Isoproterenol induced Chronic Heart Failure Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs, with decades of specialized expertise, is dedicated to providing a variety of well-established and highly translational animal models to accurately evaluate the efficacy of potential treatments for HF.
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) remains a major global health challenge, characterized by the heart's inability to pump sufficient blood, leading to significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. The complex and progressive nature of this disease necessitates robust preclinical models for advanced research and the development of effective new therapies.
Isoproterenol-Induced Chronic HF Model
The isoproterenol (ISO)-induced chronic HF model is a widely adopted and critical tool in cardiovascular research, leveraging a pharmacological approach to induce cardiac damage and subsequent remodeling in rodents. This model effectively mimics several key aspects of chronic cardiac stress and maladaptive changes observed in human HF.
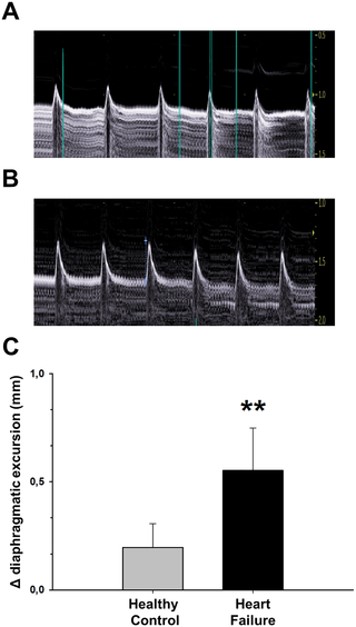 Fig.1 Study of the diaphragm function of ISO-induced HF model.1,3
Fig.1 Study of the diaphragm function of ISO-induced HF model.1,3
Model Construction Steps
The construction of the ISO-induced chronic HF model involves a controlled administration of the β-adrenergic receptor agonist to induce sustained cardiac stress.
01Animal Selection
Typically, healthy rodents, most commonly mice or rats, are selected, with careful consideration of strain, age, and gender due to their influence on cardiac remodeling responses.
02ISO Administration
ISO is administered, usually via daily subcutaneous injections (e.g., 5-10 mg/kg/day for 7-14 days) or through continuous infusion using surgically implanted osmotic pumps, ensuring a sustained adrenergic challenge.
03Induction of Cardiac Stress
Chronic exposure to ISO leads to persistent sympathetic overstimulation, initiating a cascade of events including oxidative stress, inflammation, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
04Progression to HF
Over time, these initial injuries result in myocardial hypertrophy, excessive fibrosis, and progressive ventricular remodeling, culminating in cardiac dysfunction characteristic of chronic HF.
05Monitoring and Validation
Throughout the induction period, animals are regularly monitored, and the model's establishment is validated through comprehensive phenotyping, including echocardiography and histological assessments, to confirm the development of chronic HF.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Reproducibility: The model is relatively straightforward to establish and consistently yields repeatable results, especially when influencing factors like animal strain, age, and gender are meticulously controlled.
- Pharmacological Induction: It provides a non-surgical or minimally invasive method for inducing HF, thereby reducing variability often associated with complex surgical procedures.
- Temporal Progression Study: The model allows for detailed examination of HF progression from acute injury through chronic remodeling, providing opportunities for intervention studies at various stages of the disease.
- Translational Relevance: The underlying mechanisms of β-adrenergic overstimulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation closely mirror pathological processes found in diverse forms of human HF.
- Cost-Effectiveness & Throughput: As a rodent model, it offers a more economical and higher-throughput platform for screening potential therapeutic compounds compared to larger animal models, with broad applicability across numerous inbred strains.
Limitations:
- Diaphragmatic Function Discrepancy: Unlike human chronic HF patients, where diaphragmatic dysfunction is common, the conventional ISO model has been observed to increase diaphragmatic contractility. This particular aspect warrants careful consideration in studies focused on cardio-respiratory interactions.
