Cerulein induced Chronic Pancreatitis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Chronic Pancreatitis (CP) is a progressive inflammatory disease of the pancreas characterized by irreversible morphological changes, leading to chronic pain, pancreatic insufficiency, malabsorption, and in some cases, diabetes mellitus. Unlike acute pancreatitis, CP involves persistent inflammation that gradually replaces functional pancreatic tissue with fibrotic tissue. The disease can result from various etiologies, including prolonged alcohol consumption, genetic mutations (such as PRSS1, SPINK1), autoimmune disorders, obstructive causes (like pancreatic duct strictures), or idiopathic factors. CP is generally categorized into different types based on the underlying cause: alcoholic CP, idiopathic CP, hereditary CP, autoimmune pancreatitis, and obstructive CP. Clinical manifestations vary depending on the stage of the disease but commonly include abdominal pain, weight loss, steatorrhea, and glucose intolerance. Despite its chronic nature, early diagnosis and therapeutic intervention are crucial for slowing progression and improving quality of life. Creative Biolabs offers well-established and customizable rodent models of Chronic Pancreatitis to support drug discovery and preclinical evaluation. These models are designed to replicate various aspects of human CP and provide a reliable platform for assessing therapeutic efficacy, mechanisms of action, and safety profiles of candidate drugs.
Disease Models and Applications
The Cerulein-Induced Chronic Pancreatitis Model is a well-established experimental approach to simulate chronic pancreatitis in rodents. This model is constructed by administering cerulein, a synthetic analog of cholecystokinin, to induce repetitive episodes of pancreatitis, leading to sustained pancreatic injury and fibrosis. The model mimics key features of human CP, such as inflammation, acinar cell injury, and fibrosis. Its advantages include the ability to evaluate the inflammatory response and the progression of pancreatic damage over time. However, the model also has limitations, such as the lack of complete replication of the human disease's complexity, and it might not fully capture the autoimmune components seen in some CP cases.
Simulates: The Cerulein-Induced Chronic Pancreatitis Model simulates chronic pancreatitis, a progressive disease that includes inflammation, acinar cell injury, fibrosis, and ultimately, pancreatic dysfunction. It serves as a reliable model for studying the pathophysiology of CP and its long-term consequences on the pancreas.
Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate a wide range of pharmacological interventions for treating chronic pancreatitis. These include anti-inflammatory agents, antioxidant therapies, fibrotic inhibitors, and pain-relieving compounds, as well as drugs aimed at reducing pancreatic damage and restoring pancreatic function. It is particularly useful for testing the efficacy of novel compounds aimed at mitigating the symptoms and progression of CP.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the Cerulein-Induced Chronic Pancreatitis Model, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: body weight, mortality rate, stool consistency, gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Immunohistochemistry: Infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in pancreatic tissues.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and pancreatic enzymes (amylase, lipase).
- Gene/protein expression profiling via RT qPCR and Western blot techniques: Analysis of key genes and proteins involved in inflammation, fibrosis, and apoptosis.
In addition to established chronic pancreatitis models, our scientific team specializes in developing customized animal models tailored to specific research needs. We provide expert guidance on experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a robust and comprehensive approach to your research.
Related Services
In addition to chronic models, acute pancreatitis models are essential for studying early-stage inflammatory responses and testing fast-acting therapeutic agents. The following section introduces commonly used acute pancreatitis models and their applications.
Advantages
- Extensive Experience: Our team has years of expertise in developing and applying rodent models for both acute and chronic pancreatitis, ensuring reliable and reproducible results.
- Comprehensive Services: From model development and validation to drug efficacy evaluation and data analysis, we provide end-to-end preclinical research support.
- Customized Solutions: We tailor experimental designs and animal models based on your specific research needs, target pathways, or drug delivery methods.
- Advanced Technology Platforms: We utilize cutting-edge techniques, including ELISA, RT-qPCR, Western blotting, histopathology, and cytokine profiling, to deliver in-depth data.
