Adriamycin induced Myocarditis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Myocarditis, an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle, can be triggered by various factors, including viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and certain drugs. It often presents with diverse clinical manifestations, ranging from mild symptoms to severe cardiac dysfunction, including heart failure and sudden cardiac death. Given its complex etiology and significant impact on cardiovascular health, robust preclinical models are essential for unraveling disease mechanisms and developing effective therapeutic interventions.
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive suite of well-established myocarditis models to evaluate the efficacy of novel compounds.
Adriamycin-Induced Myocarditis Model
The adriamycin (doxorubicin)-induced myocarditis model is a widely recognized and valuable preclinical tool for investigating drug-induced cardiac inflammation and injury. It faithfully mimics the acute and subacute inflammatory processes that often precede chronic adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in humans. This model serves as a critical platform to understand cardiotoxicity's molecular and cellular mechanisms, identify early damage biomarkers, and evaluate cardioprotective efficacy of new therapeutic strategies. Its primary function is to provide a controlled environment to study the inflammatory component of adriamycin cardiotoxicity and test interventions for its mitigation.
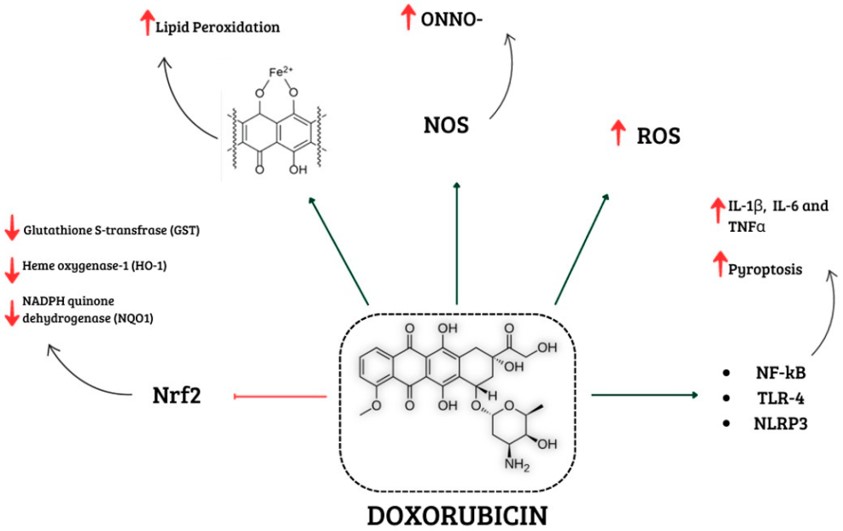 Fig.1 Mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.1,3
Fig.1 Mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.1,3
Model Construction Steps
The construction of the adriamycin-induced myocarditis model typically involves the systemic administration of adriamycin to rodents, commonly mice or rats, to induce cardiac inflammation and damage.
01Animal Selection
Healthy, age-matched rodents are selected.
02Adriamycin Administration
Adriamycin is administered via intraperitoneal (IP) or intravenous (IV) injection. Dosing regimens vary by study objective; a single high dose (e.g., 15-20 mg/kg for mice) induces acute injury, while multiple lower doses (e.g., 2-4 mg/kg/week) over weeks simulate chronic exposure.
03Monitoring
Animals are closely monitored for signs of toxicity, weight changes, and overall health status throughout the study period.
04Endpoint Collection
Cardiac tissues and blood samples are collected at various time points (e.g., 3 days, 1 week, 2 weeks, 4 weeks post-administration) to assess the acute inflammatory response, early myocardial damage, and subsequent progression.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- Translational Relevance: Accurately recapitulates key pathological features of human adriamycin-induced cardiac inflammation and injury.
- Mechanism Elucidation: Provides a robust platform for dissecting the molecular and cellular pathways involved in drug-induced myocarditis.
- Reproducibility: Established protocols ensure consistent and reliable induction of cardiac pathology.
- Versatility: Adaptable for studying acute inflammatory responses, subacute injury, and the efficacy of various cardioprotective interventions.
Limitations:
- Species Differences: Rodent models may not fully capture all aspects of human cardiac physiology and drug metabolism.
- Variability: Individual animal responses can exhibit some variability, necessitating adequate group sizes.
- Ethical Considerations: Requires careful monitoring of animal welfare due to the toxic nature of adriamycin.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs offers a state-of-the-art evaluation platform for comprehensive assessment of cardiac health and disease progression in the adriamycin-induced myocarditis model. Our integrated approach combines advanced biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, behavioral, and imaging techniques to provide a holistic understanding of therapeutic efficacy.
Test Indicators:
- Functional: Echocardiography (EF, FS, LVIDd, LVIDs), ECG (arrhythmias, conduction).
- Histopathological: H&E (inflammation, necrosis), Masson's Trichrome (fibrosis), TUNEL (apoptosis).
- Biomarkers: Cardiac Troponins (cTnI/T), BNP, inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6), oxidative stress markers (MDA, SOD, GSH).
- Molecular: RT-qPCR (gene expression), Western Blot (protein expression).
Applications
- Disease Modeling: This model accurately simulates drug-induced myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, inflammatory heart diseases, and chemotherapy-induced cardiac dysfunction. It is essential for understanding the complex progression of these conditions and validating new therapeutic approaches.
