- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
Myocarditis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Myocarditis, an inflammatory condition affecting the heart muscle, represents a significant global health concern, frequently leading to acute heart failure, life-threatening arrhythmias, and even sudden cardiac death. Its diverse origins, spanning viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and adverse drug reactions, contribute to its unpredictable clinical course. Given the limited specific therapeutic options currently available, there is an urgent and critical need for innovative diagnostics and effective treatments.
At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to addressing this unmet need by providing a comprehensive array of meticulously developed and validated preclinical models to evaluate potential myocarditis therapies.
Available Myocarditis Models at Creative Biolabs
Preclinical myocarditis models are indispensable tools for unraveling the intricate mechanisms of myocardial inflammation and injury, identifying novel therapeutic targets, and rigorously evaluating the efficacy and safety of new compounds before clinical translation. These models are meticulously constructed to recapitulate key aspects of human disease, offering controlled environments for in-depth scientific investigation. Our strategic approach involves inducing inflammation, infection, or autoimmune responses in rodents, rabbits and dogs, allowing for precise study of disease progression and therapeutic intervention.
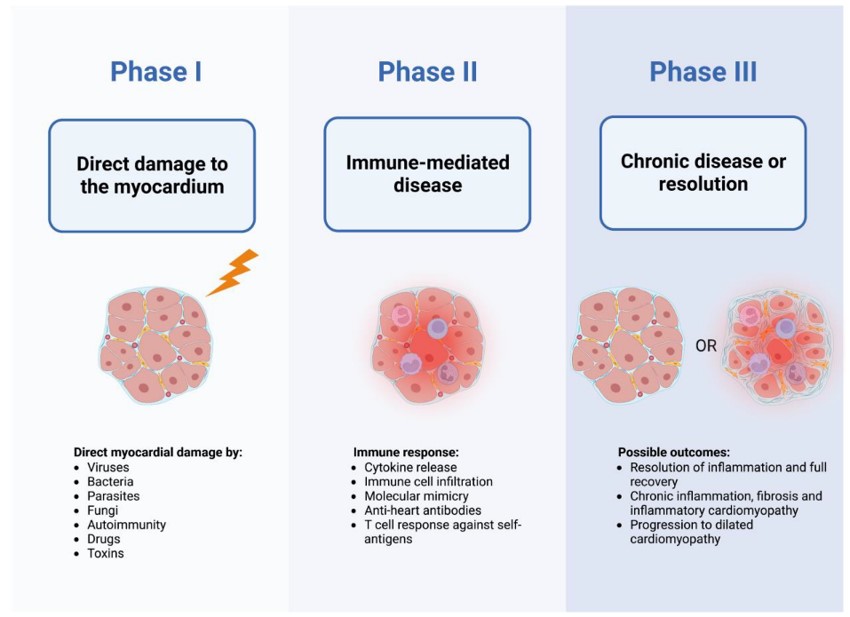 Fig.1 Triphasic model of myocarditis.1,3
Fig.1 Triphasic model of myocarditis.1,3
Our team provides the following Myocarditis models for comprehensive preclinical evaluation:
| MyocarditisModels | Modeling | Animal species |
|---|---|---|
| Adriamycin induced Myocarditis Model | This model is crucial for studying drug-induced cardiotoxicity, a growing concern. It replicates myocardial damage driven by oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to cardiac decline. Ideal for assessing cardioprotective agents and understanding molecular pathways in chemotherapy-induced injury, offering mitigation insights. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Dog |
| Myosin induced Immune Myocarditis Model | Designed to mimic autoimmune myocarditis, this model is established by immunizing rodents with cardiac myosin. This elicits a robust immune response targeting myocardial antigens, leading to cardiac inflammation, necrosis, and fibrosis. It's invaluable for investigating immunomodulatory therapies and immunosuppressants to rebalance the immune response in autoimmune conditions. | Mouse |
| Coxsackievirus induced Myocarditis Model | As coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) is a prevalent cause of viral myocarditis, this model accurately reproduces acute viral replication and subsequent immune-mediated myocardial damage. It often progresses to chronic dilated cardiomyopathy, making it highly translational. This model is extensively utilized for evaluating antiviral compounds, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, and strategies to prevent long-term sequelae. | Mouse |
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs offers a state-of-the-art evaluation platform, encompassing a full spectrum of biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, and advanced imaging techniques to ensure comprehensive data generation:
- Cardiac Function Assessment: Echocardiography, pressure-volume loop analysis, cardiac MRI.
- Histopathology: H&E, Masson's trichrome, immunohistochemistry for immune cell phenotyping.
- Molecular Analysis: Quantitative PCR, Western blotting, ELISA, multiplex cytokine/chemokine profiling.
- Cellular Analysis: Flow cytometry for immune cell populations, cellular viability assays.
- Biochemical Markers: Cardiac troponins, BNP, inflammatory cytokines.
Applications
Disease Simulation: Our models accurately simulate the diverse forms of myocarditis, including viral, autoimmune, and drug-induced etiologies, as well as their progression to dilated cardiomyopathy.
Drug Evaluation: We facilitate the rigorous evaluation of a wide range of therapeutic agents, including antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory compounds, and novel cardioprotective agents.
