Adriamycin induced Left Heart Failure Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in providing a variety of well-established rodent HF models, meticulously characterized to evaluate the efficacy of novel therapeutic compounds.
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) represents a major global health challenge, characterized by the heart's inability to pump sufficient blood to meet the body's metabolic demands. It results from diverse etiologies, including myocardial infarction, hypertension, and exposure to cardiotoxic agents like certain chemotherapies. Understanding HF pathogenesis and developing effective therapies requires robust preclinical models.
Adriamycin-Induced Left HF Model
The adriamycin (doxorubicin)-induced left HF model is a gold standard for investigating chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity and HF progression. This model faithfully recapitulates key clinical and pathological features observed in human patients, including progressive cardiac dysfunction, histological damage, and molecular alterations.
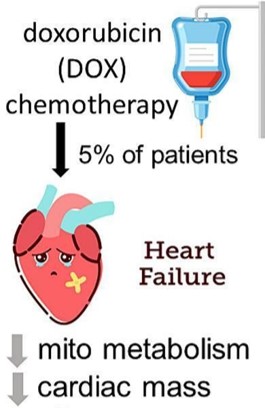 Fig.1 Schematic of doxorubicin-induced HF.1
Fig.1 Schematic of doxorubicin-induced HF.1
Model Construction Steps
The construction of the Adriamycin-induced HF model typically involves a controlled administration strategy to induce reproducible cardiac damage:
01Animal Selection
Begin by selecting appropriate rodent strains, most commonly mice or rats. For studies requiring an understanding of inter-individual variability, diverse genetic backgrounds such as Collaborative Cross (CC) mouse strains may be employed.
02Dosing Regimen Design
Establish the Adriamycin administration schedule. This can involve a single high dose or multiple lower doses. A common approach for chronic cardiotoxicity is weekly administration of 5 mg/kg doxorubicin over 5 weeks, culminating in a total cumulative dose of 25 mg/kg.
03Drug Administration
Administer Adriamycin via intraperitoneal injection or intravenous routes, strictly adhering to sterile techniques and ethical guidelines.
04Monitoring and Progression
Allow sufficient time for the cardiotoxicity to develop, typically several weeks post-administration. Continuous monitoring of physiological parameters and cardiac function (e.g., body weight, activity levels, and initial echocardiography) is crucial during this period.
05Endpoint Confirmation
At the study's conclusion, confirm the development of HF through comprehensive functional, histological, and molecular assessments.
Animals:
Rat, Rabbit, DogStrengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Translational Relevance: Closely mimics the clinical pathology of doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in humans, including delayed onset and progressive dysfunction.
- Reproducibility: Well-established protocols ensure consistent and reliable induction of cardiotoxicity, enabling robust data generation.
- Versatility: Suitable for evaluating diverse therapeutic strategies, from prophylactic cardioprotection to treatment for established HF.
- Genetic Diversity Studies: Can be adapted to investigate genetic susceptibility to cardiotoxicity using specific strains like Collaborative Cross mice.
- Biomarker Discovery: Enables the identification and validation of novel diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers for cardiotoxicity.
Limitations:
- Systemic Toxicity: Adriamycin can cause systemic side effects (e.g., myelosuppression, gastrointestinal distress) that may confound cardiac-specific observations.
- Acute vs. Chronic: While effective for chronic cardiotoxicity, dose-dependent acute effects can sometimes obscure longer-term pathological changes without careful experimental design.
- Species Differences: Rodent models, while highly valuable, may not fully replicate all aspects of human disease complexity.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs' cutting-edge, multi-modal platform precisely assesses cardiac function and pathology in the Adriamycin-induced HF model, utilizing advanced instruments for biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, and imaging analyses.
Key test indicators:
- Functional Imaging: Echocardiography (LVEF, FS, LVEDD/LVESD, LVPW, LVAW, LV Mass), Electrocardiography (ECG), and Invasive Hemodynamics (LVEDP, dP/dt).
- Histopathology: H&E staining (myocardial morphology, vacuolization, myofibrillar disarray), Masson's Trichrome (fibrosis), Immunohistochemistry (e.g., α-SMA, Collagen I/III, inflammatory markers), and TUNEL staining (apoptosis). TEM provides ultrastructural analysis.
