High-Fat Diet (HFD) & CHOL induced Aorta Atherosclerosis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs, with extensive expertise, provides a diverse range of well-established rodent atherosclerosis models to precisely evaluate the efficacy of novel therapeutic interventions.
Introduction
Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory condition, is characterized by the accumulation of lipid plaques within arterial walls, leading to the hardening and narrowing of arteries. This progressive disease is the primary underlying cause of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes, posing a significant global health burden. Effective therapeutic development hinges on reliable preclinical models that accurately mimic human disease pathology.
High-Fat-Diet & CHOL-Induced Aorta Atherosclerosis Model
The high-fat-diet (HFD) & CHOL-induced aorta atherosclerosis model is a cornerstone in preclinical cardiovascular research, widely utilized for its ability to replicate key features of human atherosclerotic disease. This robust model serves as an invaluable platform for screening and evaluating the efficacy of potential anti-atherosclerotic agents, investigating disease mechanisms, and validating novel biomarkers. By inducing systemic dyslipidemia and accelerating plaque formation, it provides a controlled environment to assess the impact of various therapeutic strategies on plaque progression, stability, and regression.
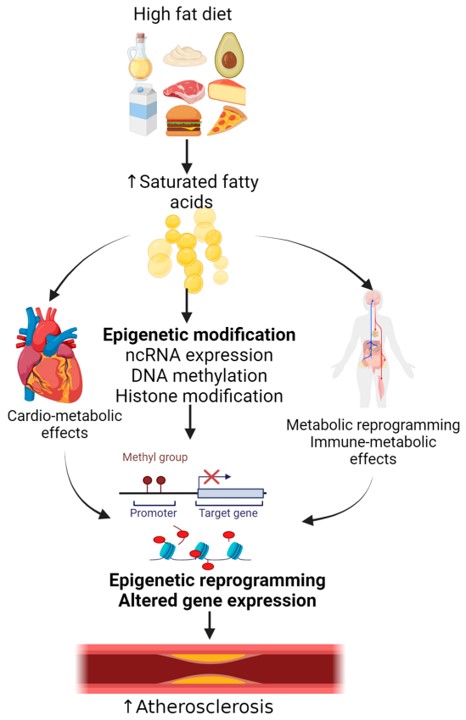 Fig.1 HFD-induced epigenetic changes contributing to atherosclerosis.1,3
Fig.1 HFD-induced epigenetic changes contributing to atherosclerosis.1,3
Model Construction Steps
The construction of this model typically involves a synergistic dietary approach in genetically predisposed mouse strains.
01Animal Selection
Utilize male or female mice, typically aged 8-10 weeks, ensuring a consistent genetic background for study homogeneity.
02Diet Preparation
Animals are transitioned from a standard chow diet to a custom high-fat, high-cholesterol diet. This diet typically contains a high percentage of calories from fat (e.g., 40-60%) and a significant amount of cholesterol (e.g., 0.15-1.25%).
03Dietary Intervention
Mice are fed the HFD & CHOL diet ad libitum for a defined period, commonly ranging from 8 to 20 weeks, depending on the desired lesion severity and study objectives.
04Environmental Control
Animals are housed under controlled environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, light/dark cycle) with strict adherence to animal welfare guidelines.
05Monitoring
Body weight, food intake, and general health are regularly monitored throughout the study duration.
06Therapeutic Intervention (if applicable)
Test compounds are administered via appropriate routes (e.g., oral gavage, intraperitoneal injection) concurrently with or after the diet initiation, based on the study design.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- Translational Relevance: Faithfully recapitulates key pathological features of human atherosclerosis, including lipid accumulation, inflammation, and fibrous cap formation.
- Reproducibility: Offers a highly reproducible and robust platform for consistent lesion development.
- Accelerated Progression: The combined HFD & CHOL approach significantly accelerates plaque formation, allowing for studies within a practical timeframe.
- Versatile Endpoints: Supports a wide array of biochemical, histological, and molecular analyses to comprehensively assess disease progression and therapeutic efficacy.
Limitations:
- Species Differences: While highly relevant, mouse models do not fully replicate all complexities of human atherosclerosis, such as plaque rupture mechanisms.
- Cost and Time: Requires specialized diets and genetically modified animals, which can contribute to higher study costs and longer durations compared to in vitro models.
- Dietary Control: Strict adherence to diet composition and feeding protocols is crucial for consistent model induction.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs' comprehensive evaluation platform utilizes state-of-the-art instruments and provides detailed analysis of various test parameters, including:
Biochemical Analysis:
- Serum lipid profiles (total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides)
- Inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6)
- Oxidative stress markers
Molecular Analysis:
- Gene expression related to lipid metabolism and inflammation
- Protein expression related to lipid metabolism and inflammation
Histopathological Analysis:
- Quantitative assessment of atherosclerotic plaque burden in the aorta
- Assessment of atherosclerotic plaque composition in the aorta
Cellular and Imaging Instruments:
- Advanced tools for cellular analysis and imaging, supporting comprehensive evaluation.
Applications
- Simulate Diseases: Primarily simulates human atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia, and aspects of metabolic syndrome that contribute to cardiovascular disease.
- Evaluate Drugs: Ideal for assessing the efficacy of novel lipid-lowering agents (e.g., statins, PCSK9 inhibitors), anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-thrombotic compounds, and therapies targeting endothelial dysfunction or oxidative stress.
- Investigate Treatments: Used to explore pharmacological interventions, gene therapies, dietary modifications, and lifestyle interventions aimed at preventing, halting, or regressing atherosclerotic plaque development.
- Biomarker Discovery: Facilitates the identification and validation of novel circulating or tissue-based biomarkers indicative of disease progression or therapeutic response.
