tMCAO Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Stroke, a devastating cerebrovascular event, remains a leading cause of disability and mortality globally. Understanding its complex pathophysiology and developing effective treatments necessitates robust preclinical models that accurately mimic the human condition.
At Creative Biolabs, we leverage decades of expertise to provide a comprehensive suite of well-established stroke models, enabling precise evaluation of novel therapeutic agents and intervention strategies.
Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Models
The transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) model is widely recognized as the gold standard for studying focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. This versatile rodent model faithfully replicates the acute phase of ischemic stroke, where a temporary blockage of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) leads to reduced cerebral blood flow, followed by reperfusion upon removal of the occlusion. It enables detailed investigation into the ischemic core, penumbra dynamics, reperfusion injury, neuroinflammation, and long-term neurological deficits, providing critical insights for drug discovery.
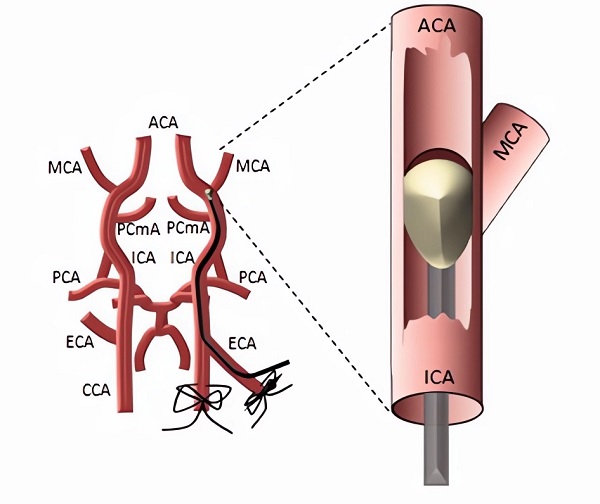 Fig.1 Schematic Illustration of the tMCAO model.1
Fig.1 Schematic Illustration of the tMCAO model.1
Model Construction Steps
tMCAO models are primarily constructed via the intraluminal suture method. The suture model involves inserting a silicon-coated monofilament into the internal carotid artery (ICA) to physically occlude the MCA. This non-invasive approach is favored for its consistency and high-throughput potential.
01Preparation
Animals are anesthetized, and body temperature is precisely maintained. The neck region is disinfected and incised.
02Vessel Dissection
The common carotid artery (CCA), external carotid artery (ECA), and ICA are carefully dissected, avoiding nerve damage. The ECA is ligated and cauterized, leaving a stump.
03Filament Insertion
A silicon-coated monofilament is introduced into the ECA stump, advanced into the ICA, and gently pushed until resistance is met at the MCA origin, confirming occlusion via cerebral blood flow (CBF) drop.
04Occlusion & Recovery
The filament is secured for a set duration. The incision is closed, and the animal recovers under close monitoring for neurological deficits.
05Reperfusion
After the ischemic period, the animal is re-anesthetized, the incision reopened, and the filament carefully withdrawn to allow reperfusion.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Clinical Translatability: Replicates key pathological features of human ischemic stroke, including ischemic core, penumbra, and reperfusion injury.
- Versatile: Adaptable across various rodent species and allows precise control over occlusion duration and severity.
- Reperfusion Dynamics: Enables detailed study of reperfusion injury, a critical determinant of stroke outcome. The intraluminal suture model specifically mimics the abrupt reperfusion seen in endovascular thrombectomy.
- Comprehensive Readouts: Compatible with a wide array of neurological, histological, and biochemical assessments.
Limitations:
- Reproducibility Challenges: Factors like animal strain, age, sex, and filament size can influence lesion size and functional outcome variability. We mitigate this through rigorous standardization.
- Surgical Expertise: Requires highly skilled surgeons to minimize complications like subarachnoid hemorrhage and ensure consistent results.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs provides a robust evaluation platform for tMCAO studies, integrating advanced instrumentation and comprehensive analytical techniques across biochemical, molecular, cellular, and histopathological domains. Our state-of-the-art facilities include sophisticated imaging instruments and behavioral testing suites, ensuring precise and reliable data collection.
Key Test Indicators:
- Regional Cerebral Blood Flow (rCBF) via Laser Doppler Flowmetry (LDF) and Laser Speckle Flowmetry (LSF)
- Quantitative rCBF via Carbon-14 Iodoantipyrine Autoradiography (14C-IAP)
- Neurological Deficit Scoring (NDS)
- Infarct Volume Measurement (e.g., TTC staining, MRI)
- Histopathological Analysis (e.g., neuronal survival, glial activation, inflammation, blood-brain barrier integrity)
- Behavioral Assessments (e.g., rotarod, grip strength, cylinder test, Morris water maze)
- Biomarker Analysis (e.g., inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress markers)
Applications
- Modeling Ischemic Stroke Pathology: Simulates acute ischemic stroke, focal cerebral ischemia, and the critical processes of reperfusion injury and neuroinflammation. It also allows for the study of long-term neurological deficits following stroke.