- Molecular Analysis: RT-qPCR (gene expression: BNP, ANP, inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress genes), and Western Blotting (protein expression, phosphorylation, apoptosis markers e.g., cleaved caspase-3).
- Biochemical Assays: Serum cardiac troponins (cTnI/T), BNP, oxidative stress markers (MDA, GSH, SOD, Catalase), ceramide profiling (LC-MS/MS), and predictive biomarkers (e.g., myosin light chain 3).
Applications
- Simulating Diseases: Primarily used to simulate chemotherapy-induced cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, and progressive chronic HF. It also provides insights into the cardiotoxic mechanisms underpinning these conditions.
- Evaluating Drugs: Ideal for evaluating novel cardioprotective agents designed to prevent or mitigate doxorubicin-induced cardiac damage.
- Assessing Therapies: Utilized for assessing new therapeutic strategies aimed at reversing or slowing the progression of established HF. This includes compounds that influence oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, DNA repair, inflammation, fibrosis, and ceramide metabolism.
- Biomarker Identification: Crucial for identifying and validating novel circulating or tissue-based biomarkers for early detection, prognosis, and prediction of cardiotoxicity.
Related Heart Failure Models
PA Constriction induced Right HF Model
Ascending Aortic Arch Constriction induced Post-Pressure Overload Heart Failure Model
Abdominal Aortic Stenosis induced Left HF Model
DOCA & Salt induced Left HF Model
Our Advantages
- Years of Expertise: Our extensive experience in preclinical model development ensures precise and reliable study execution.
- Customizable Study Design: We collaborate closely with clients to tailor study protocols to specific research objectives, optimizing outcomes.
- Comprehensive Endpoint Analysis: Our advanced evaluation platform provides a holistic understanding of cardiac function and pathology.
- Robust Data Interpretation: Our team of expert biologists and statisticians provides insightful analysis, guiding your research effectively.
- Reproducible Results: Meticulous adherence to established protocols guarantees highly reproducible and publishable data.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive preclinical services utilizing our validated adriamycin-induced left HF model. We are dedicated to supporting your research efforts in cardiotoxicity and HF. Contact us today to discuss how our specialized expertise can accelerate your drug discovery programs.
FAQs
-
Q1: How is the Adriamycin-induced HF model typically established in rodents?
A: The model is commonly established by administering adriamycin (doxorubicin) to rodents, typically mice or rats, following specific dosing regimens. This might involve a single high dose or, more frequently for chronic effects, multiple lower doses over several weeks. For instance, a common regimen involves weekly injections of 5 mg/kg doxorubicin for five consecutive weeks, achieving a cumulative dose of 25 mg/kg, which reliably induces cardiac damage.
-
Q2: What key pathological features of human cardiotoxicity does this model mimic?
A: This model effectively recapitulates several critical aspects of human Adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity. These include progressive reductions in left ventricular function (e.g., ejection fraction), myocardial fibrosis, increased oxidative stress within heart tissue, cardiomyocyte apoptosis (programmed cell death), and the accumulation of detrimental lipids like ceramides.
-
Q3: What are the primary functional endpoints evaluated in studies using this model?
A: Functional endpoints are predominantly assessed through non-invasive echocardiography, which provides critical insights into cardiac performance. Key parameters measured include left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), fractional shortening (FS), and various ventricular dimensions such as left ventricular end-diastolic and systolic diameters (LVEDD/LVESD). Additionally, changes in wall thickness and overall left ventricular mass are often monitored.
-
Q4: How do you ensure the reproducibility of its Adriamycin-induced HF model?
A: We uphold stringent standards for model reproducibility through meticulous protocol adherence. This encompasses precise Adriamycin administration, rigorous animal monitoring, and standardized functional and pathological assessments. Our experienced team follows validated procedures and applies robust statistical analysis to ensure consistent and reliable data generation across all studies.
-
Q5: Do you offer customized study designs for this model?
A: Yes, we specialize in providing tailored research solutions. We work collaboratively with our clients to design bespoke study protocols that precisely align with their unique research objectives. This ensures that the experimental design is optimized for specific efficacy testing, mechanistic investigations, or biomarker identification efforts.
-
Q6: What advanced histological and molecular techniques are available for endpoint analysis?