- Mechanism of Action Studies: Provides a robust platform for dissecting the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which a therapeutic agent exerts its anti-atherosclerotic effects, including epigenetic modulation.
Related Atherosclerosis Models
- ApoE-/- Mice Model
- Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Deficient Mice (LDLR-/-) Model
- ApoE*3 Transgenic (E3L) Mice Model
- Fatty Zucker Rats Model
- Carotid Artery Endothelial Denudation Model
- Blood Flow-Induced Arterial Intimal Thickening Model
Our Advantages
- Expertise: Partner with a team boasting decades of specialized expertise in cardiovascular research.
- Customization: We offer highly customizable study designs, ensuring your unique research objectives are met with precision.
- Quality Control: Our commitment to rigorous quality control guarantees the reliability and reproducibility of your data.
- Advanced Capabilities: Benefit from our state-of-the-art analytical capabilities, coupled with GLP-compliant services.
- Accelerated Development: We provide comprehensive and insightful results that accelerate your drug development pipeline and support regulatory submissions.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing comprehensive preclinical research services utilizing the HFD & CHOL-induced aorta atherosclerosis model. Our extensive expertise and advanced capabilities are designed to guide your cardiovascular drug discovery efforts. We invite you to contact our scientific team to discuss how we can support your next groundbreaking project.
FAQs
-
Q1: Can this model be used to study plaque regression, or is it primarily for progression?
A: While the HFD & CHOL model is most commonly employed to study plaque progression and the prevention of lesion development, it can also be adapted to investigate plaque regression. This typically involves an initial period of HFD & CHOL feeding to establish lesions, followed by a switch to a less atherogenic diet or the introduction of a therapeutic agent to assess its ability to reduce existing plaque burden.
-
Q2: What are the key endpoints Creative Biolabs typically evaluates in HFD & CHOL atherosclerosis studies?
A: Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of endpoints to provide a holistic view of disease modulation. These commonly include quantitative assessment of aortic plaque area and volume through histopathology (e.g., Oil Red O staining), analysis of plaque composition (e.g., macrophage content, collagen, smooth muscle cells), serum lipid profiles, inflammatory markers, and gene/protein expression analysis in relevant tissues.
-
Q3: Is it possible to customize the diet composition or duration for specific research needs?
A: Absolutely, customization of the diet composition and duration is a key aspect of our flexible service offerings. We collaborate closely with our clients to tailor the HFD & CHOL diet's fat and cholesterol content, as well as the feeding period, to align with specific research questions, desired disease severity, and the mechanism of action of the therapeutic compound being investigated.
-
Q4: Can this model be combined with other disease models, such as diabetes or obesity?
A: Yes, the HFD & CHOL model is highly adaptable and can be integrated with other disease models to investigate comorbidities. Given that high-fat diets often induce obesity and insulin resistance, this model inherently has relevance to metabolic syndrome. We can design studies that specifically explore the interplay between atherosclerosis and conditions like type 2 diabetes or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
-
Q5: How can I interpret the results from this model in terms of human relevance?
A: While mouse models are not perfect replicas of human disease, the HFD & CHOL-induced atherosclerosis model is highly regarded for its translational relevance. The key pathological features and molecular pathways observed in this model closely mirror those in human atherosclerosis. Our scientific team assists in interpreting the data, highlighting its implications for human disease, and discussing its predictive value for clinical outcomes.
Published Data
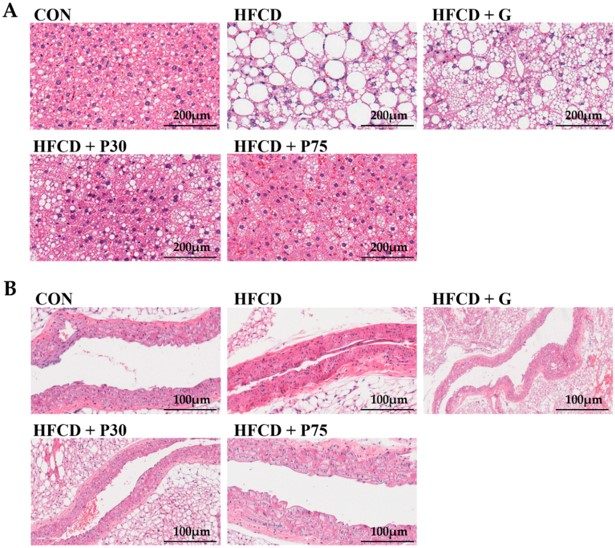 Fig.2 Impact of PEITC supplementation on the livers and aortas of mice.2,3
Fig.2 Impact of PEITC supplementation on the livers and aortas of mice.2,3
The study demonstrated the utility of the HFD & CHOL-induced atherosclerosis model in evaluating novel therapeutic compounds. Researchers investigated the effects of phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) supplementation in mice fed an HFD & CHOL diet. The study found that PEITC significantly ameliorated histopathological changes in the liver and improved the serum lipid profile. Notably, PEITC supplementation also modulated specific histone modifications and reduced the expression of inflammatory genes in liver tissue, showcasing its potential anti-atherosclerotic effects through epigenetic mechanisms. This research exemplifies how the HFD & CHOL model can effectively reveal the molecular underpinnings of therapeutic interventions.
References
- Rai, Vikrant. "High-Fat Diet, Epigenetics, and Atherosclerosis: A Narrative Review." Nutrients vol. 17,1 127. 31 Dec. 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010127
- Gwon, Min-Hee et al. "Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Protects against High Fat/Cholesterol Diet-Induced Obesity and Atherosclerosis in C57BL/6 Mice." Nutrients vol. 12,12 3657. 27 Nov. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123657
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