Therapy Development: Our platforms are ideal for testing the efficacy of pharmacological interventions, biologics, cell therapies, and gene therapies aimed at preventing, treating, or reversing myocardial inflammation and damage.
Related Cardiovascular Models
Our Advantages
- Diverse Animal Species: Access to a variety of well-characterized animal models tailored to your specific research needs.
- One-Stop Evaluation: Comprehensive in vitro and in vivo services for integrated and efficient study execution.
- Expert Team & Quality Systems: A highly professional scientific team supported by a robust and perfect management system, ensuring scientific rigor and reliable results.
Work with Us
Inquiry Stage
Project Start
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
Project Progress
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
Project Completion
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
After-Sales Support
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Leverage Creative Biolabs' extensive experience and scientific capabilities to accelerate your myocarditis research. Our commitment to excellence and client-centric approach ensures that your therapeutic development programs are supported by the highest quality preclinical data. We invite you to contact us to discuss how our specialized models can advance your next breakthrough.
FAQs
-
Q1: What are the primary advantages of utilizing rodent models for myocarditis research?
A: Rodent models offer several key benefits for myocarditis studies, including their genetic tractability, relatively short reproductive cycles, and the ability to control environmental factors. These characteristics enable researchers to investigate complex disease mechanisms, test therapeutic interventions efficiently, and generate reproducible data in a controlled experimental setting.
-
Q2: How do you ensure the translational relevance of your myocarditis models to human disease?
A: We meticulously select and characterize our models based on their ability to recapitulate key pathological features and immunological responses observed in human myocarditis. Our comprehensive phenotyping, including cardiac function assessment and molecular profiling, is designed to provide data that closely correlates with clinical outcomes, thus maximizing translational potential.
-
Q3: Can your models differentiate between acute and chronic phases of myocarditis?
A: Absolutely. Our established myocarditis models are designed to exhibit distinct acute inflammatory phases, followed by progression to chronic myocardial remodeling and dysfunction in many cases. This allows for precise investigation of therapeutic interventions at different stages of disease progression, from initial inflammation to chronic fibrotic changes.
-
Q4: How do you handle the variability often seen in myocarditis models?
A: To mitigate variability, we employ standardized induction protocols, use genetically uniform animal strains, and perform rigorous quality control throughout our studies. Our experienced scientists also utilize appropriate statistical methods and sample sizes to ensure the robustness and reliability of the data generated.
-
Q5: Can I request a custom myocarditis model not explicitly listed on your service page?
A: Indeed, we welcome inquiries for custom model development. Our scientific team possesses extensive expertise in cardiovascular disease modeling and is adept at developing bespoke solutions tailored to unique research objectives. We encourage you to discuss your specific needs with our specialists.
-
Q6: What is the typical timeline for a myocarditis efficacy study?
A: The duration of a myocarditis efficacy study can vary significantly depending on the specific model chosen, the number of experimental groups, and the desired endpoints. Typically, studies can range from a few weeks for acute models to several months for chronic progression models. We provide detailed project timelines during the study design phase.
-
Q7: What are the key considerations for selecting the most appropriate myocarditis model for my research?
A: Choosing the right model depends on your specific research question, the target mechanism of your therapeutic agent, and the desired disease stage to investigate. We recommend a consultation with our scientific team to discuss your objectives, which will enable us to recommend the most suitable and cost-effective model for your program.
Published Data
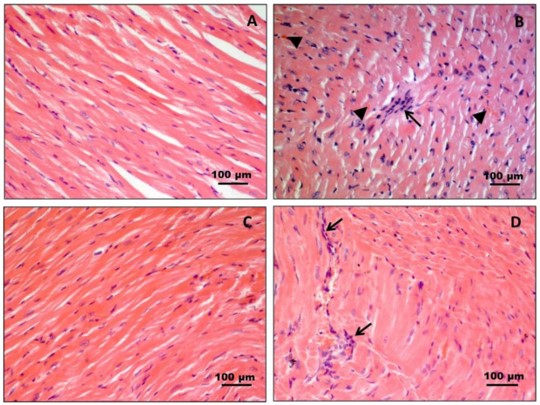 Fig.2 Histology of heart muscle tissue in CB3V-induced myocarditis.2,3
Fig.2 Histology of heart muscle tissue in CB3V-induced myocarditis.2,3
The relevant preclinical study investigated the therapeutic effects of a synthetic anti-inflammatory sterol, HE3286, in a murine model of CVB3-induced myocarditis. Researchers observed that HE3286 significantly inhibited the establishment and progression of myocarditis, demonstrating better histological outcomes compared to conventional treatments. Specifically, hearts from treated mice showed an almost complete resolution of inflammatory infiltration. This highlights the potential of novel anti-inflammatory compounds in mitigating myocardial damage in inflammatory heart conditions.
References
- Brociek, Emil et al. "Myocarditis: Etiology, Pathogenesis, and Their Implications in Clinical Practice." Biology vol. 12,6 874. 17 Jun. 2023, DOI:10.3390/biology12060874.
- Castrogiovanni, Paola, et al. "Effects of synthetic anti-inflammatory sterol in CB3V-induced myocarditis: a morphological study on heart muscle tissue." Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 1.1 (2016): 69-89, DOI: 10.3390/jfmk1010069.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