- Evaluating Neurotherapeutic Agents: Ideal for assessing neuroprotective, thrombolytic (e.g., rtPA), neurorestorative, and regenerative agents. This includes compounds targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation, as well as adjunct therapies for endovascular thrombectomy.
- Assessing Diverse Treatment Modalities: Applicable for evaluating pharmacological interventions, cell-based therapies, gene therapies, and various combination treatments, including the impact of mechanical reperfusion strategies.
Related Stroke Models
- pMCAO Model
- Photochemically induced Ischemic Stroke Model
- Collagenase induced Hemorrhagic Stroke Model
- Sodium Laurate induced Cerebral Microvascular Injury Model
Our Advantages
- Years of Expertise: Unparalleled experience in preclinical stroke model development and execution.
- Standardized & Validated Protocols: Meticulously optimized SOPs for superior data quality and reliability.
- Advanced Models: Pioneering the use of awake tMCAO models for enhanced clinical translatability.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: A full suite of cutting-edge outcome measures from behavioral to molecular.
- Ethical Compliance: Strict adherence to animal welfare and ethical research guidelines.
- Customizable Study Designs: Flexible and tailored approaches to meet your specific research objectives.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Leverage Creative Biolabs' extensive expertise and advanced tMCAO models to accelerate your stroke research. We are dedicated to providing high-quality, reproducible data that drives informed decision-making. Contact us today to discuss your specific project needs and explore how our services can support your therapeutic development.
FAQs
-
Q1: Can you customize tMCAO model parameters, such as occlusion duration or reperfusion time?
A: Absolutely. Our highly collaborative and flexible approach allows full customization of tMCAO model parameters. We tailor the duration of ischemia, reperfusion timing, therapeutic agent administration, and specific endpoints to your unique research requirements. Our team works closely with you to design bespoke study protocols, ensuring the most relevant and impactful data for your drug development program.
-
Q2: What types of outcome measures do you provide for tMCAO studies, beyond infarct volume?
A: We provide comprehensive outcome measures for stroke pathology and recovery. Beyond infarct volume (TTC, MRI), our platform includes neurological deficit scoring, behavioral assessments (e.g., rotarod, grip strength, Morris water maze), and histopathological analyses (neuronal survival, glial activation, inflammation, blood-brain barrier integrity). We also offer real-time cerebral blood flow monitoring and analyze biochemical/molecular biomarkers.
-
Q3: How does your "awake tMCAO model" enhance preclinical data translational relevance?
A: The awake tMCAO model significantly advances preclinical stroke research. Traditional models often use anesthesia, which can exert neuroprotective effects, masking true injury or therapeutic efficacy. By performing ischemia in awake animals, this model eliminates anesthetic neuroprotection, providing a more accurate, clinically relevant representation of human stroke. This yields more predictive, robust preclinical data, increasing translation likelihood.
-
Q4: Can you assist with interpreting complex tMCAO data and provide scientific consultation?
A: Absolutely. Our service extends beyond data generation. With years of experience, our expert biologists and neuroscientists provide in-depth scientific consultation and assist with comprehensive interpretation of your tMCAO study results. We help you understand data implications, identify key findings, and strategize next steps in your drug development pipeline, ensuring maximum value from your preclinical research investment.
-
Q5: How do you ensure quality and consistency of biological materials used in tMCAO?
A: Quality control is integral. We source high-quality, silicon-coated monofilaments from reputable suppliers, conducting internal checks for consistent diameter and coating. This rigorous attention to material quality and preparation consistency minimizes variability and maximizes ischemic insult reproducibility across all experimental animals.
Published Data
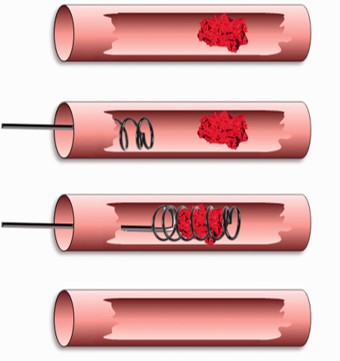 Fig.2 Illustration of endovascular thrombectomy after acute ischemic stroke.1
Fig.2 Illustration of endovascular thrombectomy after acute ischemic stroke.1
This work demonstrates that the abrupt reperfusion profile characteristic of filament tMCAO closely mirrors the rapid blood flow restoration achieved by modern endovascular thrombectomy in human stroke. The authors advocate for the filament tMCAO model as the preferred preclinical model for evaluating neuroprotective agents as adjunct therapies to mechanical clot removal, reinforcing its translational value in the evolving landscape of acute stroke treatment. This publication exemplifies how these models provide data directly applicable to cutting-edge clinical interventions.
Reference
- Sutherland, Brad A et al. "The transient intraluminal filament middle cerebral artery occlusion model as a model of endovascular thrombectomy in stroke." Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism vol. 36,2 (2016): 363-9. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X15606722
For Research Use Only.
