Metabolic/Liver Disease Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs provides a range of advanced and reliable models for evaluating the pharmacological effects of therapies targeting metabolic/liver diseases. We offer genetically engineered and induced animal models that replicate key aspects of metabolic/liver disorders, such as insulin resistance, obesity, and hyperlipidemia. These models enable comprehensive preclinical studies to assess drug efficacy, safety, and mechanism of action, helping accelerate the development of effective treatments.
Introduction
Metabolic diseases refer to a group of disorders that disrupt the normal processes of metabolism, including the regulation of glucose, fat, and energy balance. Key metabolic diseases include diabetes mellitus (Type 1 and Type 2), obesity, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, and disorders like hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. These diseases are often interconnected and can lead to serious health complications such as cardiovascular diseases, fatty liver, and kidney dysfunction. Liver diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that affect liver function, leading to impaired detoxification, metabolism, and nutrient processing. These diseases can be caused by infections, excessive alcohol consumption, metabolic disorders, genetic factors, or exposure to toxins. Metabolic diseases often result from genetic factors, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, or a combination of these. They affect the body's ability to properly process and store nutrients, leading to altered blood sugar levels, abnormal lipid metabolism, and increased risk of systemic diseases.
Disease Models
Creative Biolabs offers a broad selection of well-established models for metabolic/liver diseases, including models for obesity, diabetes, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome. These models are carefully developed to replicate key aspects of human metabolic/liver disorders, providing an accurate platform for preclinical evaluation of therapeutic candidates. Our models are accompanied by comprehensive assessments of metabolic parameters such as glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity, body weight, and lipid profiles, ensuring detailed insights into the effects of potential treatments. Our team of skilled scientists will support you throughout the project, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring high-quality and dependable results. To learn more about the metabolic disease models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
- Non-Obese Type I Diabetes Mouse Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetes Model
- Alloxan induced Type I Diabetes Model
- db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model
- Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR)-Diabetic Model
- STZ-NA induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetes Model
- Combined Spleen & Partial Pancreas Resection & Glucocorticoid induced Type II Diabetes Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Peripheral Vascular Disease Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Cataract Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model
- db/db Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model
- Diet induced Obesity (DIO) Mouse NASH Model
- High-Fat Diet induced NASH Model
- Methionine Choline-Deficient (MCD) Diet induced NASH Model
- Choline-Deficient L-Amino Acid-Defined (CDAA) Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet & Fructose induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Fructose induced NASH Model
- Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) & High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & CCL₄ induced NASH Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat induced NASH Model
- MC4R KO Mouse Model
- LDLR KO Mouse Model
- CCL₄ induced Acute Liver Injury Model
- Concanavalin A (Con A) induced Acute Liver Injury Model
- Poly I:C induced Acute Liver Injury Model
- Acetaminophen (APAP) induced Acute Liver Injury Model
- Alcohol induced Acute Liver Injury Model
- Ischemia-Reperfusion induced Liver Injury Model
- Alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) induced Acute Liver Injury Model
- DDC (3,5-Diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-Dihydrocollidine) induced Acute Liver Injury Model
- CCL₄ induced Liver Fibrosis/Cirrhosis Model