- Drug Efficacy: It effectively evaluates a wide range of cardioprotective agents, including antioxidants, anti-inflammatories, and iron chelators. Furthermore, it assesses novel chemotherapy drugs with potentially reduced cardiotoxicity, and the efficacy of combinatorial therapies designed to mitigate adverse cardiac effects, enhancing overall treatment safety.
- Therapeutic Interventions: The model facilitates the assessment of diverse therapeutic interventions, encompassing pharmacological agents, advanced gene therapies targeting specific pathways, innovative cell-based therapies for cardiac repair, and various non-pharmacological strategies such as exercise regimens and dietary supplements.
Related Myocarditis Models
Our Advantages
- Unparalleled Expertise: Our team comprises seasoned biologists and toxicologists with deep knowledge of cardiac disease models.
- Validated Protocols: We employ rigorously tested and optimized protocols for consistent and reliable study outcomes.
- Customizable Study Designs: Studies are meticulously tailored to align precisely with your unique research objectives.
- Comprehensive Analytical Capabilities: We provide a full spectrum of advanced analyses, from functional imaging to molecular profiling.
- Accelerated Discovery: Our efficient processes and scientific acumen help expedite your drug development timeline.
- Commitment to Excellence: We are dedicated to scientific integrity, data quality, and fostering successful client partnerships.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs is your premier partner in advancing cardioprotective drug discovery. Leveraging our extensive expertise and the robust adriamycin-induced myocarditis model, we offer unparalleled services to guide your research. Contact us today to explore how our specialized capabilities can accelerate your therapeutic development efforts.
FAQs
-
Q1: What distinguishes the adriamycin-induced myocarditis model from other cardiotoxicity models?
A: This model is uniquely valuable because it specifically induces an inflammatory response in the heart, mimicking the acute and subacute phases of adriamycin cardiotoxicity that can precede chronic cardiomyopathy. Unlike models focused solely on chronic structural damage, it allows for the investigation of early inflammatory mechanisms and the efficacy of anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory cardioprotective agents.
-
Q2: Can this model differentiate between direct cardiomyocyte toxicity and secondary inflammatory effects?
A: While adriamycin directly damages cardiomyocytes, the model's design and comprehensive evaluation platform allow for the careful dissection of direct cellular injury versus the subsequent inflammatory cascade. By analyzing specific biomarkers, immune cell infiltration, and various histological markers, researchers can gain insights into the interplay of these mechanisms.
-
Q3: Is it possible to evaluate long-term cardioprotective effects using this model?
A: Absolutely. While the initial insult induces myocarditis, the model can be extended to evaluate chronic cardiomyopathy development and the long-term efficacy of cardioprotective agents. By extending the study duration and employing chronic adriamycin dosing regimens, researchers can assess sustained improvements in cardiac function and reduced fibrosis over several weeks or months.
-
Q4: Can your evaluation platform identify novel biomarkers for adriamycin-induced myocarditis?
A: Yes, our comprehensive evaluation platform is well-equipped for biomarker discovery. By combining advanced molecular techniques like gene expression profiling (RT-qPCR) and proteomics (Western Blot) with traditional biochemical assays, we can identify and validate novel circulating or tissue-specific biomarkers indicative of early cardiac inflammation and injury.
-
Q5: How does Creative Biolabs assist in tailoring the study design for specific research needs?
A: Our scientific team collaborates closely with each client from the outset. We hold in-depth consultations to understand your specific research objectives, compound characteristics, and desired outcomes. Based on this, we propose customized dosing regimens, time points, animal strains, and endpoint assessments to ensure the study directly addresses your unique scientific questions.
Published Data
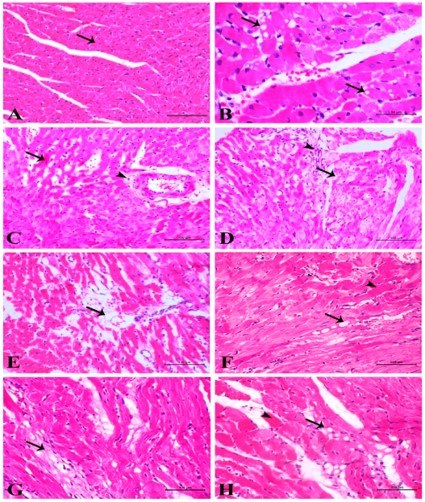 Fig.2 Doxorubicin induced cardiac myocytes changes.2,3
Fig.2 Doxorubicin induced cardiac myocytes changes.2,3
The study utilizing this model investigates the sequential progression of adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity. Research explored the acute and delayed adriamycin-induced myocardiotoxicity in rats. The study demonstrated features of acute toxic myocarditis, including degenerative and necrotic changes, mitochondrial damage, elevated cardiac biomarkers, and depleted antioxidant enzymes. After a cumulative dose with a withdrawal period, chronic changes like myocyte disorganization, atrophy, and fibrosis were reported, providing valuable insights into the dose-dependent mechanisms of this toxicity.
References
- Vitale, Roberta et al. "Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Brief Account." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 25,13 7477. 8 Jul. 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137477
- Abdelatty, Alaa et al. "Acute and Delayed Doxorubicin-Induced Myocardiotoxicity Associated with Elevation of Cardiac Biomarkers, Depletion of Cellular Antioxidant Enzymes, and Several Histopathological and Ultrastructural Changes." Life (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,9 880. 27 Aug. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090880
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
