Gastric Ulcer Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Gastric ulcers are open sores that develop on the stomach lining due to an imbalance between the stomach's protective mechanisms and aggressive factors like acid. They are commonly induced by factors such as Helicobacter pylori infection, excessive use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and stress. To study gastric ulcers, a variety of preclinical models are employed. These include chemical models using agents like ethanol or acetic acid to induce ulceration, as well as models utilizing H. pylori infection or stress-induced ulcers. Rodent models are most used for evaluating the effects of drugs, providing insights into the ulcerative process, tissue repair, and the role of various signaling pathways. Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive services for establishing gastric ulcer models, tailored to meet specific therapeutic needs. These models can be utilized to assess drug efficacy, perform histological analysis, and evaluate biomarkers of inflammation and healing. Our platform includes both acute and chronic ulcer models to ensure a thorough understanding of therapeutic responses. By leveraging these models, researchers can advance the development of treatments targeting gastric ulcer disease.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive range of well-established rodent models for gastric ulcer research, designed to mimic the human condition of gastric ulcers induced by factors like ethanol, NSAIDs, and H. pylori infection. These models are carefully crafted to replicate the pathophysiology of gastric ulcers, enabling accurate assessment of potential therapeutic candidates. Our service includes thorough evaluations of ulcer formation, healing processes, and inflammation, providing essential insights into drug efficacy. Our experienced team will assist you throughout the project, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring precise and reliable results. To explore more about our gastric ulcer models for preclinical research, please refer to the links below:
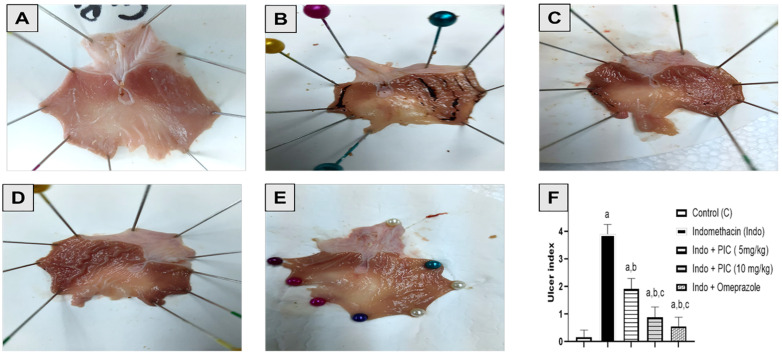 Fig. 1 Macroscopic photographs of rat's stomachs.1
Fig. 1 Macroscopic photographs of rat's stomachs.1
-
Ethanol induced Gastric Ulcer Model
- Simulates: This model mimics alcohol-induced gastric ulcers, a common condition observed in chronic alcohol consumption. It replicates the gastric mucosal injury caused by ethanol, which disrupts the balance between aggressive and protective factors in the stomach lining.
- Drug Evaluation: This model is widely used to assess drugs that aim to protect the gastric mucosa, reduce gastric acid secretion, and promote mucosal healing. Drugs such as prostaglandin analogs, cytoprotective agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antioxidants are often tested for their ability to mitigate ethanol-induced damage.
-
Acetic Acid induced Gastric Ulcer Model
- Simulates: This model simulates chronic gastric ulcers, often used to replicate long-term gastric mucosal injury that can result in persistent ulcers. Acetic acid induces a severe ulcerative injury, leading to deeper tissue damage and more significant inflammation.
- Drug Evaluation: This model is suitable for testing healing-promoting agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, growth factors (e.g., EGF), and cytoprotective agents that aid in ulcer healing and reduce scar tissue formation. It is particularly useful for evaluating drugs that target fibrosis, angiogenesis, and gastric mucosal regeneration.
-
Indomethacin induced Refractory Gastric Ulcer Model
- Simulates: This model is used to replicate refractory gastric ulcers, which are resistant to conventional treatment. Indomethacin (a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, NSAID) creates a chronic, persistent ulcer that is difficult to heal and represents a more severe, treatment-resistant form of gastric ulceration.
- Evaluates Drugs: It is ideal for testing anti-ulcer drugs that target both inflammatory pathways and gastric protection mechanisms. Drugs such as prostaglandin analogs, NSAID-induced ulcer protectors, anti-inflammatory drugs, and regenerative agents are evaluated for their ability to promote healing in difficult-to-treat ulcers.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in rodent gastric ulcer models, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General Observations: Body weight, mortality rate, ulceration size, and healing rate.
- Cytokine Profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and COX-2.
- Gastric Juice pH Measurement: Acid secretion and gastric pH levels in ulcer models.
- Serum Biomarkers: Assessment of liver enzymes, gastric mucosal injury markers, and oxidative stress markers (e.g., MDA, SOD).
- Gene/Protein Expression Profiling: RT qPCR and Western blot for key genes and proteins involved in ulceration, such as cyclooxygenase (COX-1, COX-2) and growth factors (e.g., EGF, VEGF).
- Immunohistochemistry: Infiltration of immune cells (e.g., neutrophils, macrophages) in gastric tissues.
- Histopathology: Tissue damage and ulcer depth assessment using H&E staining; analysis of epithelial cell regeneration and gastric mucosal injury.
In addition to these established gastric ulcer models, we also specialize in developing customized models tailored to specific research needs, informed by the latest literature. Our expert team is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a personalized approach to every project.
