High-Fat & High-Fructose induced Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs provides a variety of preclinical models for evaluating NASH drug efficacy, utilizing advanced techniques and customized approaches to meet your specific research needs. Our models replicate key aspects of NASH progression, offering a reliable platform for testing new therapeutic strategies.
Introduction
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a progressive liver disease characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, along with inflammation and varying degrees of fibrosis, in individuals who consume little to no alcohol. It is considered a more severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is the most common liver condition globally. NASH is closely linked to metabolic disorders, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and hyperlipidemia, and it can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, and even hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). The condition often goes undiagnosed until significant liver damage has occurred, as early stages typically lack symptoms. NASH is a major health concern due to its rising prevalence and the lack of approved pharmacological treatments. Early detection and intervention are critical to slowing or preventing its progression.
Disease Models and Applications
The High-Fat & High-Fructose induced NASH Model is one of the widely used preclinical models to simulate NASH in rodents. This model is induced by feeding animals a diet rich in fat and fructose, mimicking the conditions seen in human patients with NASH. The method involves feeding the rodents a high-fat, high-fructose diet over a prolonged period, typically 8 to 16 weeks, to induce fatty liver changes, inflammation, and fibrosis. The model closely mimics human NASH progression, including the development of insulin resistance, liver steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. However, the model has limitations, such as not fully replicating the complex human metabolic environment and differences in species response. Despite these drawbacks, it remains an essential tool for testing new drug candidates for NASH treatment.
- Simulates: The High-Fat & High-Fructose induced NASH Model simulates human NASH, offering insights into the progression of liver inflammation, fibrosis, and fat accumulation. It provides a reliable representation of metabolic disorders contributing to NASH, including insulin resistance and fatty liver disease.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate the efficacy of drugs aimed at reducing liver inflammation, fibrosis, and steatosis. It is commonly used for testing compounds targeting metabolic dysfunctions, anti-inflammatory agents, antifibrotic drugs, and potential liver regeneration therapies.
 Fig. 1 DEXA scan images for mice in the HFF-induced obesity group.1
Fig. 1 DEXA scan images for mice in the HFF-induced obesity group.1
Measurements
For the High-Fat & High-Fructose induced NASH Model, we utilize various advanced techniques to assess the disease's progression and evaluate drug efficacy. These include:
- General Observations: Body weight, liver size, and morphology, along with the presence of steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis.
- Histological Analysis: H&E staining to assess liver tissue damage, presence of fat vacuoles, and inflammatory cell infiltration.
- Liver Enzyme Analysis: Measurement of ALT, AST, and alkaline phosphatase levels to assess liver damage.
- Cytokine Profiling: ELISA to quantify inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in liver and serum samples.
- Gene/Protein Expression: RT qPCR and Western blot for assessing expression levels of key genes involved in inflammation and fibrosis, such as TGF-β, COL1A1, and PPAR-γ.
- Fibrosis Assessment: Sirius Red staining for collagen deposition and fibrosis scoring.
Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to the High-Fat & High-Fructose induced NASH Model, we offer other NASH models induced by different methods. Our team helps you choose the most suitable model based on the disease characteristics you want to study and the drugs you aim to evaluate.
- Diet induced Obesity (DIO) Mouse NASH Model
- High-Fat Diet induced NASH Model
- Methionine Choline-Deficient (MCD) Diet induced NASH Model
- Choline-Deficient L-Amino Acid-Defined (CDAA) Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet & Fructose induced NASH Model
- Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) & High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & CCL4 induced NASH Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat induced NASH Model
- MC4R KO Mouse Model
- LDLR KO Mouse Model
Advantages
- Comprehensive Model Selection: A wide range of models to study NASH and other liver diseases.
- Advanced Measurement Techniques: State-of-the-art technologies to provide accurate, reliable results for drug efficacy studies.
- Expertise and Support: Our team assists in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis to ensure successful outcomes.
- Tailored Solutions: Customized approaches based on specific research objectives.
- Quality and Reproducibility: Consistent and high-quality results that are reproducible across studies.
- Global Reach: Our services are available to clients worldwide, ensuring accessibility for researchers everywhere.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What is NASH, and why is it important to study?
A: NASH is a liver disease caused by fat buildup and inflammation without alcohol use, which can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and cancer. Studying NASH is crucial to finding effective treatments for this common yet often underdiagnosed condition.
-
Q: What types of NASH models do you offer?
A: We offer various rodent models of NASH, including High-Fat & High-Fructose, CDAA-induced, STZ-induced, and genetic models. These models replicate different aspects of NASH progression.
-
Q: How do you assess drug efficacy in these models?
A: Drug efficacy is assessed using a range of measurements, including liver enzyme levels, histological analysis, cytokine profiling, and gene/protein expression studies.
-
Q: Can your models be customized?
A: Yes, we offer customized solutions based on specific research needs. Our team works closely with clients to design experiments and select the most appropriate model.
Published Data
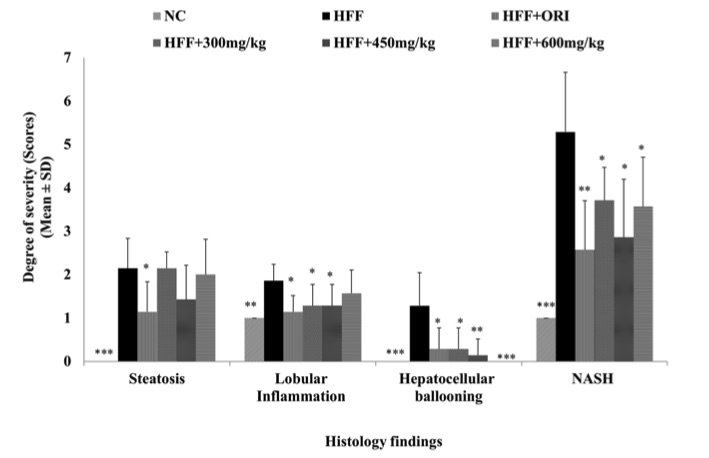 Fig. 2 Non-alcoholic Steato-Hepatitis (NASH) Scores for mice in the HFF study group treated with Orlistat and UP601.1
Fig. 2 Non-alcoholic Steato-Hepatitis (NASH) Scores for mice in the HFF study group treated with Orlistat and UP601.1
This chart illustrates the severity scores of four histological findings—steatosis, lobular inflammation, hepatocellular ballooning, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)—across different treatment groups. The NC group consistently exhibited the lowest scores across all parameters, indicating minimal liver pathology. In contrast, the HFF group demonstrated the highest scores, reflecting severe liver damage. The HFF+ORI group showed slightly reduced scores compared to the HFF group, suggesting a modest therapeutic effect. Notably, the HFF groups treated with increasing doses of the UP601 (300 mg/kg, 450 mg/kg, and 600 mg/kg) displayed a dose-dependent reduction in all histological scores. These findings indicate that the UP601 may effectively mitigate diet induced liver injury in a dose-responsive manner.
Reference
- Yimam, Mesfin et al. "UP601, a standardized botanical composition composed of Morus alba, Yerba mate and Magnolia officinalis for weight loss." BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine vol. 17,1 114. 16 Feb. 2017, DOI:10.1186/s12906-017-1627-1. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