- Strict Quality Control: All studies are conducted under standardized protocols and monitored closely to ensure data accuracy, reproducibility, and compliance with ethical guidelines.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q1: What animal species are used in your Cerulein-Induced Chronic Pancreatitis model?
A1: We primarily use mice and rats for this model, as both species respond reliably to cerulein-induced pancreatic injury and fibrosis, and are well-characterized in the literature.
-
Q2: How long does it take to establish a chronic pancreatitis model using cerulein?
A2: Typically, repeated intraperitoneal injections of cerulein are administered over 4 to 6 weeks to induce chronic pancreatic injury and fibrosis.
-
Q3: Can the model be customized for specific research goals?
A3: Yes. We can adjust dosing regimens, duration, and combine with other interventions (e.g., high-fat diet, alcohol exposure) to meet your project's objectives.
-
Q4: What endpoints can you measure in this model?
A4: We evaluate clinical signs, histopathological changes, inflammatory markers (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6), fibrosis indicators (e.g., collagen deposition), and serum enzymes (amylase, lipase), among others.
-
Q5: Do you provide support with experimental design and data interpretation?
A5: Absolutely. Our scientific team works collaboratively with clients throughout the study—from model selection and design to final data analysis and reporting.
Published Data
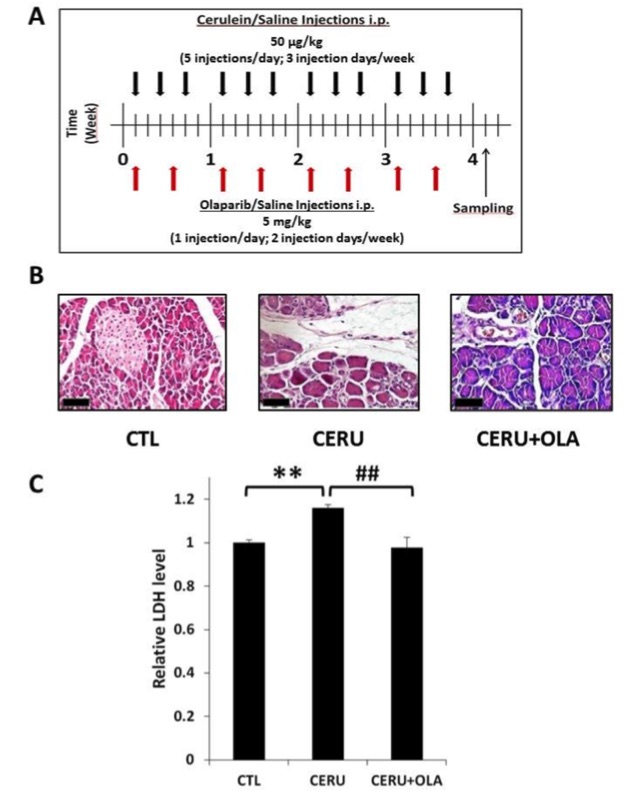 Fig.1 The poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib reduces pancreatic injury in cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis.1
Fig.1 The poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib reduces pancreatic injury in cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis.1
The study investigated the therapeutic effects of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib on pancreatic injury in a cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis mouse model. (A) The experimental protocol involved repeated intraperitoneal injections of cerulein, with black arrows indicating treatment days. Olaparib was administered at a dose of 5 mg/kg twice per week, as marked by red arrows. Tissue and serum samples were collected four days after the final cerulein injection. Control mice received saline injections. (B) Pancreatic tissues were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Microscopic examination (40× magnification; scale bar 50 µm) showed that control mice exhibited normal pancreatic architecture, while cerulein-treated mice displayed significant histopathological damage, including interstitial edema, mononuclear cell infiltration, fibroplasia, acinar cell degeneration, and lobular atrophy. In contrast, olaparib-treated mice demonstrated substantial improvement in these parameters. (C) Serum LDH levels, an indicator of tissue damage, were quantified in all groups.
Reference
- El-Hamoly, Tarek et al. "Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 Promotes Inflammation and Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Chronic Pancreatitis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 22,7 3593. 30 Mar. 2021, DOI:10.3390/ijms22073593. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
