Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established, reliable models for evaluating diabetes complications. Our services enable the thorough testing of new drugs and therapies targeting diabetic wounds, neuropathy, retinopathy, and other diabetes-related complications.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus, particularly Type 1 and Type 2, is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels due to impaired insulin production or function. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes leads to a range of severe complications that affect multiple organ systems. Diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, and cardiovascular disease are common long-term consequences of poorly managed blood glucose levels. Additionally, diabetic patients often suffer from impaired wound healing and increased susceptibility to infections, particularly in the skin, making diabetes-related skin defects a significant concern. These complications arise due to chronic hyperglycemia, which disrupts normal tissue repair mechanisms and increases inflammatory responses, impairing the body's ability to heal wounds effectively. Diabetic skin defects, including delayed wound healing and poor response to burns, are common complications in individuals with diabetes and can significantly impact their quality of life. Therefore, investigating the mechanisms underlying these complications is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat diabetic complications.
Disease Models and Applications
The Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Model is an established method to simulate the effects of Type 1 diabetes on skin healing. STZ is administered to induce hyperglycemia in rodents, leading to complications such as poor wound healing and skin defects. The model is beneficial in studying delayed healing responses, tissue regeneration, and evaluating therapeutic interventions for diabetic wounds and burns. One of the key advantages is its ability to mimic the chronic hyperglycemia observed in human diabetic conditions, providing valuable insights into the pathophysiology of skin defects in diabetes. However, a limitation is the variability in response, as STZ induced diabetes can lead to varying degrees of severity in skin defects among different subjects, which may influence results.
- Simulates: The STZ induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Model simulates complications arising from poor wound healing, infections, and increased susceptibility to burns in Type I diabetes. It is an essential tool for understanding how diabetes exacerbates skin defects and impairs tissue regeneration.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate a variety of drugs aimed at improving wound healing, skin regeneration, and reducing infection rates in diabetic conditions. It can assess the efficacy of pharmaceutical compounds, including growth factors, anti-inflammatory agents, and novel wound-healing accelerants, in a diabetic context.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Model, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Monitoring body weight, skin condition, wound area, and healing rate.
- Histological examination: Evaluating skin tissue for regeneration, collagen deposition, and inflammatory cell infiltration.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of cytokines and immune cell infiltration (e.g., macrophages, T-cells) in the wound tissue.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Quantification of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: Analyzing the expression of growth factors (e.g., VEGF), collagen, and ECM proteins through RT-qPCR and Western blot techniques.
Additionally, we offer real-time monitoring of wound healing progression and detailed analysis of tissue regeneration, aiding researchers in evaluating the effectiveness of novel drug candidates.
Related Services
Aside from the STZ induced diabetic skin defect model, we also offer other methodologies to induce diabetes complications, including models for diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy. These alternative models provide diverse platforms for evaluating the multifaceted nature of diabetes and its complications.
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Peripheral Vascular Disease Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Cataract Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model
- db/db Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model
Advantages
- Expertise and Customization: We provide extensive expertise in developing specialized, customizable animal models tailored to your research needs, ensuring the most relevant and accurate outcomes.
- Comprehensive Services: Our services cover all stages of research, from model selection and experimental design to data analysis, providing comprehensive support for your projects.
- Well-Established Models: We offer a wide range of validated and reliable diabetes complication models, including those for neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, and skin defects, allowing for efficient drug testing and efficacy evaluation.
- Cutting-Edge Technologies: Our models incorporate the latest technologies and advanced techniques, including immunohistochemistry, gene/protein expression profiling, and cytokine analysis, ensuring precise and detailed results.
- High-Quality Results: We prioritize reproducibility and accuracy, ensuring that the results from our models provide reliable insights into drug efficacy and diabetes complications.
- Timely and Professional Support: Our dedicated scientific team provides expert guidance and prompt assistance throughout your research, ensuring your project runs smoothly and on schedule.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What types of diabetes complications can your models simulate?