- Thioacetamide (TAA) induced Liver Fibrosis/Cirrhosis Model
- Bile Duct Ligation (BDL) induced Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Model
- α-Naphthyl isothiocyanate (ANIT) induced Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Model
- 3,5-Diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-Dihydrocollidine (DDC) induced Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Model
- High-Fat & High Cholesterol & High Bile Salts induced Pancreatic Fibrosis Model in db/db Mice
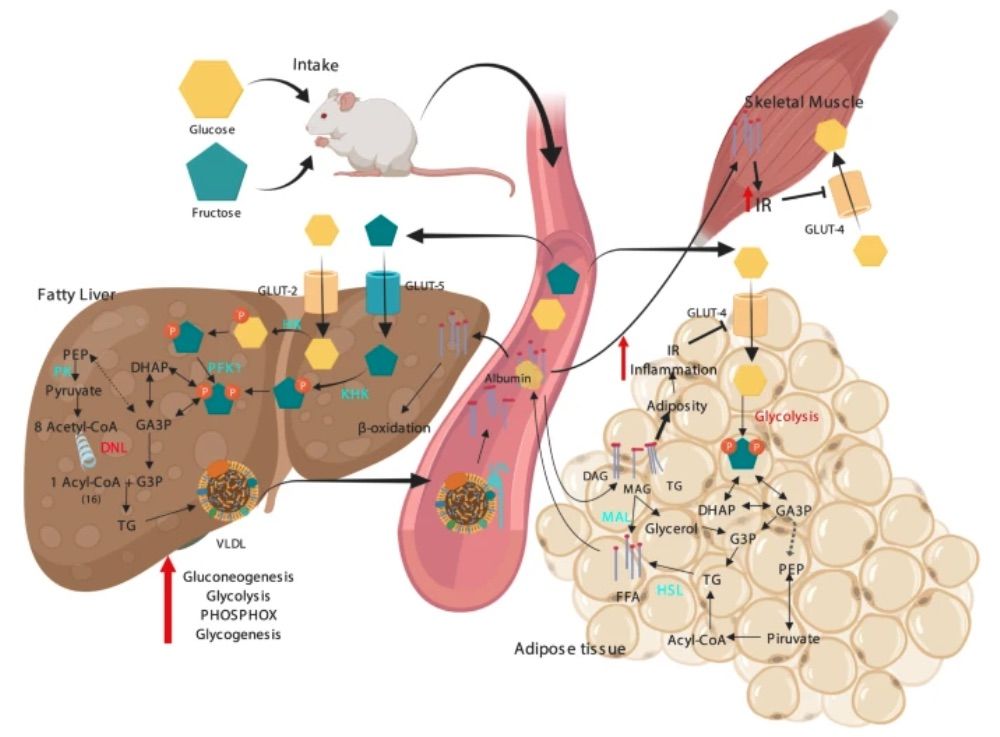
Fig. 1 Metabolic alterations induced by a high carbohydrate diet.1
Our Capabilities
- Animals: Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Rabbit, Cat, Dog, NHPs.
-
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in metabolic/liver disease models, employing a range of advanced techniques, including but not limited to:- General observations: body weight, food/water intake, activity levels, and mortality rate.
- Glucose tolerance test (GTT): Assessment of insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): Monitoring blood glucose levels post-glucose administration to evaluate metabolic function.
- Serum biomarkers: Levels of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), bilirubin, triglycerides, cholesterol, and fasting blood glucose.
- Histopathological analysis: Examination of liver tissue for fatty infiltration, fibrosis, and inflammation.
- Immunohistochemistry: Infiltration of immune cells (e.g., macrophages, T-cells) in liver tissues.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blotting to assess the expression of genes and proteins involved in metabolic pathways (e.g., PPAR-γ, SREBP-1c).
- Lipid profiling: Quantification of serum lipids, including HDL, LDL, and total cholesterol.
- Liver histology: Liver fibrosis and steatosis evaluation via H&E and Masson's trichrome staining.
In addition to our established metabolic/liver disease models, we also specialize in developing novel animal models customized to meet specific research objectives, guided by relevant literature and previous studies. Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data interpretation, ensuring a tailored approach to your research at every phase.
Related Services
In addition to metabolic and liver disease models, we also offer a wide range of models for other diseases. These models enable comprehensive evaluation across diverse therapeutic areas.
Musculoskeletal Disease Models
Inflammation & Immunological Disease Models
Infectious Disease Animal Models
Ear Disorder Models
Reproductive System Disease Models
Skin Disease Models
Advantages
- Extensive Expertise: With years of experience in preclinical research, we specialize in developing and providing advanced disease models, offering deep insights across multiple therapeutic areas, including metabolic, liver, cancer, and autoimmune diseases.
- Tailored Solutions: We understand that every research project is unique. Our team works closely with you to design customized experimental protocols and select the most suitable models, ensuring the best fit for your specific research needs.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: We employ the latest technologies in genomics, histopathology, immunohistochemistry, and molecular analysis, delivering comprehensive and accurate results that are critical for successful drug development.
- Reliable and Reproducible Results: Our well-established models are carefully validated, ensuring consistent and reproducible data. This high level of reliability helps accelerate your research timeline and improve decision-making in drug development.
- Comprehensive Support: From project inception to data analysis, our team provides continuous support throughout the entire research process, ensuring high-quality, scientifically sound outcomes at every stage.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What types of disease models do you offer?
A: We offer a wide range of disease models, including those for metabolic diseases, liver diseases, cancer, autoimmune disorders, and more. Each model is carefully optimized to reflect human disease conditions for accurate preclinical evaluations.
-
Q: Can you customize disease models for my specific research needs?
A: Yes, we specialize in developing customized disease models tailored to your research requirements. Our team works with you to create models that best fit your study objectives.
