Obesity related Glomerulopathy Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive model systems that simulate the pathophysiology of ORG in rodents. Our models facilitate the evaluation of drug candidates targeting metabolic dysfunction and renal injury, helping researchers identify effective treatment options for ORG and related renal conditions.
Introduction
Glomerulopathy refers to a range of kidney diseases that affect the glomeruli, which are the tiny filtering units of the kidneys. These disorders can lead to impaired renal function and are often associated with proteinuria, reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and eventual kidney failure if left untreated. The most common types of glomerulopathy include diabetic nephropathy, hypertensive nephropathy, and obesity-related glomerulopathy, with each presenting unique challenges in both diagnosis and treatment. The disease often progresses through stages of glomerular damage, including glomerular hypertrophy, fibrosis, and podocyte injury. In many cases, glomerulopathy results from chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or metabolic syndrome, which contribute to kidney damage over time. Early detection and intervention are critical in preventing irreversible kidney damage and end-stage renal disease. Given the complexity of these conditions, reliable disease models are essential for understanding the mechanisms of glomerulopathy and for testing potential therapeutic interventions.
Obesity-related Glomerulopathy Model
The Obesity-related Glomerulopathy model is established by inducing obesity in rodents through high-fat diets or genetic modifications. This model reflects the metabolic and renal abnormalities seen in human obesity, including insulin resistance, altered lipid metabolism, and kidney structural changes such as glomerular hypertrophy and fibrosis. Key features of the model include the development of albuminuria, a hallmark of glomerular damage, and progressive renal dysfunction. Its main advantage lies in its ability to closely mimic the pathophysiology of obesity-induced kidney disease, making it ideal for preclinical drug testing. However, the model may be limited by the genetic variations in animals and the need for long-term studies to fully assess chronic kidney damage. Overall, it offers a powerful tool for understanding obesity-induced renal dysfunction and evaluating potential therapies.
- Simulates: The model simulates obesity-related glomerulopathy, providing insights into glomerular hypertrophy, tubulointerstitial fibrosis, and metabolic dysfunction, including insulin resistance and dyslipidemia.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is ideal for evaluating drugs targeting obesity-induced renal injury, including those aimed at reducing albuminuria, mitigating glomerular hypertrophy, controlling blood pressure, and regulating lipid metabolism.
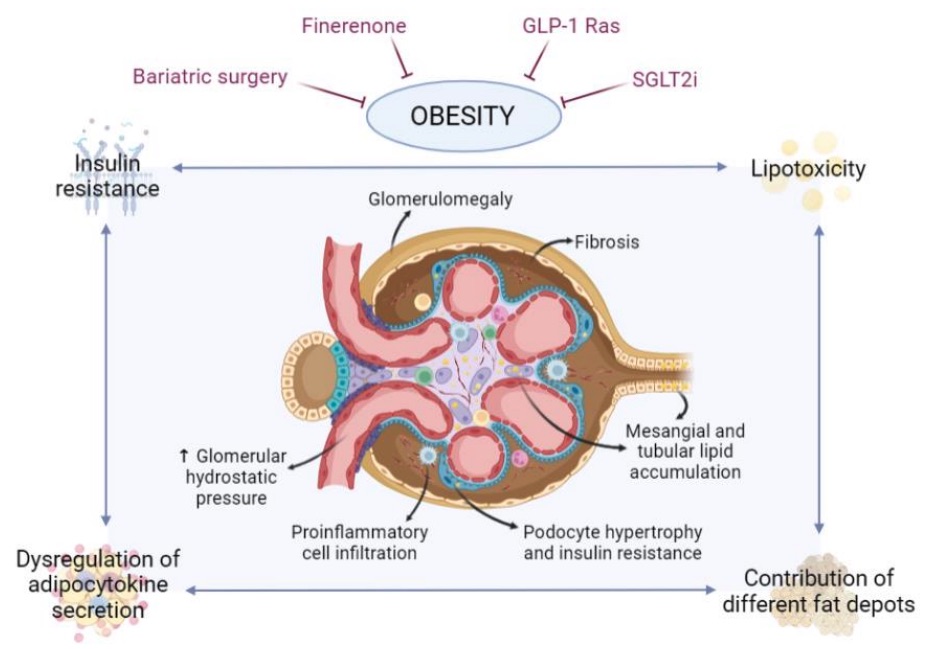 Fig. 1 Involvement of adipose tissue in obesity-related glomerulopathy.1
Fig. 1 Involvement of adipose tissue in obesity-related glomerulopathy.1
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat.
-
Measurements
We offer a range of advanced techniques for evaluating drug efficacy in the Obesity-related Glomerulopathy Model, such as:- General Observations: Body weight, food intake, kidney function markers, and albuminuria levels.
- Histological Analysis: Kidney tissue examination for glomerular hypertrophy, fibrosis, and tubular damage.
- Biomarker Analysis: Serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and cystatin C for renal function assessment.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of inflammatory cell infiltration (e.g., macrophages, T-cells) in kidney tissues.
- Gene/Protein Expression Profiling: Analysis of pro-fibrotic markers such as TGF-β1, collagen I, and α-SMA via RT-qPCR and Western blotting.
- Cytokine Profiling: Measurement of inflammatory mediators like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β.
Our team is equipped to assist in the design, model selection, and analysis of experiments, ensuring tailored solutions for specific research needs.
Related Services
In addition to the Obesity-related Glomerulopathy Model, we offer services for models of glomerulopathy induced by other factors, including diabetes, hypertension, and nephrotoxic agents. These models provide complementary insights into the progression of renal disease under different pathological conditions.
- Diabetic Nephropathy Model
- HDF-CHOL & Salt Feed & 5/6 Nephrectomy-Induced Nephropathy Model
Our advantages
- Comprehensive Model Systems: Our models mimic key features of obesity-related glomerulopathy, enabling detailed preclinical studies.
- Customized Drug Testing: Tailored protocols for testing a wide range of pharmacological interventions.
- Advanced Measurement Technologies: Utilization of cutting-edge techniques for accurate and reliable data collection.
- Experienced Scientific Team: Expert support in experimental design, data analysis, and result interpretation to maximize the success of your research.
- High Reproducibility: Consistent results across studies ensure the reliability and reproducibility of findings.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What is the duration required to establish the Obesity-related Glomerulopathy model?
The model can be established within 4-6 weeks, depending on the induction method (diet or genetic modifications).
-
2. How do you evaluate the kidney function in this model?
Kidney function is assessed through blood markers such as creatinine, BUN, and albuminuria, alongside histopathological analysis of kidney tissues.
-
3. Can this model be used for long-term studies?
Yes, this model is suitable for chronic studies, enabling the evaluation of progressive renal injury over several months.
-
4. What therapeutic agents can be tested using this model?
It is ideal for testing anti-hypertensive, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and lipid-lowering drugs aimed at mitigating obesity-related kidney damage.
Reference
- Sandino, Justo et al. "Novel Insights in the Physiopathology and Management of Obesity-Related Kidney Disease." Nutrients vol. 14,19 3937. 22 Sep. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193937 Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