A: Our models simulate a wide range of diabetes complications, including diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, skin defects, and delayed wound healing, providing valuable insights into these chronic conditions.
-
Q: Can I use your models to test new drugs for diabetes-related skin defects?
A: Yes, our STZ induced diabetic skin defect models are specifically designed to evaluate the efficacy of new treatments for diabetic wounds, skin defects, and burns.
-
Q: How reliable are the results from your diabetes complication models?
A: We ensure the highest standards of reliability and reproducibility through validated models and rigorous testing protocols, providing accurate data to support your research.
-
Q: What kind of measurements and data analysis do you provide?
A: We offer a variety of measurements including histology, cytokine profiling, gene expression analysis, and general observations, and our team provides expert guidance for detailed data analysis.
-
Q: Can you customize models to suit my specific research needs?
A: Yes, we specialize in tailoring models to meet the specific requirements of your research, ensuring the most relevant conditions for evaluating diabetes complications and drug efficacy.
Published Data
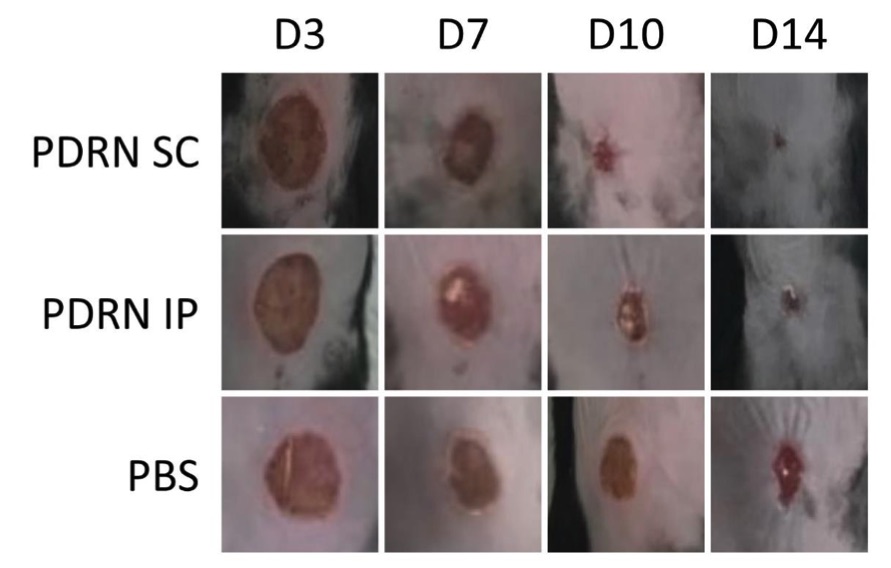 Fig. 1 Gross examinations of the diabetic wounds were performed at 3, 7, 10 and 14 days.1
Fig. 1 Gross examinations of the diabetic wounds were performed at 3, 7, 10 and 14 days.1
The efficacy of polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) in promoting diabetic wound healing was assessed using a murine model of streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetes. Diabetic wounds were created in mice, which were then divided into three groups: the PDRN subcutaneous (PDRN SC), PDRN intraperitoneal (PDRN IP), and PBS control (PBS) groups. The PDRN SC and PDRN IP groups received subcutaneous and intraperitoneal injections of PDRN, respectively, while the PBS group received subcutaneous PBS injections. After euthanasia, time-dependent changes in wound diameter and histological scores were measured. The results showed that both the PDRN SC and PDRN IP groups exhibited significantly smaller wound diameters and higher histological scores compared to the PBS group, indicating improved wound healing. These findings suggest that PDRN may effectively promote the healing of diabetic wounds in the STZ induced diabetes model.
Reference
- Yun, Jiyoung et al. "Efficacy of Polydeoxyribonucleotide in Promoting the Healing of Diabetic Wounds in a Murine Model of Streptozotocin induced Diabetes: A Pilot Experiment." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 24,3 1932. 18 Jan. 2023, DOI:10.3390/ijms24031932. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