- Sensitivity to Experimental Factors: The extent and characteristics of cardiac remodeling can be significantly influenced by variables such as specific drug dosage, duration of administration, animal strain, age, and gender. Precise control over these factors is paramount for obtaining consistent and reliable data.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs provides a robust evaluation platform for the ISO-induced chronic HF model, integrating cutting-edge instruments and assays to deliver comprehensive insights into cardiac function and pathology. Our capabilities span various analytical levels, ensuring a holistic understanding of disease progression and therapeutic impact. Key indicators assessed include:
- Biochemical Analysis: Measurement of circulating cardiac biomarkers (e.g., BNP, troponins), and biochemical assessment of fibrosis markers like Hydroxyproline (HYP) concentration.
- Molecular Analysis: Gene and protein expression profiles related to hypertrophy, fibrosis (e.g., TGF-β1), inflammation, and energy metabolism (e.g., qPCR, Western Blot, ELISA).
- Cellular Analysis: Assessment of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, apoptosis, and necrosis.
- Histopathological Evaluation: Detailed analysis of myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis (Picrosirius Red, Masson's Trichrome, Collagen I immunohistochemistry), and inflammation, including Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) for ultrastructural analysis.
- Imaging Instruments: Advanced echocardiography for non-invasive assessment of cardiac structure and function (ejection fraction, fractional shortening, wall thickness, chamber dimensions).
- Hemodynamic Tests: Invasive measurements of left ventricular pressure, contractility, and relaxation using pressure catheters.
Applications
- Simulated Diseases: Effectively models conditions characterized by chronic cardiac stress, hypertrophy, and fibrosis, relevant to diverse forms of human HF, including those arising from hypertension, myocardial infarction, and dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Drug Evaluation: Serves as a critical platform for the preclinical evaluation of novel therapeutic compounds, biologics, and small molecules aimed at mitigating cardiac remodeling and dysfunction.
- Treatment Modalities: Utilized to assess the efficacy of various treatment strategies, including anti-fibrotic agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, antioxidant therapies, and interventions targeting neurohumoral activation.
- Mechanism of Disease: Provides a valuable in vivo system for elucidating the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the progression of chronic HF.
Related Heart Failure Models
PA Constriction induced Right HF Model
Ascending Aortic Arch Constriction induced Post-Pressure Overload Heart Failure Model
Abdominal Aortic Stenosis induced Left HF Model
DOCA & Salt induced Left HF Model
Our Advantages
- Decades of Expertise: Unparalleled experience in biological models, ensuring deep scientific understanding and robust study execution.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: State-of-the-art phenotyping capabilities, from advanced imaging to detailed molecular analysis, providing a holistic view of cardiac health.
- Customized Study Design: Flexible and tailored protocols that precisely align with your unique research objectives and regulatory requirements.
- Expert Data Interpretation: A team of seasoned biologists offers insightful analysis and guidance, transforming data into actionable scientific conclusions.
- Proven Reproducibility: Meticulous control over experimental variables ensures consistent, reliable, and high-quality results for your critical drug discovery programs.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to supporting your cardiovascular research endeavors by providing meticulously executed ISO-induced chronic HF model services. We invite you to contact our expert team to explore how our comprehensive preclinical solutions can specifically address your research needs and accelerate your path to novel therapeutic discoveries.
FAQs
-
Q1: What animal models are typically used for ISO-induced chronic HF studies?
A: Our standard protocols primarily utilize rodent models, specifically mice and rats. The choice between these species often depends on the specific research question, the desired scale of the study, and genetic manipulation possibilities, as various inbred strains within both species exhibit distinct responses to ISO-induced cardiac stress.
-
Q2: What are the key advantages of this model for preclinical drug discovery?
A: A significant advantage of this model lies in its ability to reliably reproduce the progressive cardiac remodeling seen in human HF. It is a non-surgical or minimally invasive method, which reduces variability. Furthermore, its cost-effectiveness and adaptability across numerous rodent strains make it a high-throughput platform for screening drug candidates.
-
Q3: What types of endpoints and parameters can be evaluated using this HF model?
