Colitis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Colitis refers to inflammation of the colon, which can be caused by various factors such as infections, autoimmune diseases, and the use of certain medications. The most common types of colitis include ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn's disease, and ischemic colitis. UC is a chronic condition that primarily affects the colon's mucosal lining, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. Crohn's disease, another type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, causing deeper tissue inflammation. Ischemic colitis occurs due to reduced blood flow to the colon, often resulting in pain and tissue damage. Colitis can lead to long-term complications like ulceration, bleeding, and an increased risk of colon cancer. Early detection and effective treatment are essential in managing the disease and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. Creative Biolabs provides a variety of well-established rodent models to evaluate the therapeutic effects of drugs targeting colitis. These include models for acute colitis, chronic colitis, and drug-induced colitis. Our models offer a comprehensive platform to study inflammation, tissue damage, and healing processes, allowing for the precise evaluation of anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and tissue-protective agents. Our expert team is available to help with model selection, study design, and data analysis, ensuring optimal results for your preclinical research.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established rodent models for colitis, including models for acute colitis, chronic colitis, and drug-induced colitis. These models are meticulously developed to mimic the pathophysiology of human colitis and are accompanied by comprehensive evaluations of various parameters such as inflammation, tissue damage, and healing processes. This ensures the accurate assessment of potential therapeutic candidates during the preclinical phase. Our experienced team of scientists will collaborate with you from experimental design through data interpretation, ensuring reliable and high-quality results. To learn more about the colitis models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
| Colitis Models | Applications |
|---|---|
| TNBS/DNBS induced Colitis Model |
Simulates: Acute inflammatory colitis, often used to study immune-mediated colitis. Drug Evaluation:
|
| DSS induced Colitis Model |
Simulates: Acute and chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly ulcerative colitis. Drug Evaluation:
|
| Indomethacin induced Small Intestinal Inflammatory Model |
Simulates: NSAID-induced enteritis and small bowel inflammation. Drug Evaluation:
|
| OXA induced Colitis Model |
Simulates: Th2-driven allergic colitis, often used to evaluate immune response-related colitis. Drug Evaluation:
|
| Acetic Acid induced IBD Model |
Simulates: Chronic colitis resembling ulcerative colitis. Drug Evaluation:
|
| Anti-CD40 Ab induced IBD Model |
Simulates: T-cell-mediated colitis (mimicking autoimmune IBD). Drug Evaluation:
|
| IL-10 KO Mouse Spontaneous IBD Model |
Simulates: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Drug Evaluation:
|
| CD4+CD45RBhi T Cells induced IBD Model |
Simulates: Chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Drug Evaluation:
|
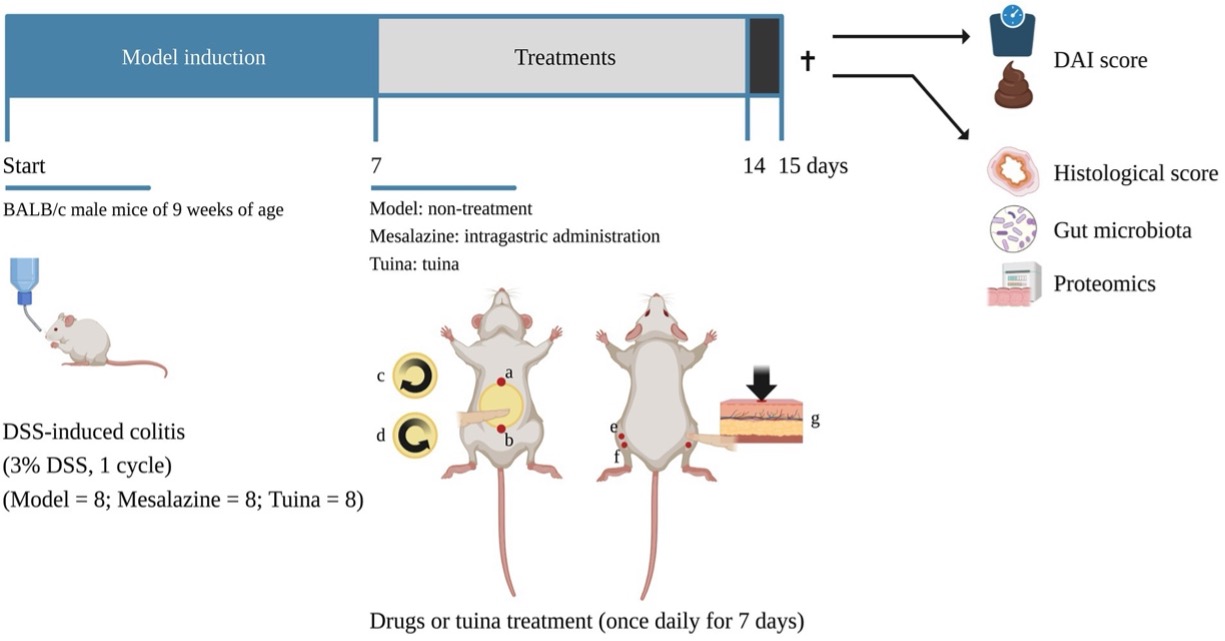 Fig. 1 DSS-induced colitis model.1
Fig. 1 DSS-induced colitis model.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in rodent colitis models, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight, mortality rate, stool consistency, gastrointestinal bleeding, and clinical symptoms of inflammation.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IFN-γ.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Evaluation of liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and inflammatory biomarkers in serum.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis to measure the expression of key genes and proteins involved in inflammation and tissue repair.
- Histopathology: Examination of tissue sections for signs of ulceration, mucosal damage, and inflammatory cell infiltration in the colon.
- Immunohistochemistry: Infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T-cells, macrophages, neutrophils) in colonic tissues.