A: Our comprehensive evaluation platform includes advanced histological and molecular techniques. Histologically, we utilize H&E staining for general morphology, Masson's trichrome for fibrosis, and immunohistochemistry for specific markers. At the molecular level, we perform RT-qPCR for gene expression and Western blotting for protein analysis, complemented by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for ultrastructural insights.
Published Data
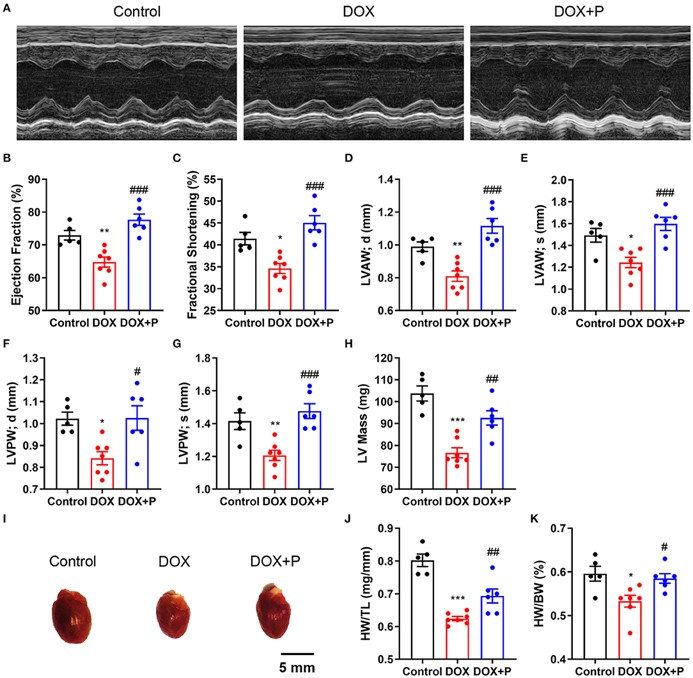 Fig.2 Evaluation of cardiac function and heart weight.2
Fig.2 Evaluation of cardiac function and heart weight.2
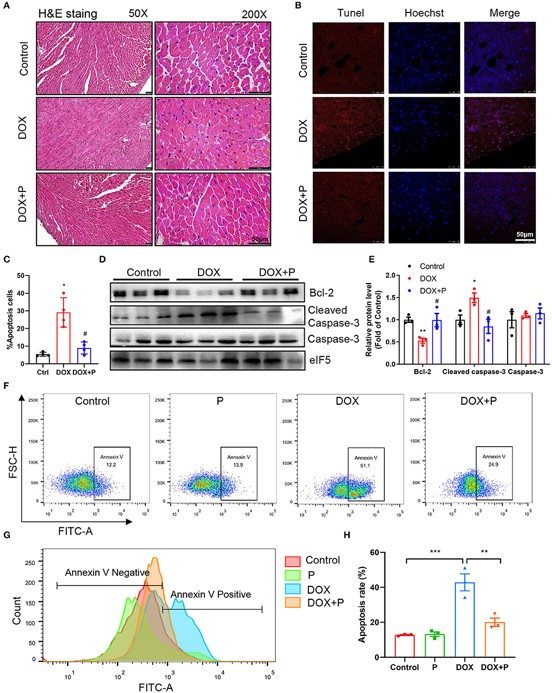 Fig.3 Evaluation of cardiomyocyte apoptosis.2
Fig.3 Evaluation of cardiomyocyte apoptosis.2
A representative study utilized the model to investigate the role of ceramide accumulation in doxorubicin-induced HF and the cardioprotective effects of specific compounds. The project results demonstrated that pretreatment with a novel agent significantly improved cardiac dysfunction parameters (e.g., EF%, FS%, LVPW, LVAW, LV mass) and attenuated cardiomyocyte apoptosis, while also reversing doxorubicin-induced ceramide accumulation. This research highlights the model's utility in identifying effective cardioprotective strategies.
References
- Choksey, Anurag et al. "AICAR confers prophylactic cardioprotection in doxorubicin-induced heart failure in rats." Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology vol. 191 (2024): 12-22. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image. DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2024.04.011
- Yun, Weijing et al. "Periplocymarin Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Heart Failure and Excessive Accumulation of Ceramides." Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine vol. 8 732554. 19 Nov. 2021. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.732554
For Research Use Only.