A: We conduct a comprehensive range of evaluations, including non-invasive echocardiography for cardiac function, invasive hemodynamic measurements, and detailed histopathological analyses of myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis. We also perform molecular assessments of gene and protein expression, alongside biochemical analyses of circulating cardiac biomarkers and fibrotic markers.
-
Q4: How do you ensure the reproducibility and consistency of results using this model?
A: Ensuring high reproducibility is paramount in our studies. We achieve this through stringent adherence to standardized operating procedures for model induction and phenotyping. Crucially, we meticulously control for all experimental variables, including the selection of animal strain, age, gender, and precise ISO dosage and administration methods, thereby minimizing variability.
-
Q5: Can this model be used to evaluate specific types of HF, or is it more general?
A: While the ISO-induced model is generally classified as a chronic stress-induced cardiomyopathy, its underlying mechanisms, such as β-adrenergic overstimulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation, are highly relevant to various forms of human HF, including those driven by hypertension, ischemia, and dilated cardiomyopathy. It serves as a valuable tool for understanding generalized cardiac remodeling.
-
Q6: Can you customize the study design for my specific research needs beyond standard protocols?
A: Absolutely. We pride ourselves on our collaborative approach and ability to customize study designs. Our expert team will work closely with you to understand your precise research objectives, enabling us to tailor the model induction protocol, choice of animal species, duration of study, and specific endpoints to ensure the most relevant and impactful results for your drug development program.
Published Data
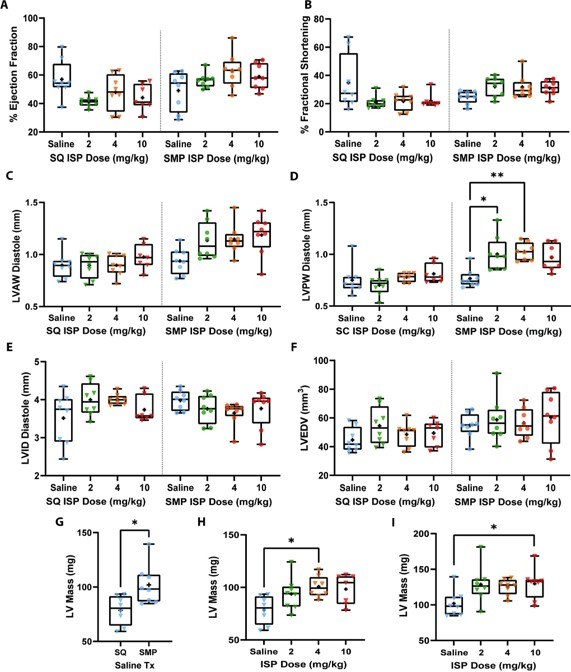 Fig.2 Heart function assessed via echocardiography.2,3
Fig.2 Heart function assessed via echocardiography.2,3
A pertinent example illustrating the utility of the ISO-induced HF model is detailed in a study by Wu et al., 2024. This research investigated the impact of varying ISO doses and delivery methods (subcutaneous injection versus osmotic pump infusion) on cardiac hypertrophy induction in C57BL/6J mice over two weeks. The findings revealed that all tested ISO doses comparably increased heart weight, with a more pronounced effect observed via osmotic pump delivery. Furthermore, the study elucidated how delivery methods influence contrasting heart rate and ECG parameters, and differentially affect indicators of heart wall thickness, left ventricular mass, and gene markers associated with hypertrophy and fibrosis. This work highlights the critical importance of selecting appropriate administration strategies to achieve specific pathological phenotypes for therapeutic assessment.
References
- Cabrera-Aguilera, Ignacio et al. "The conventional isoproterenol-induced heart failure model does not consistently mimic the diaphragmatic dysfunction observed in patients." PloS one vol. 15,7 e0236923. 30 Jul. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236923
- Perez-Bonilla, Patricia et al. "Isoproterenol induced cardiac hypertrophy: A comparison of three doses and two delivery methods in C57BL/6J mice." PloS one vol. 19,7 e0307467. 22 Jul. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0307467
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