In addition to the established colitis models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, based on current literature and prior studies. Our scientific team is available to assist you throughout the process, from experimental design and model selection to data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to colitis models, we also offer a wide range of other rodent disease models for comprehensive preclinical research.
Advantages
- Expertise and Experience: With years of experience in preclinical research, our team of experts is well-versed in developing and optimizing rodent models for various diseases, including colitis, gastritis, IBD, and more.
- Customized Solutions: We provide tailored solutions that cater to your specific research needs, ensuring that the models and services we offer align with your project's objectives.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: We utilize the latest technologies and methodologies for data collection and analysis, ensuring high-quality, reliable, and reproducible results.
- Comprehensive Support: From experimental design to data interpretation, our scientists are available to guide you through every stage of your project, ensuring a seamless and efficient process.
- Flexible and Timely Delivery: We understand the importance of time in research, and we are committed to providing timely services without compromising on quality, helping you meet your project deadlines.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q1: What types of models do you provide for preclinical research?
A1: We offer rodent models for diseases like colitis, gastritis, IBD, gastric ulcers, and liver disorders.
-
Q2: How can your models help in drug development?
A2: Our models enable testing of drug efficacy by assessing inflammation, cytokine levels, histopathology, and therapeutic effects.
-
Q3: Do you offer customized models for specific research needs?
A3: Yes, we can develop custom models tailored to your specific research objectives.
-
Q4: What kinds of therapeutic agents can be tested in your models?
A4: Our models are suitable for testing anti-inflammatory drugs, biologics, immune modulators, small molecules, and probiotics.
-
Q5: What type of support do you provide during the research process?
A5: We offer support from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring reliable results throughout the study.
-
Q6: How long does it take to receive results?
A6: Timelines vary by model and study, but we aim to deliver timely results without compromising quality.
Published Data
This study aims to investigate potential treatment pathways for ulcerative colitis through the gut microbiota and proteomics approaches. Thirty-two male BALB/c mice were randomly assigned to four groups: control, model, mesalazine, and tuina. An ulcerative colitis model was induced by allowing the mice to drink a 3% dextran sulfate sodium solution freely for 7 days. The mesalazine and tuina groups received 7 days of treatment with mesalazine and tuina, respectively. The study assessed several parameters, including body weight, fecal properties, colon length, histological changes, gut microbiota composition, and colon proteomics. Results showed that the tuina group exhibited significant recovery in body weight, disease activity index, colon histological scores, and microbiota diversity, suggesting that tuina treatment had a positive effect on ulcerative colitis.
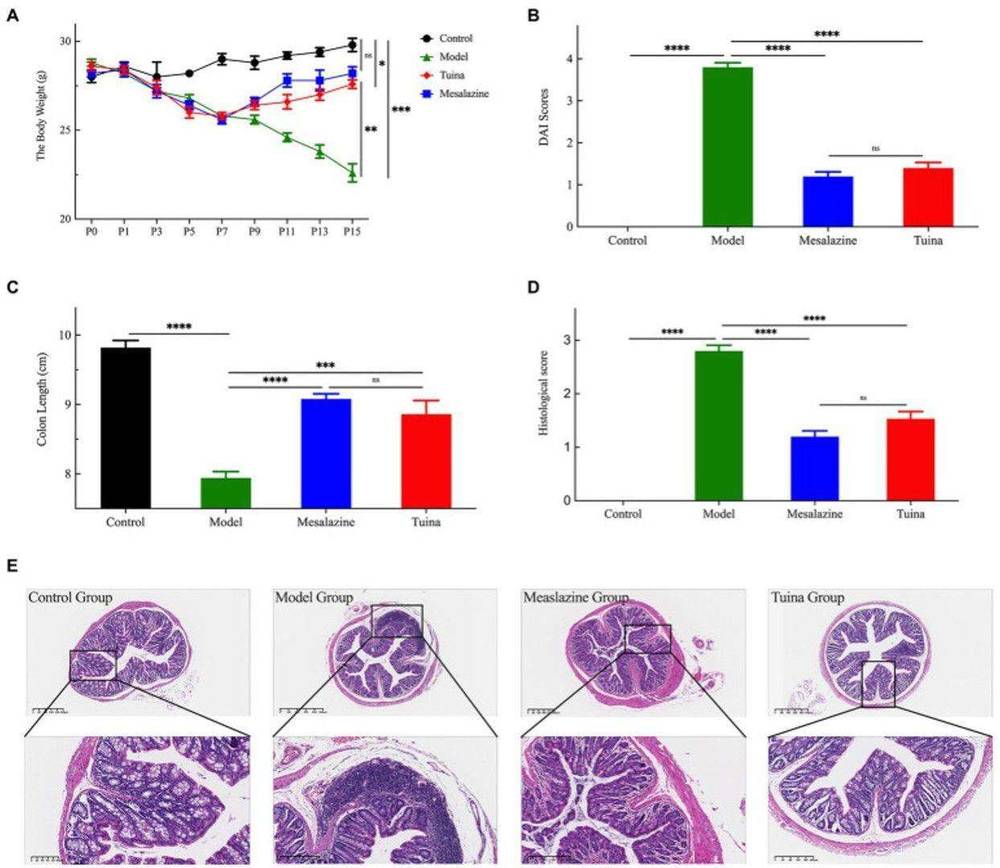 Fig. 2 Tuina treatment prevents UC-related symptoms in model mice.1
Fig. 2 Tuina treatment prevents UC-related symptoms in model mice.1
Reference
- Wang, Hourong et al. "The effect of tuina on ulcerative colitis model mice analyzed by gut microbiota and proteomics." Frontiers in Microbiology vol. 13 976239. 29 Nov. 2022, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.976239. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
