pathophysiology.
- Biomarker Discovery: Instrumental in identifying and validating novel biomarkers, the model supports early diagnosis, risk prediction, disease monitoring, and therapeutic response assessment, accelerating development of critical diagnostic and prognostic tools.
Related Thrombosis Models
- Transient Blood Flow Occlusion induced Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis Model
- Arteriovenous Fistula Thrombosis Model
- Fe2O3 induced Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Foreign Matter induced Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Ferric Chloride induced Thrombosis Model
Our Advantages
- Deep Scientific Acumen: Our team comprises expert biologists and pharmacologists with extensive experience in hemostasis and thrombosis, ensuring rigorous study design.
- State-of-the-Art Facilities: We utilize cutting-edge laboratories equipped with advanced analytical platforms for comprehensive thrombus characterization.
- Customized Study Design: We collaborate closely with clients to develop tailored protocols that align precisely with their specific research objectives.
- Robust Quality Control: Our stringent quality control measures and adherence to GLP-like principles guarantee reliable and high-quality data.
- Accelerated Timelines: Optimized workflows and dedicated project management ensure efficient execution and timely delivery of results.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to empowering your research endeavors. Our deep expertise and advanced capabilities in the Thrombin-Induced IVC Thrombosis Model enable us to provide exceptional preclinical services. Contact us today to discuss how our specialized models can accelerate your journey toward groundbreaking antithrombotic therapies.
FAQs
-
Q1: Why is the thrombin-induced IVC thrombosis model considered a gold standard for venous thrombosis research?
A: This model is highly regarded because it accurately replicates the key pathological factors of human venous thrombosis: blood flow stasis and hypercoagulability. The controlled application of thrombin combined with vessel ligation ensures consistent and reproducible thrombus formation, making it an ideal and reliable platform for evaluating the efficacy of novel antithrombotic compounds in a physiologically relevant setting.
-
Q2: How is thrombus formation quantitatively assessed in studies utilizing this model?
A: Thrombus formation can be precisely quantified using various methods. Commonly, researchers measure the thrombus weight, length, and volume. Histological analysis provides insights into the thrombus composition, identifying components such as fibrin, red blood cells, and platelets. These quantitative measurements are crucial for objectively evaluating the impact of therapeutic agents.
-
Q3: Can this model be used to evaluate both the prevention and treatment of thrombosis?
A: Absolutely. The thrombin-induced IVC thrombosis model is versatile enough to assess both prophylactic and therapeutic strategies. For prevention studies, compounds are administered before thrombus induction. For treatment studies, agents are given after the thrombus has formed, allowing for the evaluation of their ability to dissolve existing clots or prevent their growth.
-
Q4: Can you customize the thrombin-induced IVC thrombosis model to fit unique research objectives?
A: Yes, customization is a core aspect of our service. We understand that each research project has unique requirements. Our expert team collaborates extensively with clients to tailor study protocols, including variations in thrombin dosage, stasis duration, animal strain, and endpoint analyses, to precisely match specific research objectives and maximize experimental relevance.
-
Q5: How do you ensure the high reproducibility of results when performing studies with this model?
A: Reproducibility is ensured through meticulous standardization of every aspect of the model. This includes precise control over surgical techniques, consistent thrombin preparation and administration, accurate timing of stasis induction, and standardized post-procedure care. Our stringent quality control measures and experienced personnel minimize variability, guaranteeing reliable and consistent data.
Published Data
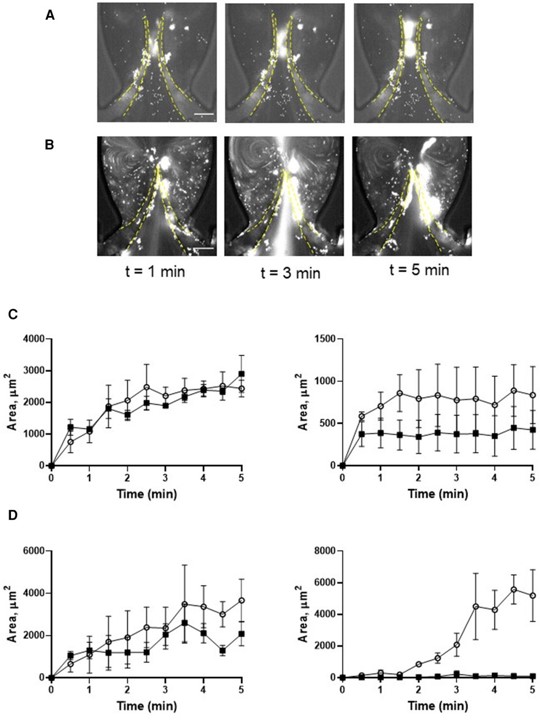 Fig.1 Deposition of platelets is increased by thrombin.1
Fig.1 Deposition of platelets is increased by thrombin.1
This research utilized a microfluidics vein-on-a-chip model that mimics the hydrodynamics and endothelial environment of a vein. The project results demonstrated that thrombin activation significantly enhanced platelet accumulation at valve leaflets, and this accumulation was critically mediated by the interaction between platelet GPIba and the A1 domain of von Willebrand factor. This highlights the importance of platelet-VWF interactions in venous thrombus development and the model's capacity for detailed mechanistic studies of prothrombotic responses.
Reference
- Baksamawi, Hosam Alden et al. "Platelet accumulation in an endothelium-coated elastic vein valve model of deep vein thrombosis is mediated by GPIbα-VWF interaction." Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine vol. 10 1167884. 27 Apr. 2023. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2023.1167884
For Research Use Only.