Related Services
In addition to gastric ulcer models, we also offer a wide range of other preclinical models for digestive diseases to support your research needs.
Advantages
- Extensive Expertise: With years of experience in developing rodent models for digestive system diseases, we have a deep understanding of the pathophysiology of gastric ulcers. This enables us to create models that accurately reflect human conditions.
- Tailored Solutions: Recognizing that each research project is unique, we offer customized experimental designs based on your specific needs. Whether it's for drug efficacy testing or biomarker evaluation, we adapt our approach to fit your study requirements.
- State-of-the-Art Technologies: We utilize advanced techniques such as histopathology, immunohistochemistry, and gene expression analysis to assess drug efficacy in multiple therapeutic endpoints. This ensures the precision and reliability of your results.
- Reliable, High-Quality Data: Our stringent methods ensure reproducibility and scientific validity, providing data you can trust. This guarantees that the findings from your research are both accurate and directly applicable to clinical trials.
- Comprehensive Support: From study design to data analysis, we offer full support throughout your project. Our team collaborates with you to refine your approach, ensuring that your objectives are met successfully.
- Flexible Services: We offer a range of models and services to accommodate various research needs, from novel therapeutic development to preclinical validation. Our flexibility ensures that you can achieve your milestones with efficiency.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving
FAQs
-
Q1: How do I get started with your services?
A1: Simply contact us with details about your research goals, and our team will assist you in selecting the appropriate models and designing the study. We'll work closely with you throughout the project to ensure your objectives are met.
-
Q2: What are your turnaround times for results?
A2: Turnaround times vary depending on the complexity of the study and the model chosen. We will provide an estimated timeline based on the scope of your research, and our team will ensure the timely delivery of high-quality results.
-
Q3: What types of data do you provide?
A3: We provide detailed data reports, including histological images, biomarker expression profiles, serum analysis results, and gene/protein expression data. These reports are designed to give you a comprehensive understanding of your drug's effects.
-
Q4: Do you provide services for other digestive system diseases?
A4: Yes, we offer a range of rodent models for other digestive system diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), colitis, liver disorders, and more. Feel free to inquire about models for other conditions related to the digestive system.
-
Q5: How can I contact you for more information?
A5: You can contact us directly through our website or via email. Our team is ready to assist with any questions you may have and provide further details about our services.
Published Data
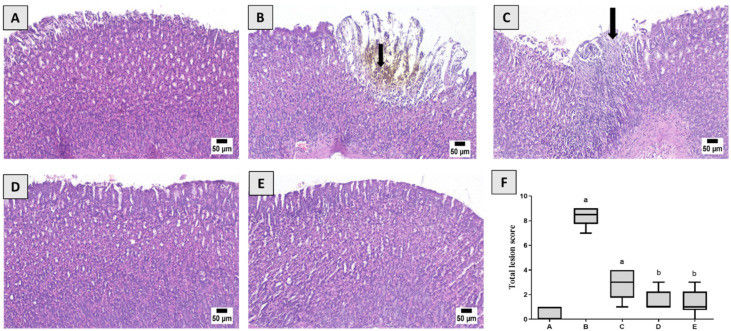 Fig. 2 Histological examination.1
Fig. 2 Histological examination.1
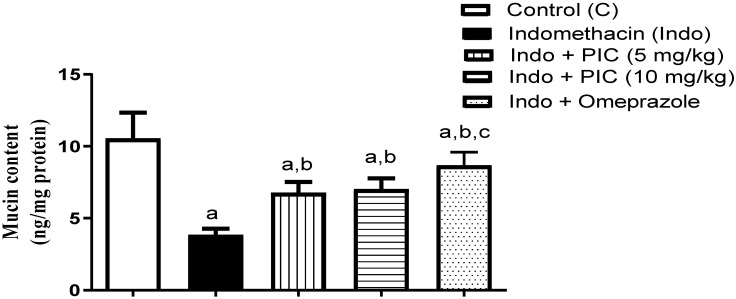 Fig. 3 The mucin level in gastric tissue after PIC treatment with Indo.1
Fig. 3 The mucin level in gastric tissue after PIC treatment with Indo.1
This study aims to investigate gastric injury induced by Indomethacin (Indo) and the protective action of piceatannol (PIC), as well as to elucidate the underlying mechanisms in a rat model. Rats were treated with the following conditions: vehicle, Indo alone, combined treatment with Indo and PIC (at doses of 5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg), and Indo with omeprazole. Histopathological analysis showed severe damage in the Indo group, including ulceration, inflammation, and tissue damage. The Indo + PIC (5 mg/kg) group showed mild changes, while Indo + PIC (10 mg/kg) and omeprazole-treated groups exhibited mostly normal structures. Additionally, mucin levels in gastric tissue were measured after treatment with PIC in the presence of Indo to evaluate its protective effects. The Indo group showed a 63.66% decrease in mucin levels, which was significantly reversed by PIC (5 & 10 mg/kg) and omeprazole treatments by 1.77-, 1.83-, and 2.26-fold, respectively.
Reference
- Shaik, Rasheed A, and Basma G Eid. "Piceatannol Affects Gastric Ulcers Induced by Indomethacin: Association of Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Angiogenesis Mechanisms in Rats." Life (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 12,3 356. 28 Feb. 2022, doi:10.3390/life12030356. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