-
Q: What technologies do you use to analyze disease models?
A: We utilize advanced technologies like immunohistochemistry, gene/protein expression profiling (RT-qPCR, Western blot), cytokine profiling (ELISA), histopathology, and metabolic assays to deliver comprehensive, reliable data.
-
Q: How can I get started with a project?
A: To get started, simply contact our team to discuss your research goals. We'll help you design your study, select the appropriate models, and guide you through the process from start to finish.
-
Q: Do you provide support throughout the project?
A: Yes, our experienced scientific team provides full support at every stage of the project, from experimental design and model selection to data interpretation and analysis.
-
Q: What are the advantages of using your models?
A: Our models are highly reproducible, customizable, and based on cutting-edge technologies. We also offer reliable and accurate preclinical data, helping you move quickly from early-stage research to clinical trials.
Published Data
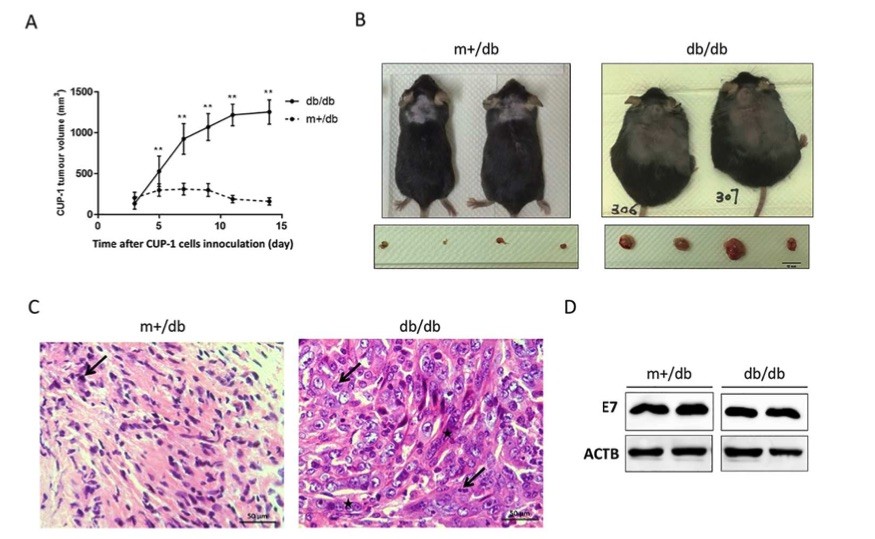 Fig 2. Diabetic (db/db) mice promoted CUP-1 xenograft growth.1
Fig 2. Diabetic (db/db) mice promoted CUP-1 xenograft growth.1
To investigate the impact of diabetes on HPV-16 E7-mediated tumorigenesis, CUP-1 cells were subcutaneously injected into diabetic db/db mice and non-diabetic m+/db littermates. Similar to nude mice, visible tumor masses appeared on day 3 following CUP-1 cell inoculation. Notably, the tumor growth kinetics differed significantly between the two groups. From day 3 to 7, the tumor volume in db/db mice increased six-fold, while in non-diabetic m+/db mice, the tumor volume only increased by 1.5-fold and began to regress after day 7 (Fig. 2A). By day 29, CUP-1 tumors were completely cleared in all m+/db mice. On day 14, the tumor volume in db/db mice was nearly four times larger than in the m+/db mice. Histological analysis of the excised tumors (Fig. 2C) revealed that both db/db and m+/db CUP-1 xenografts exhibited an increased nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio and cell density, typical features of dysplasia and malignant cells. Tumors from db/db mice showed pronounced nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic figures, indicating increased mitotic activity and excessive cell proliferation, characteristic of malignant neoplasms. Additionally, western blot analysis of excised CUP-1 xenografts confirmed successful E7 expression in both db/db and m+/db mice. Overall, db/db mice enhanced CUP-1 tumor growth and delayed tumor clearance.
References
- Rodríguez-Correa, Eduardo et al. "Biochemical and nutritional overview of diet induced metabolic syndrome models in rats: what is the best choice?" Nutrition & diabetes vol. 10,1 24. 2 Jul. 2020, DOI:10.1038/s41387-020-0127-4. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- He, Lan et al. "Increased Growth of a Newly Established Mouse Epithelial Cell Line Transformed with HPV-16 E7 in Diabetic Mice." PloS one vol. 11,10 e0164490. 17 Oct. 2016, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164490. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
